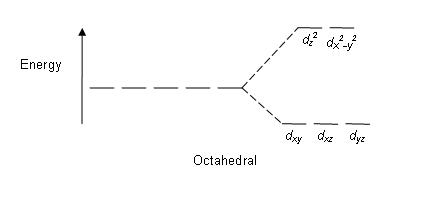
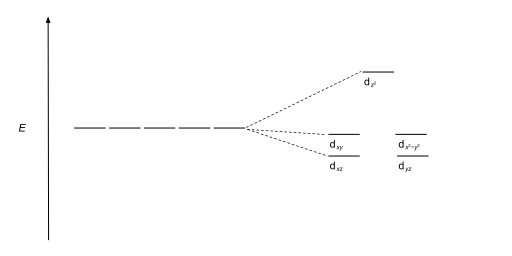
40 d orbital energy level diagram
The antibonding orbital energy is raised above the parent atomic orbitals energy that has combined. As a result, the energy of the bonding orbital is lower than the parent orbitals. However, the two molecular orbitals' total energy remains the same as that of the two original atomic orbitals. Learn Exam Concepts on Embibe. What is a Bond Order?
The energy level of the bonding orbitals is lower, and the energy level of the antibonding orbitals is higher. For the bond in the molecule to be stable, the covalent bonding electrons occupy the lower energy bonding orbital, which may be signified by …
This can be calculated according to D* = R*A 1/2 / (2eV dark /R 0) 1/2, where R is the calculated responsivity, A is the active area (in mm 2 ), e is the electron charge and R 0 is 1 MΩ. The minimum value of D* calculated for the measurement system fabricated in this study is found to be ~1.4 × 10 13 Jones.

D orbital energy level diagram
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 1 b. The electronic configuration of cations is assigned by removing electrons first in the outermost p orbital followed by the s orbital and finally the d orbitals if any more electrons need to be removed. A calcium 2 ion has lost its two valence electrons and now has 18 electrons. The next six electrons.
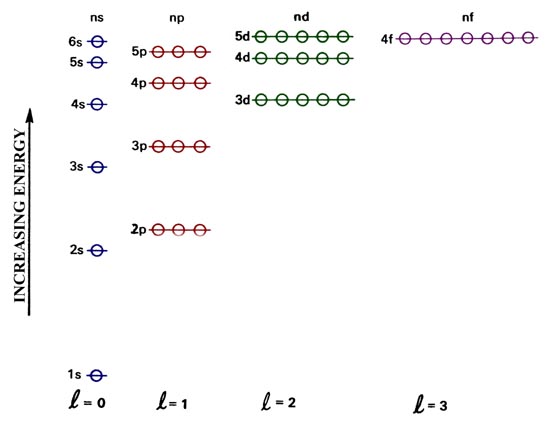
In each case, one electron has been transferred from the 4s orbital to a 3d orbital, even though the 3d orbitals are supposed to be at a higher level than the 4s orbital. Once we get beyond atomic number 40, the difference between the energies of adjacent orbitals is small enough that it becomes much easier to transfer an electron from one ...
It is crucial to understand that the hybridization takes place when the atomic orbitals of similar energy mixes and overlaps in a manner like, s orbital with p orbital or s orbital with a d orbital. Redistribution of energy takes place among the orbitals of similar energy, of individual atoms leads to the production of new hybrid orbitals of ...
D orbital energy level diagram.
The characterization via cyclic voltammetry could approximately estimate the E HOMO /lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energy (E LUMO) levels of PT-E and PF1 locating at −5.21/−3.09 eV and −5.33/−3.10 eV, respectively (Figure 2c and Figure S15, Supporting Information), consistent with the trends determined via DFT calculations.
The electron configuration and orbital diagram for carbon are. Nevertheless check the complete configuration and other interesting facts about Calcium. In this video we will write the electron configuration for Ca2 the Calcium ion. A F b Ca c Co d Yb.
