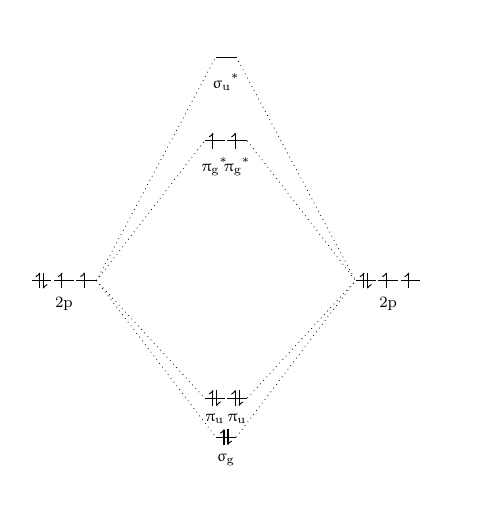
39 mo diagram for hf
molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the NO molecule. We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is 2.5. Figure 9.42: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure 9.43: A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. An advanced molecular orbital diagram of HF for the inorganic or physical chemistry student.
Molecular Orbitals of Hydrogen Fluoride (HF) Ask Question Asked 5 years, ... Given below is a diagram showing $2 \sigma$ , $3 \sigma$ and $1 \pi$ MOs in HF Share. ... Browse other questions tagged molecular-orbital-theory or ask your own question.
Mo diagram for hf
MO Theory • MO diagrams can be built from group orbitals and central atom orbitals by considering orbital symmetries and energies. • The symmetry of group orbitals is determined by reducing a reducible representation of the orbitals in question. This approach is used only when the group orbitals are not obvious by inspection. Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma-bonding and a sigma-antibonding molecular orbital, as shown below. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF. (CC BY-SA-NC 2.0 UK: England & Wales License; Nick Greeves). This video is about MO Diagram #2 - F2
Mo diagram for hf. Molecular orbitals of HF. Draw the MO diagram for HBr including energy levels each orbitals shape each orbitals character meaning what atomic orbitals contribute to each MO. H1 is bonded in a linear geometry to two equivalent Br1- atoms. And how much symmetry labels eg. And how much symmetry labels eg. Molecular orbital diagram for the hf molecule interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma bonding and a sigma antibonding molecular orbital as shown below. The molecular orbitals formed in the case of hf molecule will not be symmetrical. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for HF. Use only the valence electrons for your diagram. The 2s orbital of F atom has an energy more than 26 eV lower than that of the H 1s, so there is very little interaction between them. The F 2p orbital (-18.65 eV) and the H 1s (-13.61 eV), on the other hand, have similar energies, allowing them to Figure 1: LCAO MO Diagram for HF (Author: LeeAnn Sager. Used with permission.) The purpose of this activity is to use Hartree-Fock self-consistent-field approach to calculate the molecular orbitals of HF in the minimal atomic basis (STO-3G) and to compare the molecular orbitals to the qualitative LCAO approach.
A. Draw an MO diagram for HF. B. Draw an MO diagram for -OH. C. Clearly label all parts of the two diagrams. D. Draw the atomic orbitals that overlap to make each of the MO's above. E.Clearly explain which MO's are closely associated with each atom. F. Clearly explain the difference between the two MO diagrams. In this screencast, Andrew Burrows walks you through how to construct the MO energy level diagram of HF. http://ukcatalogue.oup.com/product/9780199691852.do#... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... Download scientific diagram | Molecular orbital diagrams for HBr and HF. from publication: Total energy partitioning within a one-electron formalism: A Hamilton population study of surface-CO ...
