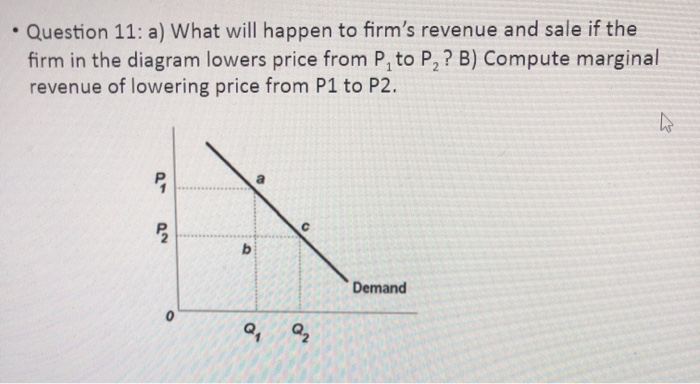
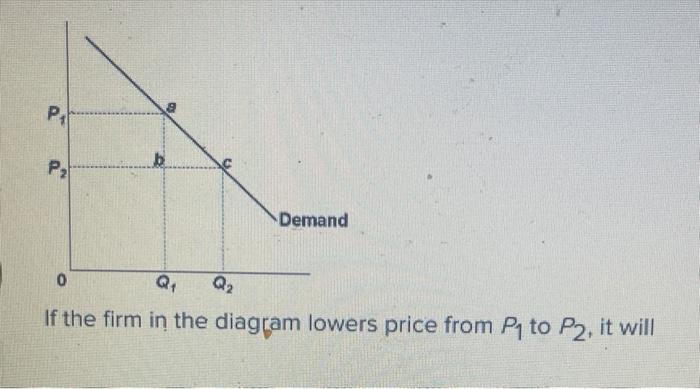
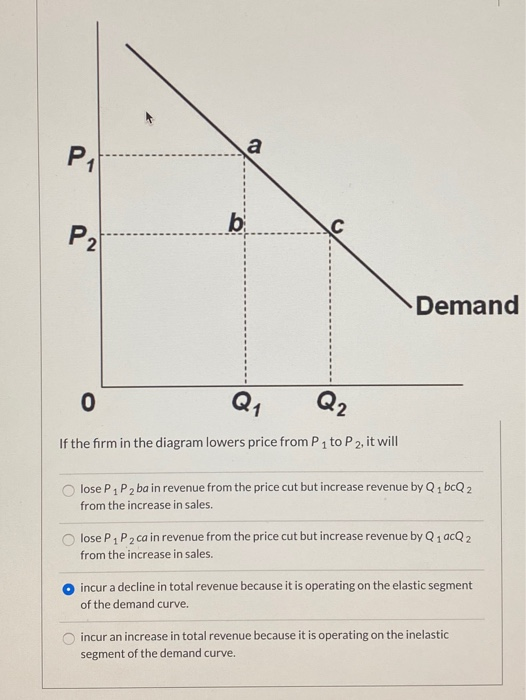
40 if the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will
Assess whether price discrimination is always undesirable ... However , in a Barber shop , lower income groups ( such as students or OAPs ) may be charged a lower price for the same good . This is more equitable for certain consumers . P1 P2 P3 P4 Q D Q4 4 Q 1 Q 2 Q 3 First degree price discrimination would completely remove all of the consumer surplus and turn it into producer surplus . chapter 12 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the above diagram for a natural monopolist. If a regulatory commission set a maximum price of P1, the monopolist would produce output: Q4 and realize a ...