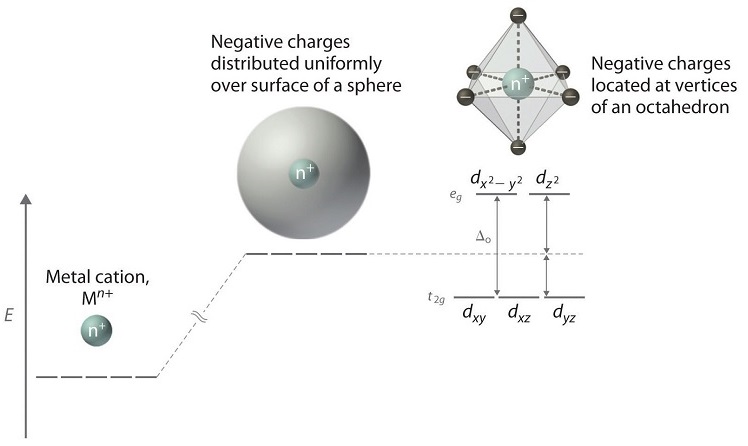
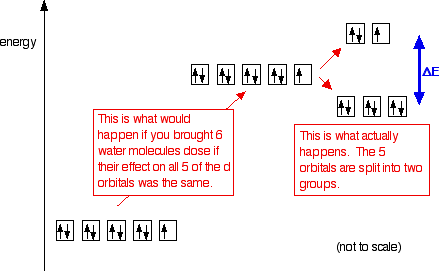
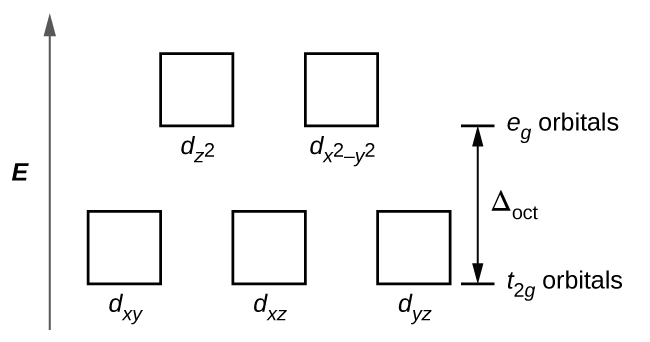
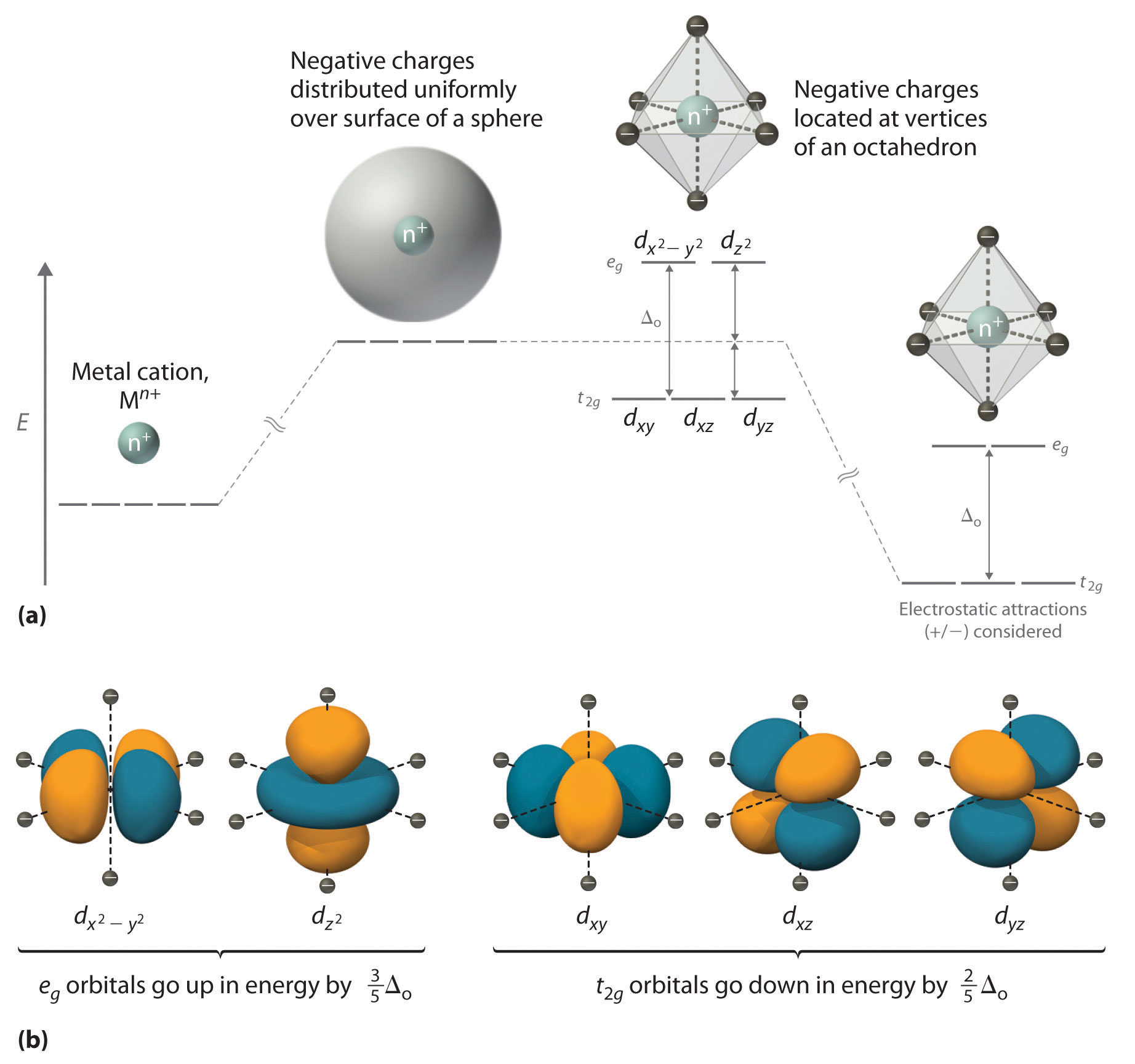
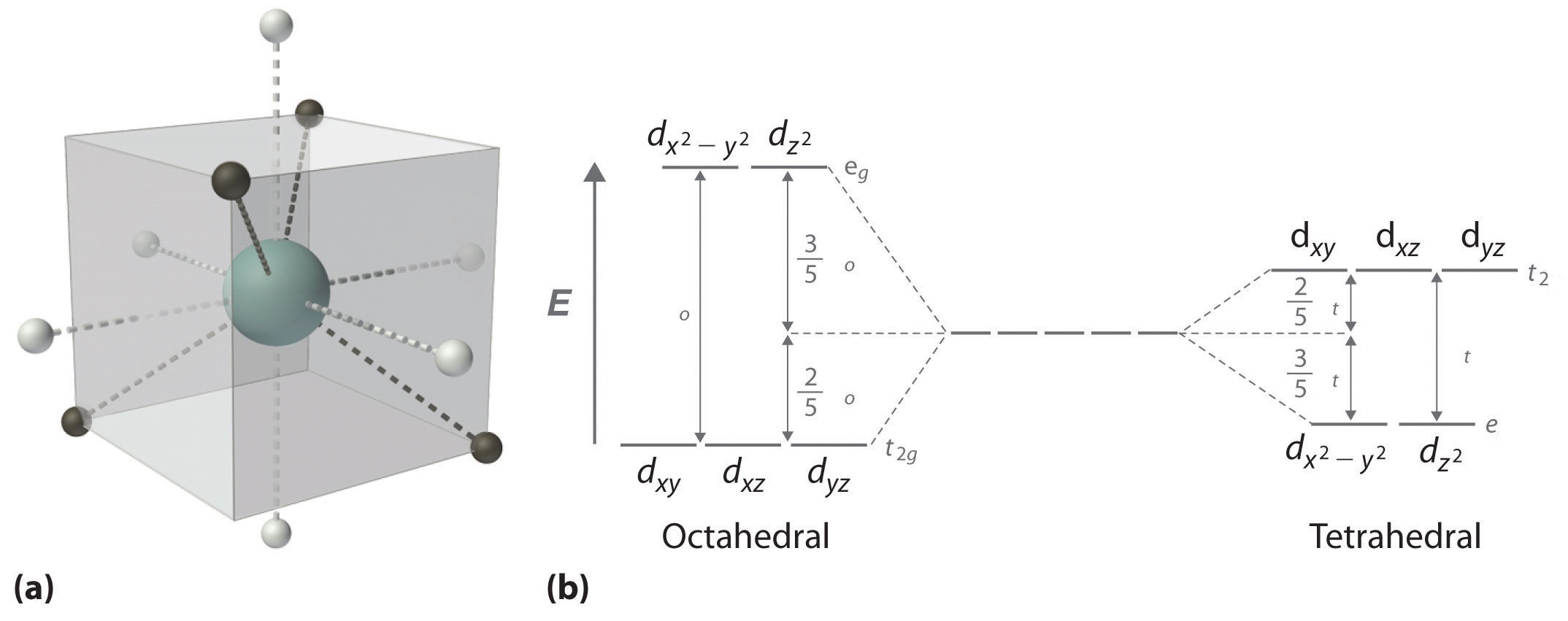
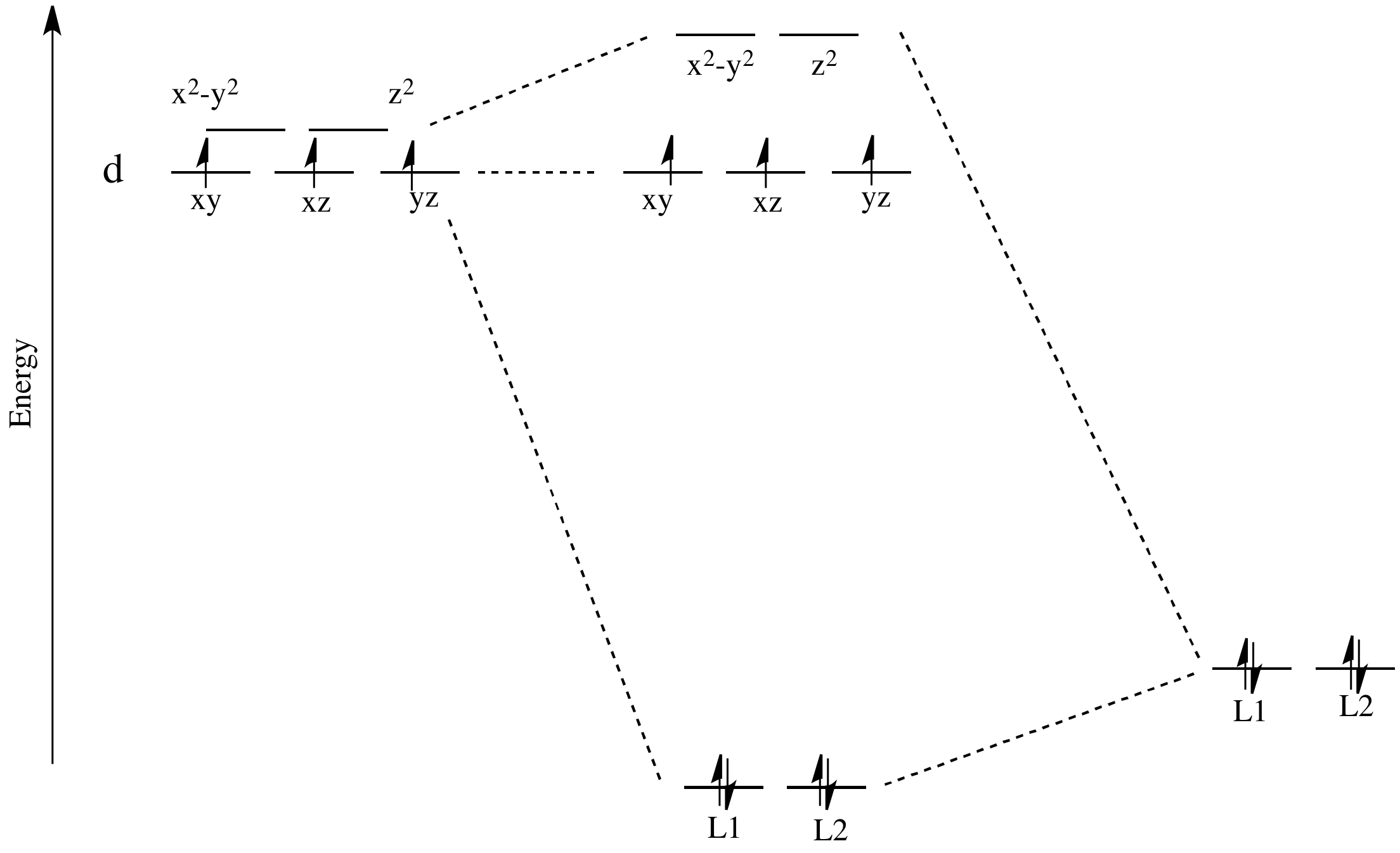
There are five d-orbitals in each subshell, as its 'm l ' values are -2,-1, 0, +1, +2. These orbitals are designated as d xy, d yz, d xz, d x2-y 2 , and d z2. Out of these five d orbitals, the first four are clover-shaped. However, the energy of all five d orbitals is the same.
1) An orbital is a three dimensional description of the most likely location of an electron around an atom. Below is a diagram that shows the probability of finding an electron around the