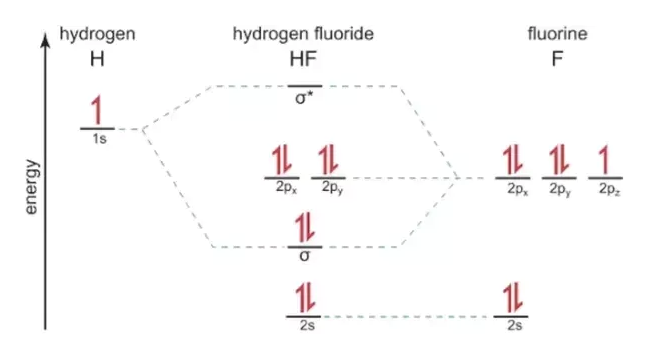
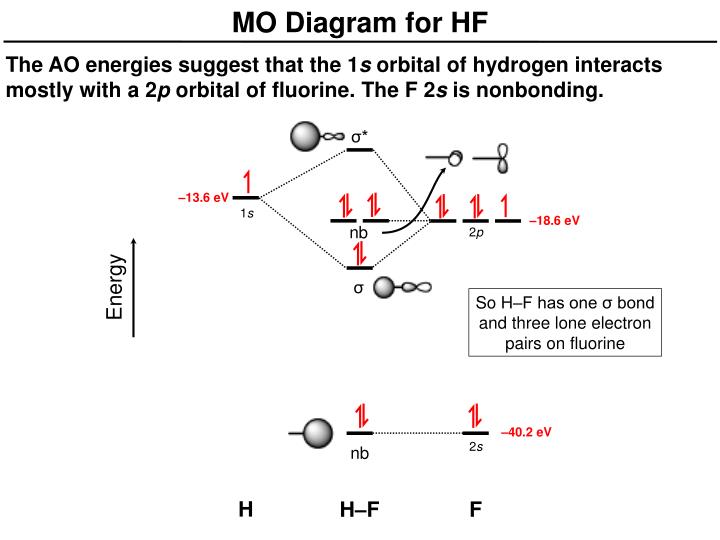
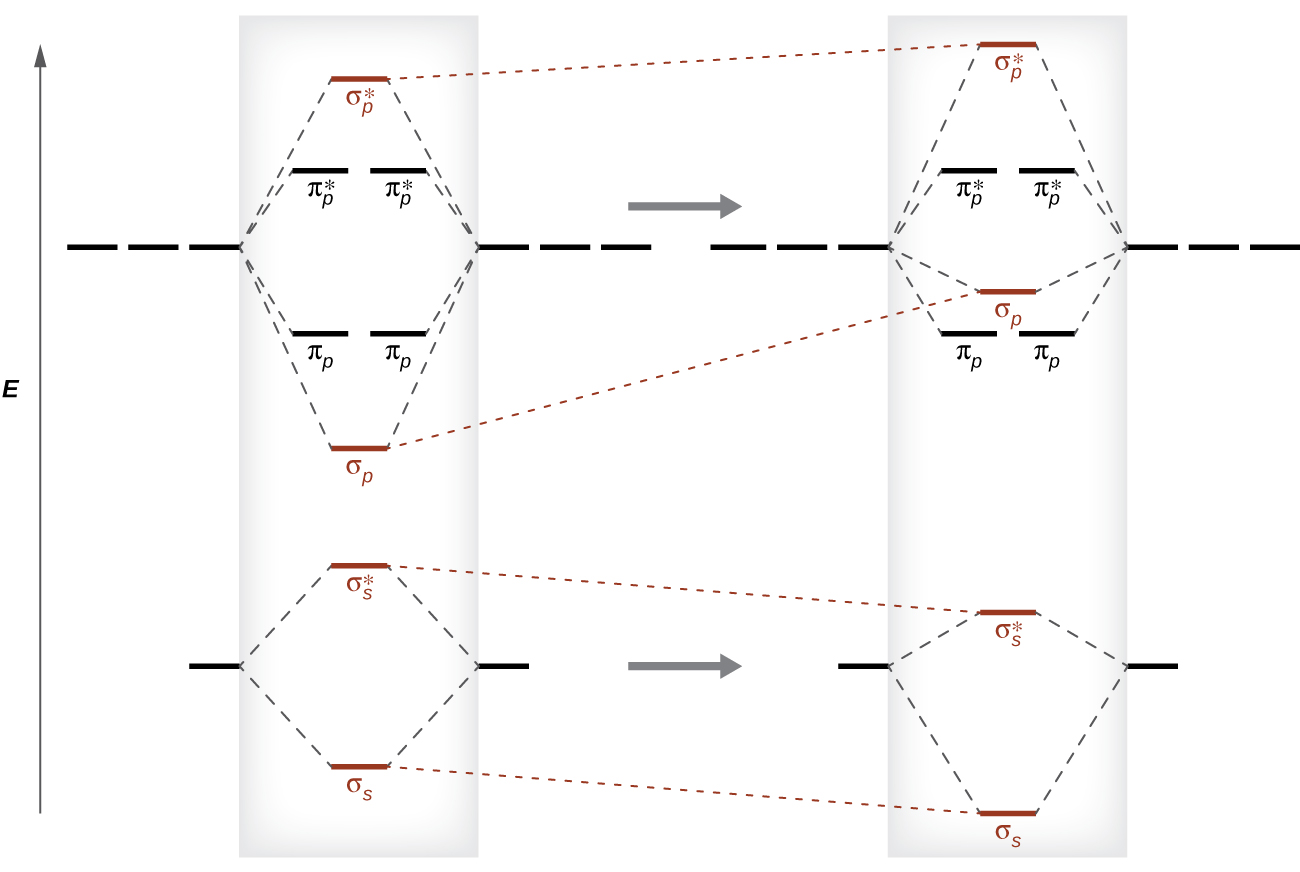
Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration. MO diagram for HF. 1, as we expect from the Lewis structure (2 electron in bonding MO, 4 electrons in non-bonding MOs). MO diagram for F2 Let's do another example. is a little more complicated. This time we'll use σ and π bonds. What orbitals we are using? and 3 2p orbitals (x,y,z). For now, let's just consider the 2p MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mo stly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine. The MO diagram for the HF molecule below will include only valence electrons of Hand F. Indicate on the diagram below atomic orbitals of the Hand Fatoms