37 trauma and the brain diagram
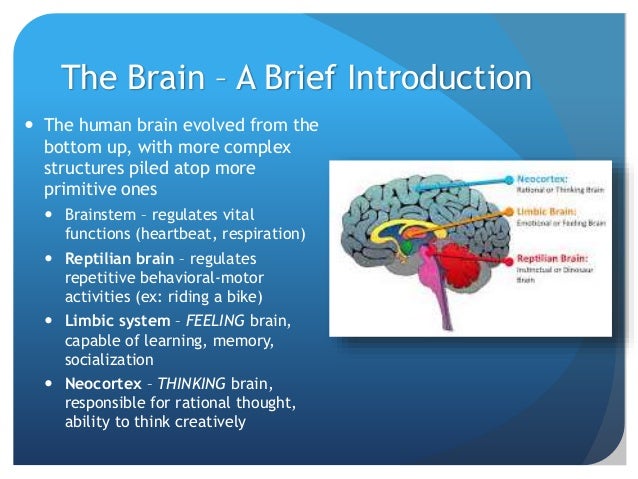
brain, or limbic system and finally the human brain, known as the cortex or neo-cortex. According to this model, the cortex sits on top of the mammalian brain, which sits on top of the reptilian brain. A Simplified Diagram of the Triune Brain The Reptilian Brain: The reptilian brain is the oldest and most primitive part of the brain. Jul 16, 2017 · The PECARN (Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network) traumatic brain injury algorithm is a clinical decision rule that aims to identify children at very low risk of clinically important traumatic brain injury (ci-TBI) 1.
Aug 30, 2018 · The skeletal system is the foundation of your body, giving it structure and allowing for movement. We’ll go over the function and anatomy of the skeletal system before diving into the types of ...

Trauma and the brain diagram
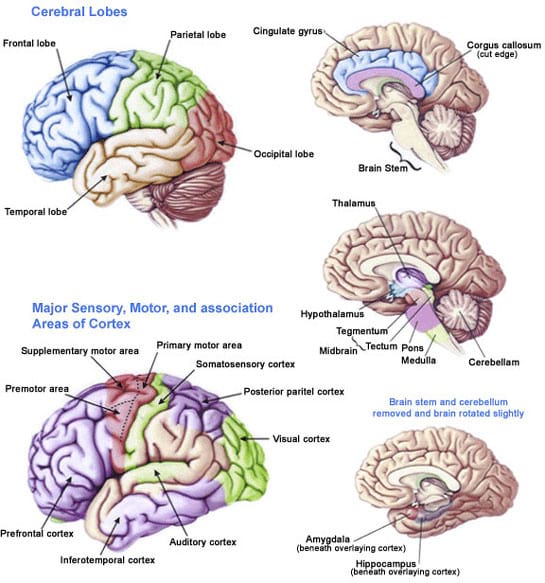
Trauma and the Brain This is a very simplistic explanation of a very complex process. There are three main parts of the brain which are greatly affected by experiencing severe or chronic traumatic events. Hippocampus The hippocampus processes trauma memories, by recycling the memory, mostly at night via dreams, which takes place over weeks or ... This consists of the two cerebral hemispheres of the cerebrum and their inter connections. Cerebrum The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Any kind of trauma or lesion in the cerebrum can lead to various diseases and disorders and mental illnesses. The cerebrum is divided into two cerebral hemispheres by the medial longitudinal fissure. A traumatic experience can change the brain areas that enable you to feel these types of emotions." Followed by: "In other words, traumatic experiences can affect your ability to connect with others or to have positive and loving feelings. These 'numbing' symptoms are common for people
Trauma and the brain diagram. response to the traumatic threat. Understanding the interaction of the cortex with the limbic system during low and high stress will help to make this loss of cortex ability clearer. The Limbic System Located in the middle part of the brain between the brain stem and cortex, the limbic system is responsible for our survival. Trauma and the structure of your brain. Trauma response and damage involves a range of areas in the brain, including: The corpus callosum - the connection between the two hemispheres (halves) of your brain: right and left ... which you can see in a very simplified version in the diagram below. It is the same action as during the original ... Traumatic brain injury is an injury to the brain and its parts, most commonly caused due to accidents, rupture of internal organs and other brain injuries, including Blood clots, Hematomas, Strokes, Concussions, Contusions, Swelling inside the skull, etc. In this disorder, tissue, neurons, and nerves of the brain are damaged by trauma. 27 Aug 2019 — The traumatic memory loops in the emotional side of the brain, disconnecting from the part of the brain that conducts reasoning and cognitive ...