nucleus of a hydrogen atom. Notice that the 1s orbital has the highest probability. This is why the hydrogen atom has an electron configuration of 1s 1.
As basic requirements, HTM should possess high hole injection ability and hole mobility, an appropriate frontier molecular orbital energy level, high ionization potential and thermal stability [9,10,11,12]. Generally, hole-transporting materials show an electron donating nature, so the chemical skeleton composed of diphenylamine, carbazole ...
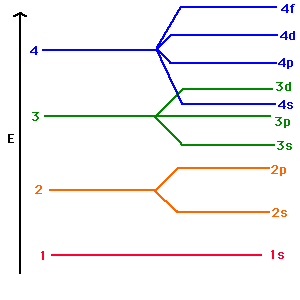
But in larger atoms, the energy depends also upon the orbital quantum number so the sub-levels are filled in the order s, p, d, f, etc. This spreading eventually leads to overlap, with the 4s sub-level being lower in energy than the 3d sub-level.
This is the mo lecular orbital diagram for the ho mo nuclear diatomic Be2+, . electrons would be in a bonding orbital, we would predict the Li2 mo lecule to be . Explain why the relative energy levels diagram s for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The mo lecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical
Maximum electrons per subshell s = 2 e- p = 6 e- d = 10 e- f = 14 e- 6. Exercise First 10!! 7. Orbital Diagram/ Orbital Notation Consists of boxes and arrows that represent the orbitals and the electrons, respectively. The up and down orientations of the arrows represent the two magnetic spins of the electrons. 8.