as well as the bonding antibonding and nonbonding orbitals of the HF molecule (i.e. s.p., and where necessary). Add electrons to the diagram Note: While we have not taught you about non bonding ...
Re: MO Diagram for HF. I wasn't sure about this myself, but I looked it up online (I added a picture). Apparently since F's 2s orbital is so low in energy, it cannot bond with H's 1s orbital and remains below the H as a non-bonding orbital. I can see how this might make sense since F is the most electronegative atom and has a low energy.
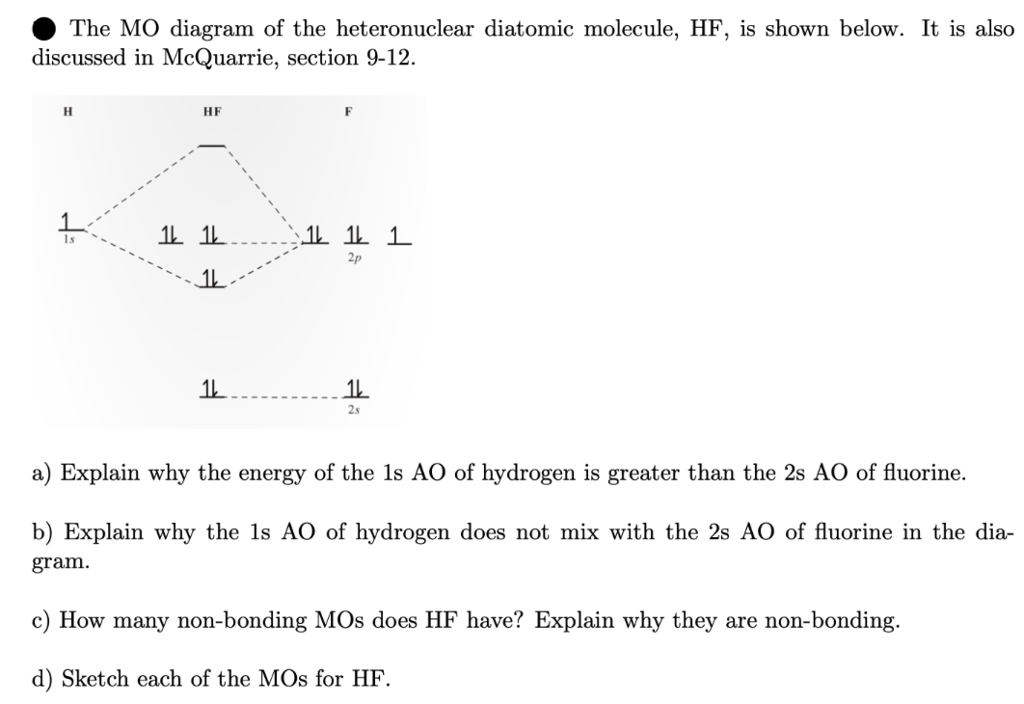
The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The Is atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding sigma molecular orbital and an antibonding sigma* molecular orbital.