Feb 10, 2019 - Explore Laura Lofy's board "Trauma and the Brain" on Pinterest. ... This diagram teaches about the autonomic nervous system and the polyvagal ... Training Objectives Synaptic Activity, Neurotransmitters, Nervous system responses, and Brain Structures associated with stress and trauma. How traumatic events impact an individual's emotional and behavioral presentations. How the brain processes and recalls traumatic events. The developing brain, adverse childhood experiences, ... The diagram below outlines some of these links from a nurturing perspective. Potential benefits of a nurturing approach, Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) awareness and trauma informed practice in an educational context 29 Jun 2020 — According to a 2006 study by NIH, trauma mainly affects three important parts of your brain: the amygdala, which is your emotional and ...
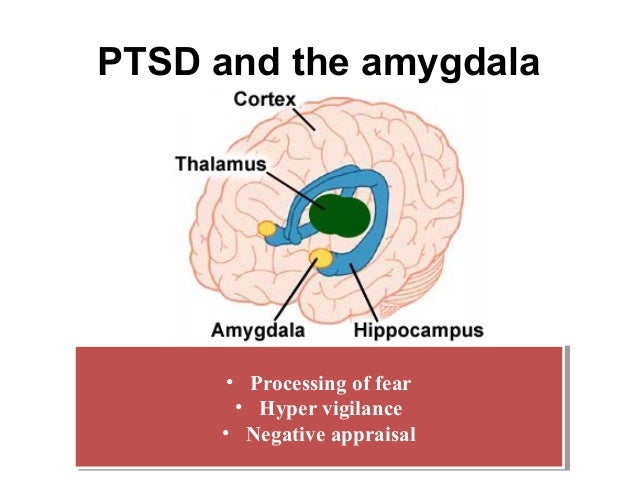
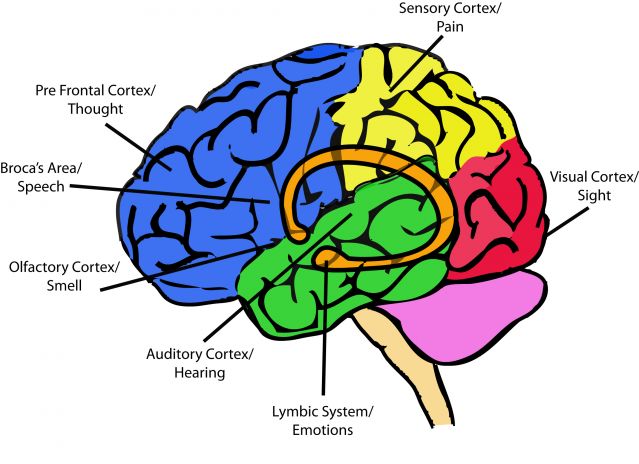
The major structures of the brain involved in processing trauma are the thalamus, the amygdala, the hypothalamus, and the hippocampus. Thalamus The thalamus sits atop of the brain stem and is responsible for processing external stimuli. Sounds, images, any of the senses are first sent through the Thalamus, or as I like to call it the "gatekeeper." The way trauma influences brain development will be different for each child. Just as each child will have different emotional responses to a traumatic event, the way that the brain responds to trauma will also vary across children. The following regions of the brain are the most likely to change following a Trauma and ADHD: The Differences and Similarities. One out of four children in the United States will experience some sort of trauma by the age of four. Four or more Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) are considered toxic to a child's emotional, cognitive, and physical wellbeing. Trauma creates changes to our biology, genetics, epigenetics ... How Trauma Affects the Brain. A traumatic experience that involves most or all of the senses — sight, hearing, smell, physical pain — as well as emotions, speech, and thought, is stored in ...