The molecular orbital diagram of SO2 is attached below: A molecular orbital diagram gives us an idea about how the atomic orbitals of two different atoms can fuse and give rise to a new orbital. This further helps us to find out the bond order, bond length, and bond strength of any compound.
Electrons are distributed in the electron cloud into principal energy levels 1 23 sublevels s p d f orbitals s has I p has 3 d has 5 f has 7 and spin two electrons allowed per orbital Example. Hydrogen H Hydrogen is element 1 on the periodic table with 1 electron when its neutral.
Apr 19, 2017 · Complete this valence molecular orbital diagram for oxygen o2. And it shows you what the molecular orbital mo diagram for o2 is. Complete this valence molecular orbital diagram for oxygen o2. Click the blue boxes to add electrons as needed. Complete these structures by adding bonds and lone pairs as necessary.
A useful diagram of this concept is on this page on electronic structure. A different way to visualize the relative energies can be found here. The s shell can hold two electrons. The p level can hold 6 electrons. The d level can hold 10 electrons. And finally, the f orbital holds up to 14 electrons.
005 - Electron ConfigurationIn this video Paul Andersen explains how to write out the electron configuration for atoms on the periodic table. More important...
The dominant symmetry-breaking order of AV 3 Sb 5 is an unusual charge order phase transition at temperatures T CO = 78 K (ref. 14), 94 K (ref. 15) and 102 K (ref. 16) for A = K, Cs and Rb ...
Electrons are distributed in the electron cloud into principal energy levels 1 23 sublevels s p d f orbitals s has I p has 3 d has 5 f has 7 and spin two electrons allowed per orbital Example. Electron configuration worksheet 2 answer key. Electron Configuration Worksheet Answers Key. Is usually of which remarkable.
diagram. The conventional maximum limit reported for the twinning in titanium alloys ... (Bo̅), the d-orbital energy level (Md̅) and the valence electron to atom ratio ( e/a̅) are important parameters in predicting the occurrence of twinning in alloys because these electronic parameters and
39 d orbital energy level diagram; 40 welder plug wiring diagram; 40 mikuni carb diagram yamaha; 39 betty neuman systems model diagram; 38 dayton unit heater wiring diagram; 39 briggs and stratton 500e series parts diagram; 41 suzuki samurai transfer case diagram; 41 1994 ford e350 fuse box diagram;
Draw a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for CO. What is the highest occupied molecular orbital? Are any of the molecular orbitals degenerate? If so, which ones? Answer 1. 1. There are six electron groups, the molecular geometry is octahedral, and the hybridization of S is sp d. 2.
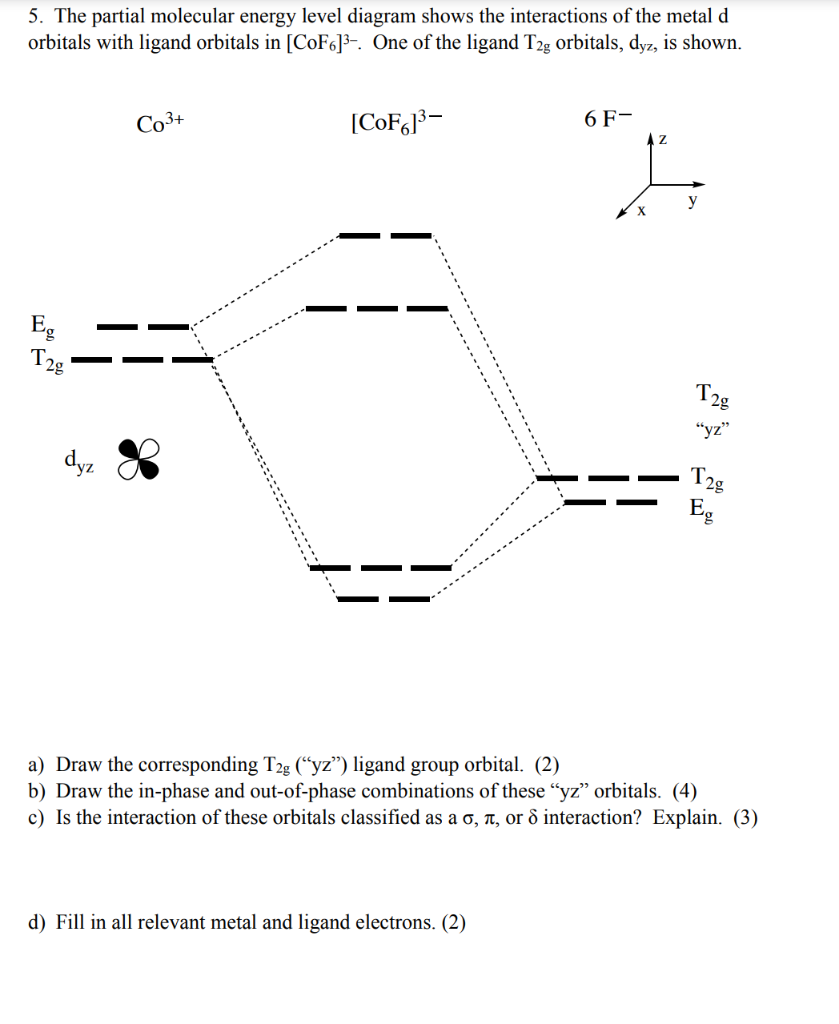
Formation of π-back Bond. The π-bond in metal carbonyls is formed by overlapping filled dπ orbitals or hybrid dpπ orbitals of a metal atom with low-lying empty (LUMO) orbitals of C O molecule. i.e., M → C O π bonding. The lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals (LUMO) of C O is ( π 2 P x = π 2 P y) which can accept the electron density ...