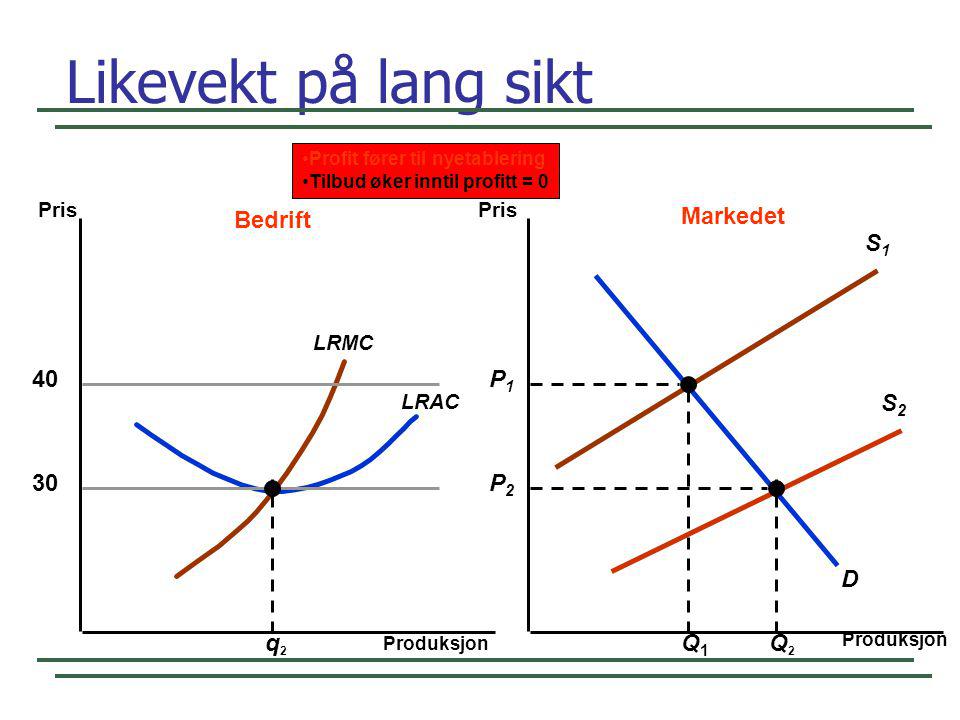
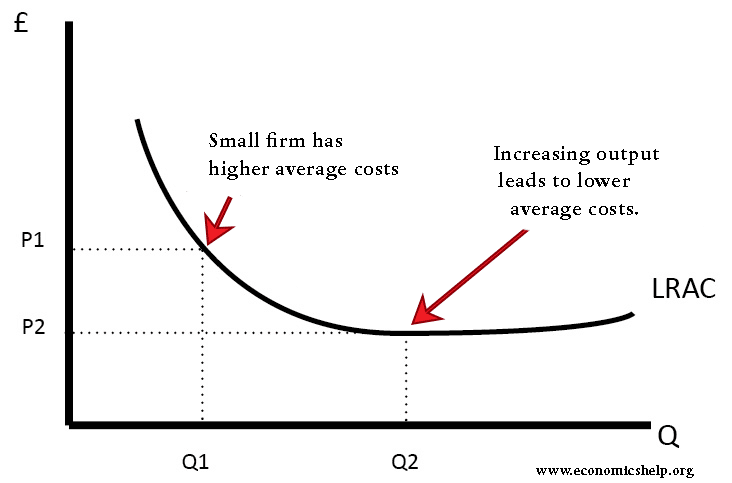
PDF The Model of Monopoly Consumers are willing to pay P1 for Q1. Unit costs are only P2 so the firm is making an abnormal profit of (P1-P2)xQ1 In competitive markets abnormal profits attract new firms and the resultant increase in supply lowers price until normal profits are earned. A monopolist can only sustain abnormal profits by erecting

If the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will
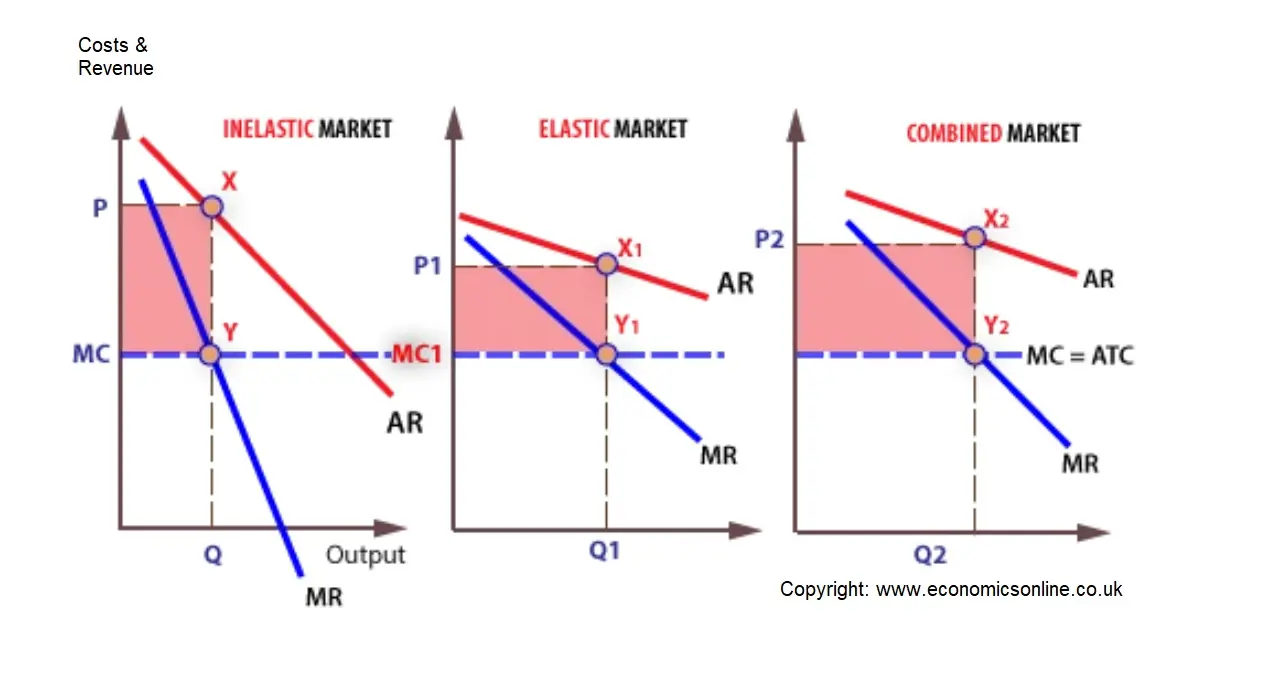
Economics corner: MCQ on market and market failures - Blogger B Economies of scale can lead to lower prices. C Inferior goods have a negative income elasticity of demand. D The government was wrong to introduce university tuition fees. 8 The diagram below shows the demand and supply curves for milk, where P1 is the initial equilibrium price. The increase in price from P1 to P2 is most likely to be a result of PDF Managerial Economics Study Questions With Solutions Price ... They plan to charge P1 for the first Q1 units and P2 for the subsequent units. The units sold at P2 are the total units sold, Q2, minus the total units sold at P1. The inverse demand curve is P = $100 - Q, and the marginal and average cost is $40. Use calculus to solve for P1, P2, Q1, Q2. 182 Refer to the two diagrams for individual firms Figure 1 ... If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: ANSWER: lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. 195. Refer to the diagram. The quantitative difference between areas Q1bcQ2 and P1P2ba in the diagram measures: ANSWER: marginal revenue. 196.
If the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will. OneClass: The diagram below shows the market demand curve ... The diagram below shows the market demand curve and the cost curves for a single firm. LRAC - MC Output FIGURE 12-6 36) Refer to Figure 12-6. Suppose the firm is being regulated using a policy of average-cost pricing. The resulting price and output would be A) P and Q2. B) Pj and QI. C) P2 and Q2 D ) P3 and Q1 E) P3 and Q2. PDF Key Diagrams A2 Business Economics - tutor2u