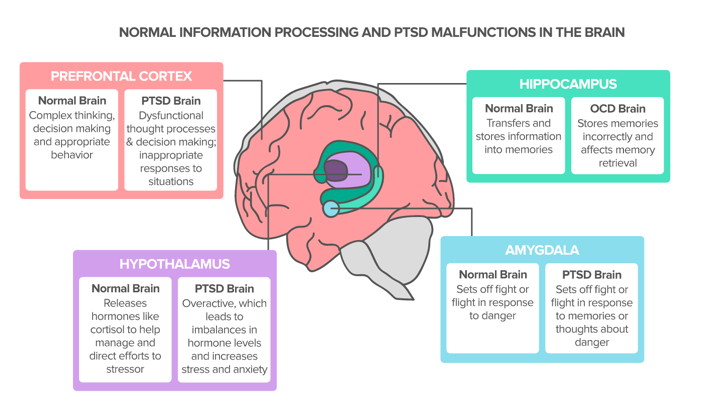
Post-traumatic stress is a normal response to traumatic events. However, PTSD is a more serious condition that impacts brain function, and it often results from traumas experienced during combat, disasters, or violence. Your brain is equipped with an alarm system that normally helps ensure your survival. With PTSD, this system becomes overly ...
Parts of the brain that are impacted by trauma: The Amygdala enlarges, stimulating "fight or flight mode.". Our emotional center in the brain, the amygdala "sounds the alarm" to the rest of the body when a threat is detected. When the amygdala is hyperactive, people may have a lower tolerance for stress and harder time controlling their ...
Role of body in trauma, trauma treatment, dissociation • Left right brain functions • Importance of mindfulness • Benefits of working with the body • Effects of trauma on cognition and emotion • Parts and effect on body • Existing resources, somatic resources • Use of movement and completion of actions Adapted from Ogden et al 2006
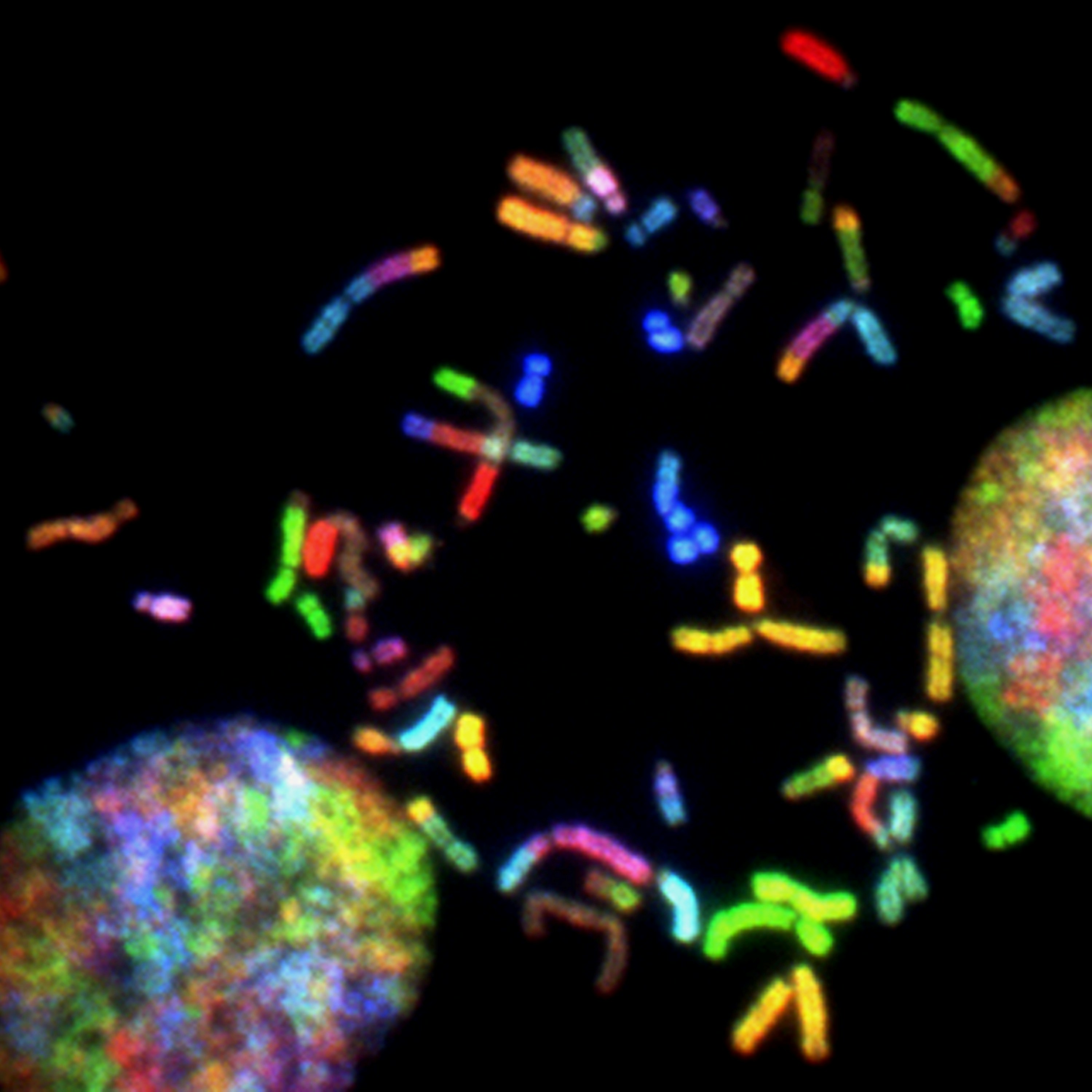
Brain Cancer Chromosomes. Chromosomes prepared from a malignant glioblastoma visualized by spectral karyotyping (SKY) reveal an enormous degree of chromosomal instability -- a hallmark of cancer. Created by Thomas Ried, 2014
Page 4 Module #5: Trauma and Brain Neurobiology Pre‐Module Assignments Student Assignment Checklist: 9 Complete the training, The Amazing Brain and Human Development and develop talking points that you would use with the adoptive parent of a child exposed to early trauma.
