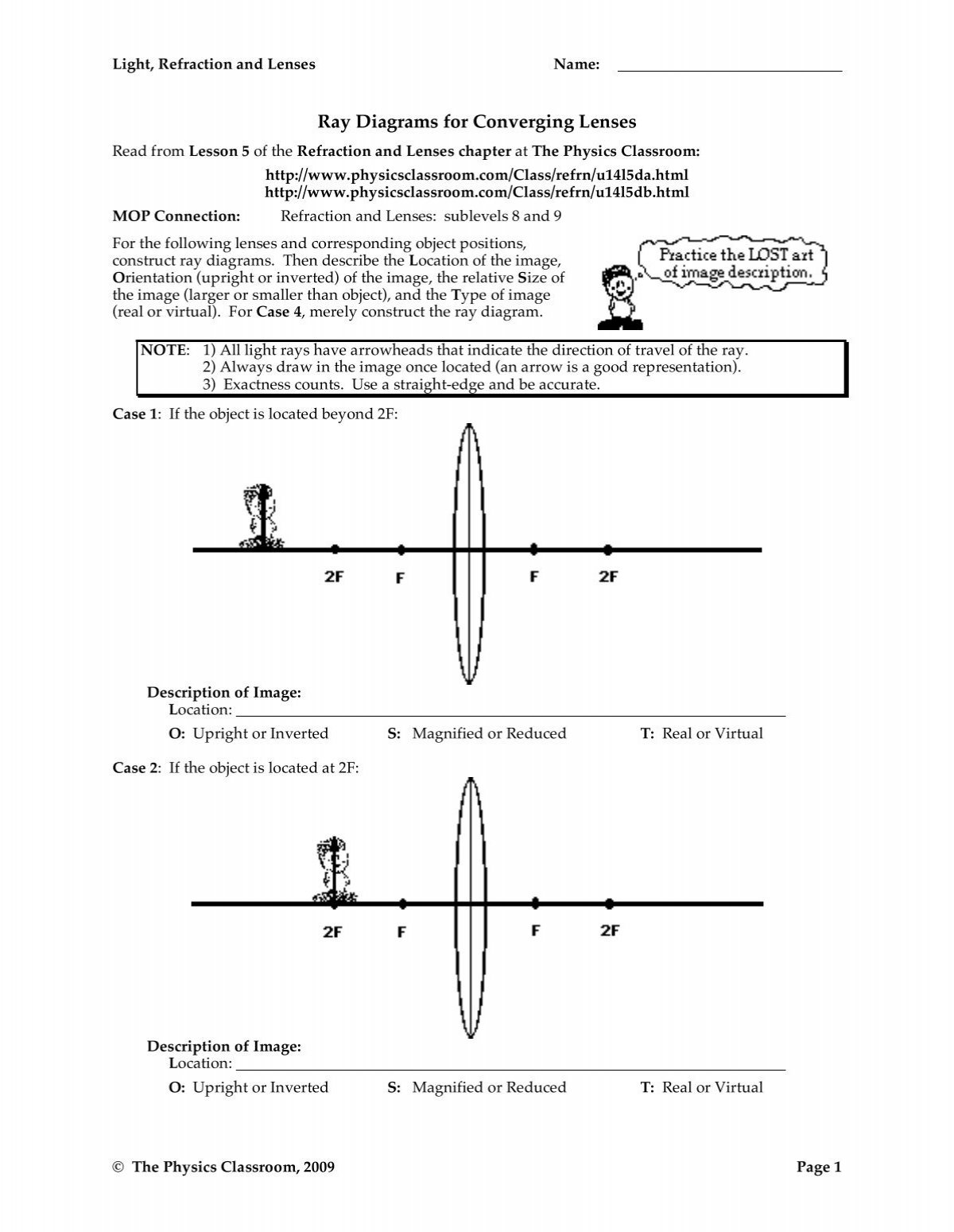
37 converging lens ray diagram
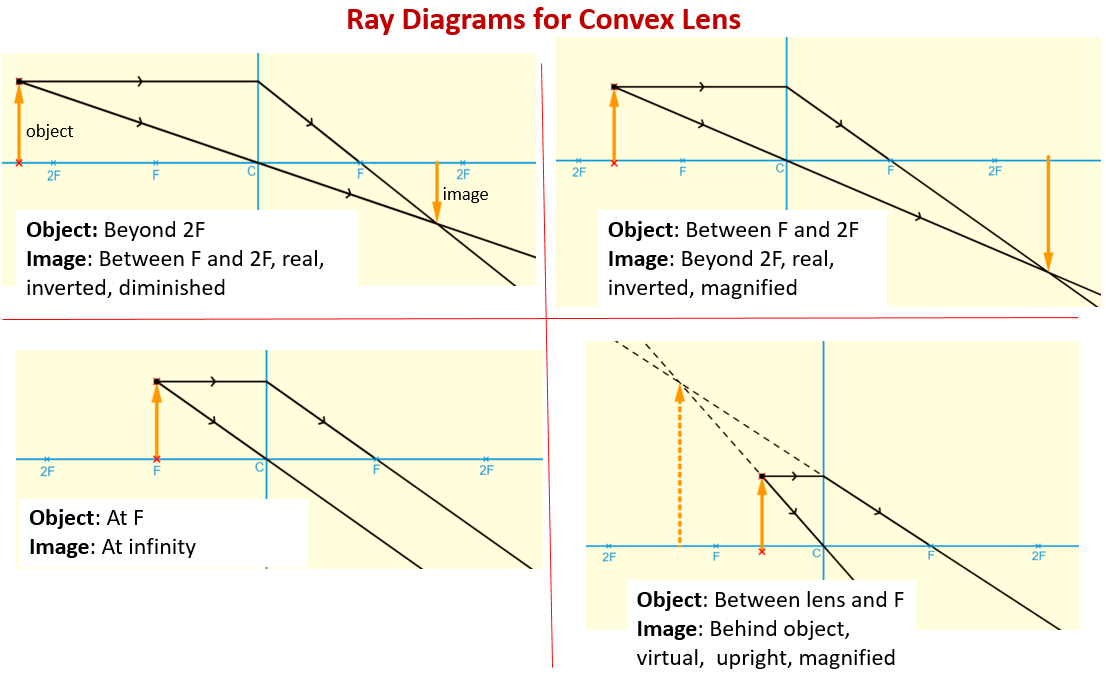
Name the lens and draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image. Solution: In a concave lens, the lens forms an upright and diminished image of an object placed at its focal point. Question: 17. Draw a ray diagram to show how a converging lens is used as a magnifying glass to observe a small object. Previously in Lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the general location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by double convex lenses.Perhaps you noticed that there is a definite relationship between the image characteristics and the location where an object placed in front of a double convex lens.