Lower costs allows a profit maximising firm to charge a lower price (P2) but make higher total profits because of the fall in AC per unit Costs Output (Q) SRAC1 SRAC3 AR (Demand) MR MC1 MC2 P1 P2 Q1 Q2 Profit at Price P1 Profit at Price P2 Costs Output (Q) SRAC1 SRAC2 SRAC3 Q1 Q2 Q3 AC1 AC2 AC3 LRAC DP Economics: Government subsidies As the diagram illustrates, the equilibrium number of students entering university in a free market would be represented by Q1. The equilibrium tuition price at this level is P1. After the subsidy the price falls to P2 and at this lower price the number of students applying to college is Q2. Solved Demand If the firm in the diagram lowers price from ... Transcribed image text: Demand If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will lose P1 P2 ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ 2 from the increase in sales. lose P1 P2 ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q 1 acQ2 from the increase in sales. o incur a decline in total revenue because it is operating on the elastic segment of the ...
Price Discrimination - A-level Economics Notes In this case to maximise profits, the firm produces quantity q2 and price p2. This price is below the original price p1 when there is no price discrimination. So the elastic group is better off under price discrimination - they face a lower price and higher consumer surplus. The right diagram shows the group with the more inelastic price ... PDF General Equilibrium Theory - Washington State University Firms demand capital and ... Edgeworth Box Diagram. 6/4/2014 16 Edgeworth Box Diagram 31 32 Edgeworth Box Diagram. 6/4/2014 17 ... Person A's consumption choices are measured from the lower left hand corner, Person B's consumption choices are measured from the upper right hand ... Chapter 12 Flashcards | Quizlet If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will Lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. Which of the following is characteristic a pure monopolist's demand curve? Econ Ch. 10-14 Flashcards | Quizlet If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase ...