19 Oct 2020 — Childhood trauma physically damages the brain by triggering toxic stress. Strong, frequent, and prolonged, toxic stress rewires several ...
The Lund and Browder chart is a tool useful in the management of burns for estimating the total body surface area affected. It was created by Dr. Charles Lund, Senior Surgeon at Boston City Hospital, and Dr. Newton Browder, based on their experiences in treating over 300 burn victims injured at the Cocoanut Grove fire in Boston in 1942.
Trauma, or adverse childhood experiences, is perceived and activates the brain's alarm system - The Low Road The alarm (Amygdala) communicates through chemicals and initiates a wave of neurotransmitters including adrenalin and the hormone cortisol (Hippocampus) The brain organizes and changes to reflect this pattern
Trauma types, personality dynamics, and posttraumatic growth. Recent research is examining the influence of trauma types and personality dynamics on posttraumatic growth. Individuals who aspire to standards and orderliness are more likely to develop posttraumatic growth and better overall mental health.
This video reframes a trauma perspective in terms of learning brain versus survival brain as a way to make it easier for teachers to talk about trauma with s...
Text in this Example: Traumatic Brain Injury Types of TBI Hypoxia a decrease in oxygen supply rather than a complete absence of oxygen Anoxia a condition in which there is an absence of oxygen supply to an organ's tissues, even if there is adequate blood flow to the tissue Hematoma heavy bleeding into or around the brain Shaking of the brain back and forth within the confines of the skull ...