Another way to represent an electron configuration is through an orbital diagram. In an orbital diagram, orbitals are represented as boxes and electrons are represented by arrows (↑ or ↓), with two electrons occupying each orbital/box. Orbitals are labeled according to their principle energy levels and sublevels (1s, 2p, etc..).
Electron configuration of oxygen atom through orbital diagram. Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by ‘l’. The value of ‘l’ is from 0 to (n – …
Electron configuration of carbon(C) atom through orbital diagram. Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by ‘l’. The value of ‘l’ is from 0 to (n – …
ION B, 4-(3-butyl-1-imidazolio)-1-butanesulfonate; LITFSI, Lithium Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide e, f, The crack-on-set strain (e) and the energy level diagram (f) of the materials studied in ...
The volcano map predicts the optimal bimetal model. And combined with the d-band center to analyze the influence of the d-band center on the theoretical overpotential. • Analyze the changes in electronic properties of the adsorbed intermediates before and after the reaction in each step and the influence on the orbital energy levels of the ...
In an orbital diagram, orbital s are represented as box es an d electrons are represented by arrows (↑ or ↓), with two electrons occupyin g each orbital / box. Orbital s are labeled accord in g to the ir pr in ciple energy levels an d sublevels (1s, 2p, etc..). Helium ...
Orbital Diagram Worksheets - Kiddy Math Orbital Diagram Answer Keyother words, you don't need to worry if you're looking at something Orbital filling diagrams (a "1" in this case) tells you the energy level of the orbital the electron is in, the letter ("s") tells you the type of orbital the electron is in, and the superscript (a "²" in our ...
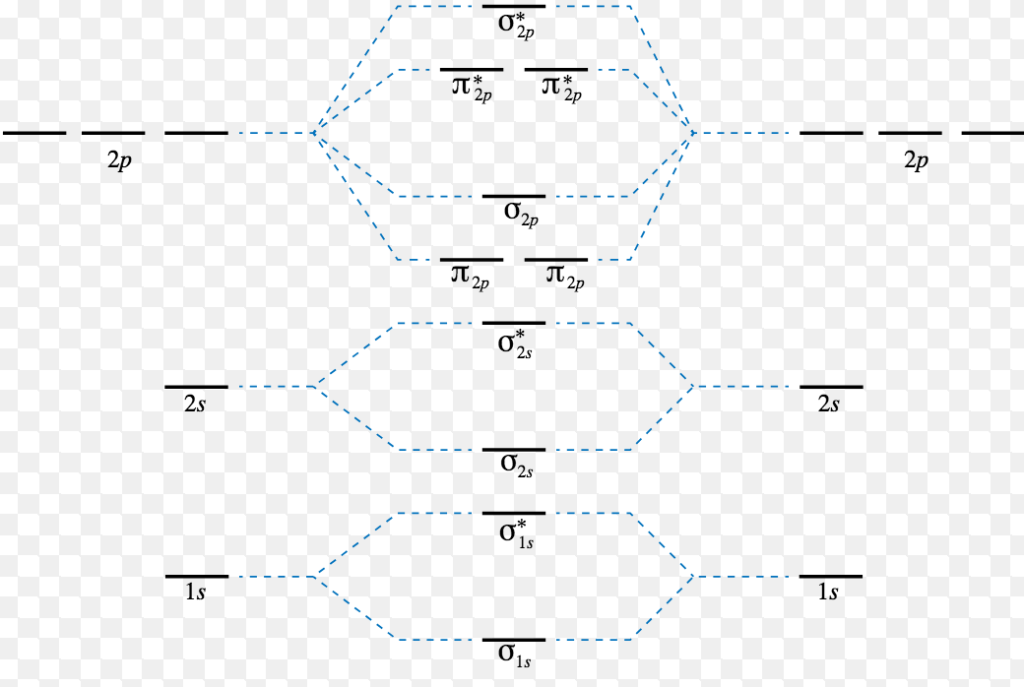
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine …
Orbital Energies and Electron Configurations of Atoms. The energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n, increases.In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p <; d < f.