ECON CH 12 Flashcards | Quizlet In the accompanying diagram, if price is reduced from P1 to P2, total revenue will: Increase by C − A. ... When a monopolist lowers price to sell more output, the lower price applies to all units sold. ... Refer to the long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q2 at an average cost of ATC3, then the firm is: ... CHAP 12 Flashcards - Quizlet If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. The demand curve faced by a pure monopolist Econ Final Flashcards | Quizlet P2. If a nondiscriminating imperfectly competitive firm is selling its 100th unit of output for $35, its marginal revenue: will be less than $35. If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. Microeconomics Flashcards - Quizlet 17. If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. B. lose P1P2ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1acQ2 from the increase in sales.
DOC Question #1-#3 are based on the following diagram When market price is P1, a profit maximizing firm's total revenue can be represented by the area. P3 ( Q2. P1 ( Q3. P1 ( Q2. P2 ( Q2. P2 ( Q4. When market price is P4, a profit maximizing firm's total cost can be represented by the area. P4 ( Q1. P1 ( Q4 . P4 ( Q4. P2 ( Q4. Total costs cannot be determined from the information in the figure.
10 Flashcards & Practice Test | Quizlet If a purely competitive firm shuts down in the short run, its loss will be zero. ... If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will
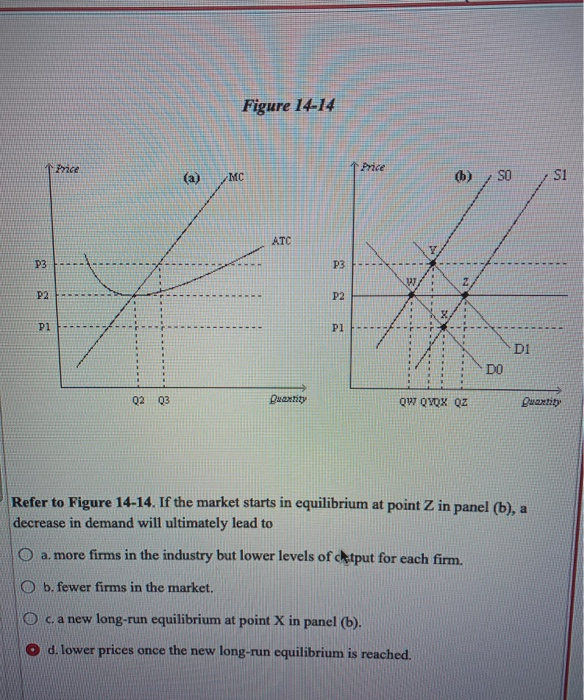
15 The more elastic the demand facing a firm A the higher ... 19) Refer to Figure 2. Suppose that the government decides to limit monopoly power with price regulation. If the government sets the price at the competitive level, it will set the price at _____. A) P1 B) P2 C) P3 D) P4
Diagram A. Shut Down Point of a Firm in Perfect Price MC ATC ... Shut Down Point for a firm in Perfect Competition 1. Shut-down occurs where P is lower than where mr = mc = avc (see X in diagram). This would be any price lower than p1. If the firm does not cover its variable costs of production it will close down in the short run- see p 23 on diagram A 2.
PERFECT COMPETITION DIAGRAM - Course Hero LONG RUN (LR) PERFECT COMPETITION Price Quantity 0 S 1 P1 D 1 MARKET SUPPLY/DEMAND (A) Price Quantity 0 AC P1 D 1 =MR 1 =AR 1 INDVIDUAL FIRM'S SUPPLY/DEMAND (B) MC Q1 The entry of new firms shifts the market supply curve in diagram A from S1 to S2, equilibrium price falls from P1-P2.
Chapter 10 - DocShare.tips 41. If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. B. lose P1P2ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1acQ2 from the increase in sales.
Econ 3 diagrams - SlideShare • Conversely, when cutting prices (P2-P3) firms are expected lower their prices to match the initial price cut. Therefore, firms fail to gain a greater market share and the firm expects the demand to be relatively inelastic for a price decrease. • Ergo, prices remain rigid 6.
SGS Micro Blog: Evaluate the view that, because price ... With price discrimination, the demand curve is divided into the elastic range down to D1 and the inelastic range down to D2. A higher price (P1) is charged to the low elasticity segment, and a lower price (P2) is charged to the high elasticity segment. The total revenue from the first segment is equal to the area P1,B,Q1,O.