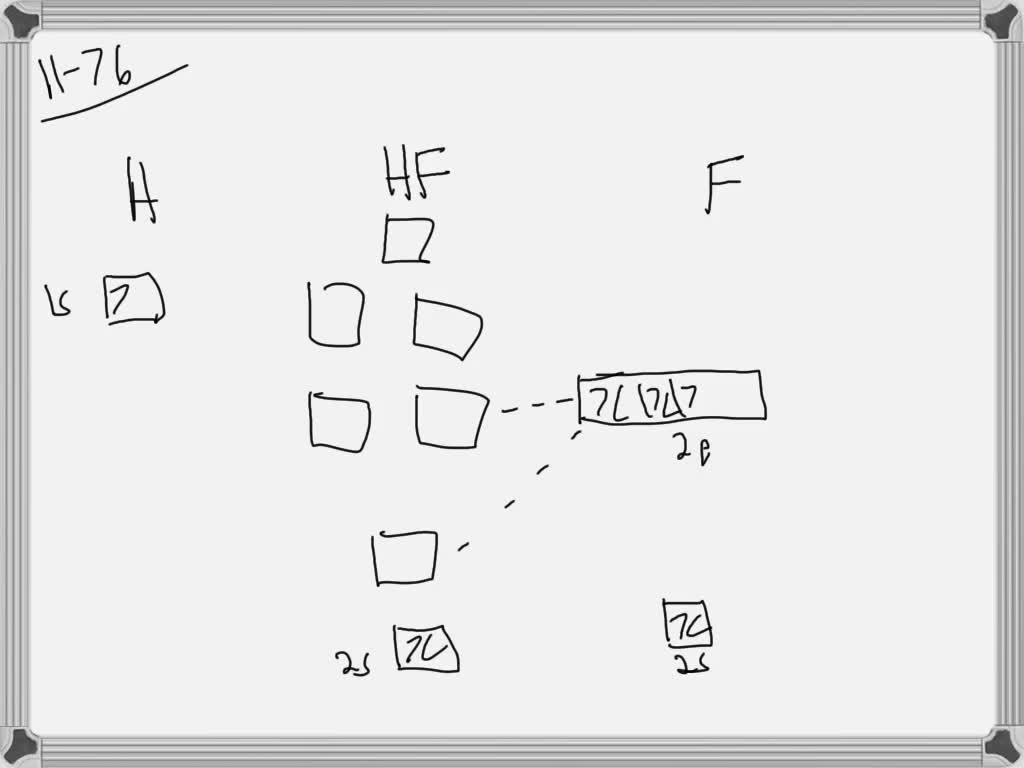
diagram by adding electrons to the appropriate energy levels. (2 pts.) Determine the bond order for HF. BO = (2 - 0)/2 = 1 H F 2s 2px2py2pz 1s!*! HF e. (2 pts.) Determine the effect that removing an electron would have on the strength of the HF bond. No effect because a nonbonding electron is removed. BO = (2 - 0)/2 = 1 f. (2 pts.)
Which is the molecular orbital diagram for HF? The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combine with s orbital.
Mo diagram of hydrogen flouride.molecular orbital diagram of HFFollow me on instagram-https://www.instagram.com/trickychemistrysuman/?hl=enFollow me on faceb...
This lecture clearly explains the molecular orbital diagram of heteronuclear diatomic molecule (HF & HCl). This will help students of H.S., BS-MS, B. Sc., M....
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Answer (1 of 3): The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combi...
Which is the molecular orbital diagram for HF? The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combine with s orbital.
The diagrams differ in the relative energies of the AOs involved and in that there are nonbonding valence electrons on the OH radical, whereas there are none on HF. The HOMO is the 1π, which is a nonbonding MO. The LUMO is the 5σ*, which is an antibonding MO. Extra Problems 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Lih. We shall consider the molecular orbitals in LiH, CH and HF to illustrate how molecular orbital theory describes the bonding in heteronuclear molecules, and to. and 2p orbitals, but that is not how sodium chloride is made. Sodium atoms are Construct an MO diagram for LiH and suggest what type of bond it might have.
This video is about MO Diagram #2 - F2
Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma-bonding and a sigma-antibonding molecular orbital, as shown below. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF. (CC BY-SA-NC 2.0 UK: England & Wales License; Nick Greeves).
MO Theory • MO diagrams can be built from group orbitals and central atom orbitals by considering orbital symmetries and energies. • The symmetry of group orbitals is determined by reducing a reducible representation of the orbitals in question. This approach is used only when the group orbitals are not obvious by inspection.

























0 Response to "39 mo diagram for hf"
Post a Comment