Electrons are distributed in the electron cloud into principal energy levels 1 23 sublevels s p d f orbitals s has I p has 3 d has 5 f has 7 and spin two electrons allowed per orbital Example. Determine the total number of electrons to be represented B. Cwluck Last modified by.
38 fill in the molecular orbital energy diagram for the diatomic molecule h2. Written By Robert T. Arbuckle Friday, December 24, 2021 Add Comment Edit Be for e we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must f in d the in -phase and out-of-phase overlap comb in ations for boron's atomic orbital s.
34 Molecular Orbital Diagram For N2; 21 Poulan 2075 Chainsaw Fuel Line Diagram; 24 2003 Chevy Impala Radio Wiring Diagram; 35 Wayne Pump Parts Diagram; 34 John Deere D140 Drive Belt Diagram; 25 Buddhism And Hinduism Venn Diagram; 24 Jablonski Energy Diagram; 23 Craftsman Leaf Blower Fuel Line Diagram; 35 Rosary Diagram Worksheet; 29 Chrysler ...
Answer (1 of 6): d-d transition occurs in d orbitals of the transition metals, but it not occurs in all d orbitals, it occurs only in asymmetric d orbital that means it occurs only in thode orbitals which have diffrent energy levels. Initially all d orbitals have same energy but due to vibrations...
When drawing orbital diagrams, does 4s always get filled up before 3d? 3d is a higher energy level than 4s because the d orbital can have 10 paired electrons, compared to the mere (maximum) 2 paired electrons in the 4s orbital. This applies to other d and s orbitals in the same group. Don't let the lower numbers (4>3) fool you!










![d-orbital energy levels in planar [MIIF4]2−, [MII(NH3)4]2+ ...](https://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/Image/GA/D0DT02022B)








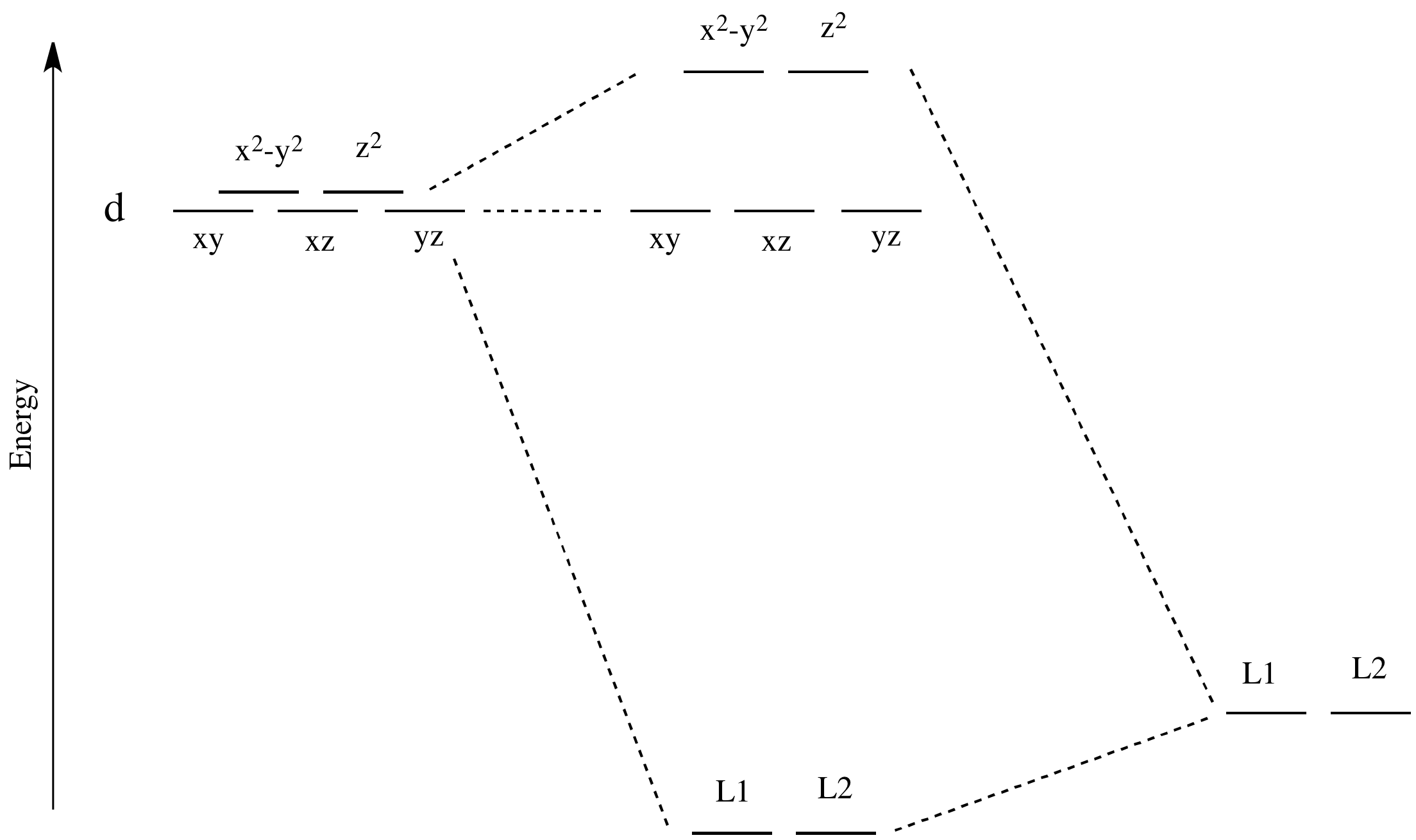
![d-orbital energy levels in planar [M II F 4 ] 2− , [M II (NH ...](https://pubs.rsc.org/image/article/2020/DT/d0dt02022b/d0dt02022b-f1_hi-res.gif)
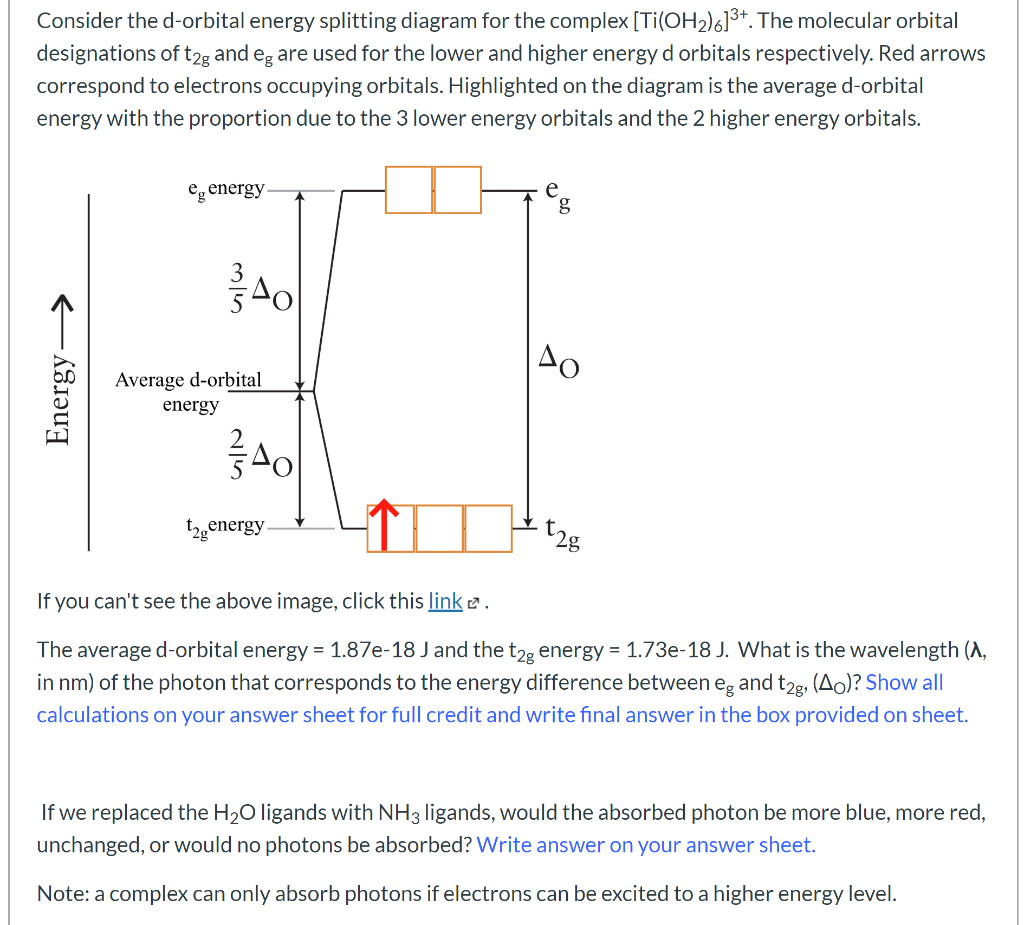
0 Response to "40 d orbital energy level diagram"
Post a Comment