[Solved] (a) An oligopolistic firm, estimates the ... (a) An oligopolistic firm, estimates the following demand functions as: P1 = 9 - 0.3Q for price increase. P2 = 10 - 0.4Q for price decrease. The firm's total cost function is: TC = 25 =+1.5q + 0.05Q2. i) Define price rigidity. ii) Prove the price is rigid. iii) Define third degree price discrimination.
MicroEconomics Final Flashcards - Quizlet When a competitive firm sees the price fall below the minimum possible average total cost in the long run, then it will decide that it could do better by moving to a different industry. True. ... If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will:
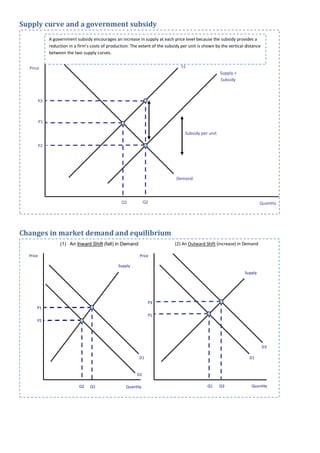
PDF 12 Key Diagrams for AS Microeconomics - tutor2u The price before the subsidy is offer is P1 and the equilibrium quantity is Q1 Following the subsidy, the price falls to P2 (this is the price paid by consumers) Output rises to Q2 i.e. the lower price has encouraged an expansion of demand The producer then receives the subsidy P2-P3 and received price P3
182 Refer to the two diagrams for individual firms Figure 1 ... If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: ANSWER: lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. 195. Refer to the diagram. The quantitative difference between areas Q1bcQ2 and P1P2ba in the diagram measures: ANSWER: marginal revenue. 196.
PDF Managerial Economics Study Questions With Solutions Price ... They plan to charge P1 for the first Q1 units and P2 for the subsequent units. The units sold at P2 are the total units sold, Q2, minus the total units sold at P1. The inverse demand curve is P = $100 - Q, and the marginal and average cost is $40. Use calculus to solve for P1, P2, Q1, Q2.
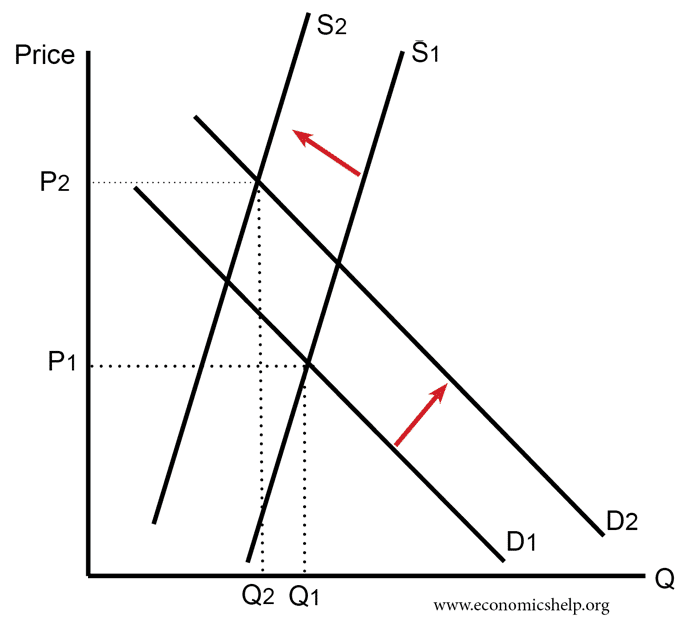
Economics corner: MCQ on market and market failures - Blogger B Economies of scale can lead to lower prices. C Inferior goods have a negative income elasticity of demand. D The government was wrong to introduce university tuition fees. 8 The diagram below shows the demand and supply curves for milk, where P1 is the initial equilibrium price. The increase in price from P1 to P2 is most likely to be a result of








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Which_Vertical_Option_Spread_Should_You_Use_Sep_2020-03-34c346d142194e909757661f6cdcd95a.jpg)





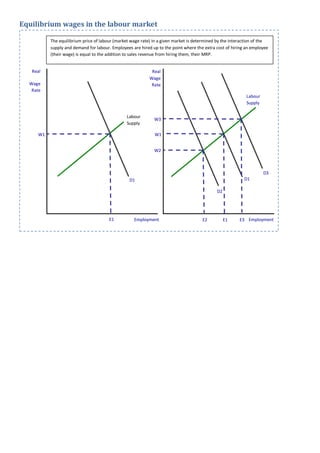
0 Response to "40 if the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will"
Post a Comment