I healed paralysis, 30 brain lesions, PTSD, and severe brain damage with this science. That was after I used it in clinical social work with combat veterans with brain trauma and PTSD. Then I woke up with holes in my brain and used it to heal myself.

He was a wood cutter working in the jungle, he was coming down a path way in the jungle, as I approached him, he sat down to take a moment of rest, I asked him if its OK for me to take his picture. he said yes, he didn’t change his expression and was very calm about it. I took the picture, he nodded and smiled, and we parted ways.
Understanding blunt force trauma and violence in Neolithic Europe: the first experiments using a skin-skull-brain model and the Thames Beater Meaghan Dyer & Linda Fibiger∗ N 0 km 1500 The difficulty in identifying acts of inten-tional injury in the past has limited the extent to which archaeologists have been able
This psychoeducational flip chart consists of 22 diagrams with text summarizing the most current research and theoretical concepts in trauma treatment in a simple graphic format understandable for most clients. The use of these simple diagrams increases the ability of the client to understand the nature of the symptoms and engage more easily in ...
by JD Bremner · 2006 · Cited by 617 — Brain areas implicated in the stress response include the amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex. Traumatic stress can be associated with lasting ...PET: positron emission tomographyUS: unconditioned stimulusHPA: hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenalMRI: magnetic resonance imagingNeurobiology of PTSD · Cognitive function and brain... · MRI assessment of brain...
Use the trauma experience diagram above to educate about normal trauma responses. When we know what normal trauma responses are, we feel a sense of relief. All the reactions in the diagram are normal at first. Knowing this helps people feel sane and less overwhelmed. 3. Use physical release tools to work with the torrent of emotions and energy.
Show Clients, friends, and colleagues how trauma affects the brain and body. Use this chart to teach clients: How the brain and body share a relationship how the brain is constantly scanning for threats and is always ready to fight, flight, or freeze How this scanning to fight, flight or freeze was designed for our pri
III. Introduction. Trauma in childhood has serious consequences for its victims and for society. For the purposes of this critical review, childhood trauma is defined according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders IV and V as exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence [1, 2].This includes experiences of direct trauma exposure, witnessing ...
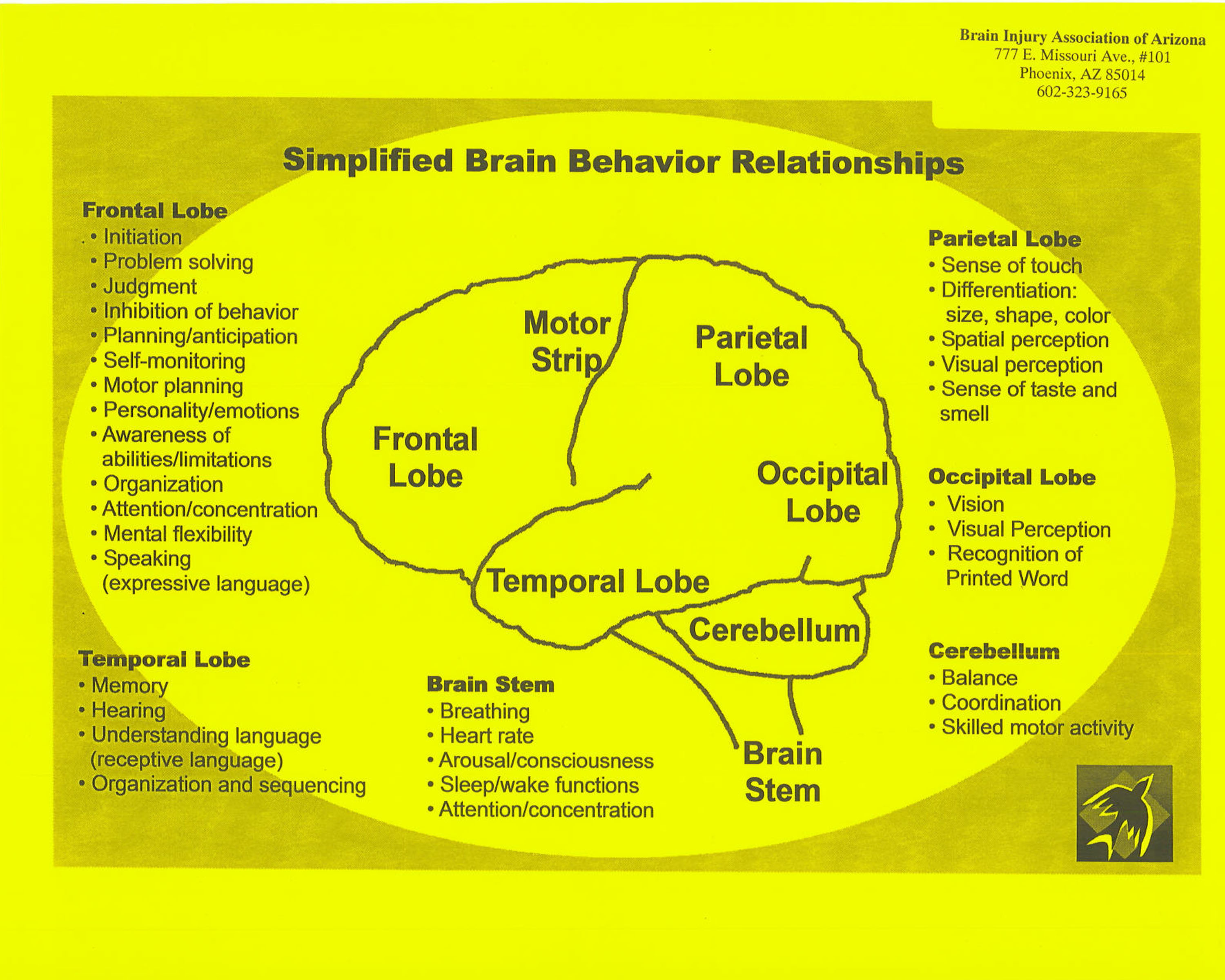
Anatomy of the Brain Overview. The brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind and soul. Intelligence, creativity, emotion, and memory are a few of the many things governed by the brain.
Trauma creates chaos in our brain. The amygdala is a small, almond-shaped portion of the brain. It's the emotional part. It's the primitive part of the brain. It interprets messages that there's danger or it's safe. It knows nothing about reasoning or cognitive functions. It deals with feelings and emotions.
NHS Lanarkshire EVA Services - Trauma and the Brain: Understanding abuse survivors responses. This animation is for any professional working with a service u...
The Anatomy of PTSD. The amygdala is the brain's stress evaluator and decides when to react. When a traumatic event occurs, the amygdala: sends out a danger signal. initiates the "fight or flight" response. stores stimuli associated with memory such as sights, sounds, smells, etc.
The brain is developed 90% by the age of 4, so early help is essential for repair. When considering a Child Looked After, intervention using this approach should be used as soon as a child has been removed from their birth parents. By waiting for a crisis we will significantly prolong and worsen the effects of trauma on the brain.
A traumatic experience can change the brain areas that enable you to feel these types of emotions." Followed by: "In other words, traumatic experiences can affect your ability to connect with others or to have positive and loving feelings. These 'numbing' symptoms are common for people
This consists of the two cerebral hemispheres of the cerebrum and their inter connections. Cerebrum The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Any kind of trauma or lesion in the cerebrum can lead to various diseases and disorders and mental illnesses. The cerebrum is divided into two cerebral hemispheres by the medial longitudinal fissure.
Trauma and the Brain This is a very simplistic explanation of a very complex process. There are three main parts of the brain which are greatly affected by experiencing severe or chronic traumatic events. Hippocampus The hippocampus processes trauma memories, by recycling the memory, mostly at night via dreams, which takes place over weeks or ...

















0 Response to "37 trauma and the brain diagram"
Post a Comment