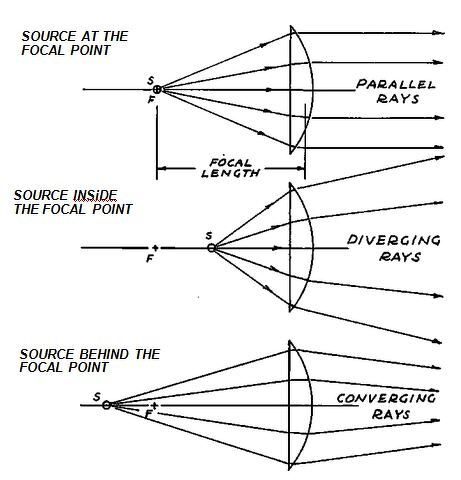
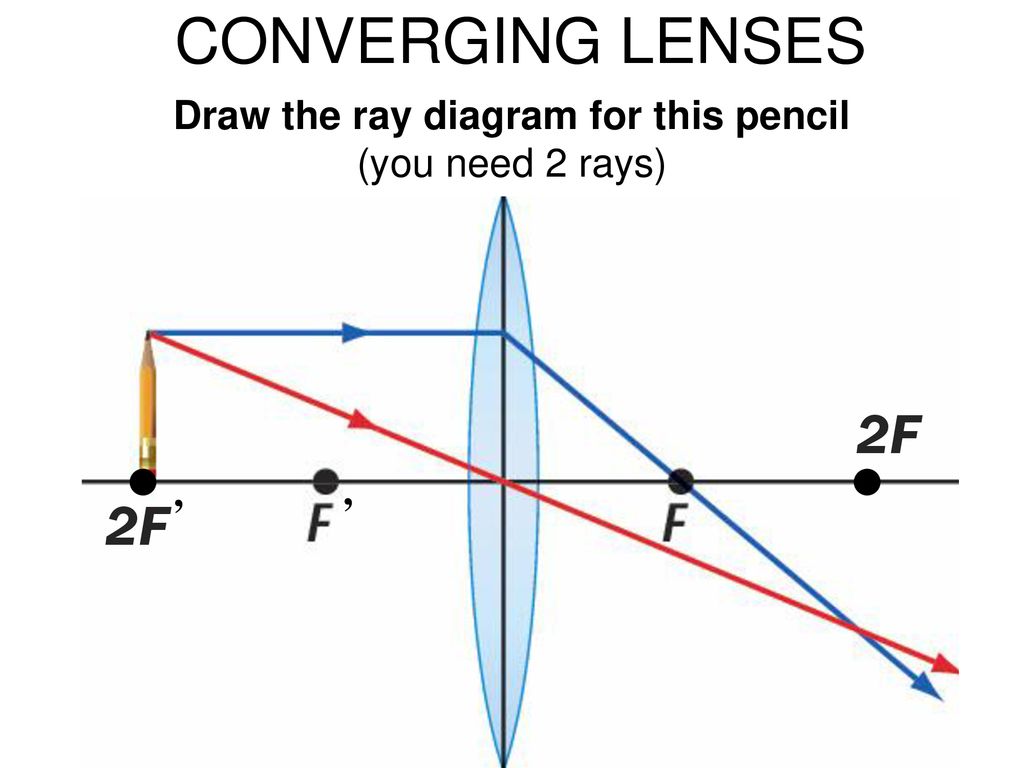
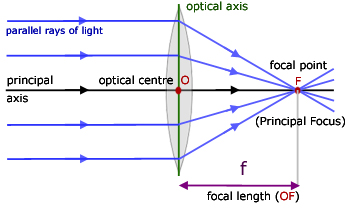
Converging Lenses A convex lens is a converging lens which bends light rays into focus. The focal length, f, is the distance to the focal point where parallel rays converge as shown. A Ray Diagram is a simple picture using only 2 or 3 light rays reflected off an object to visualize how images are formed.
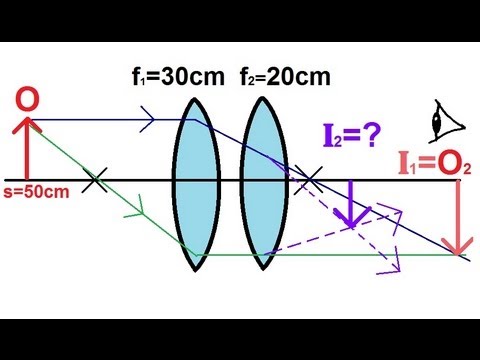
Converging lens ray diagram
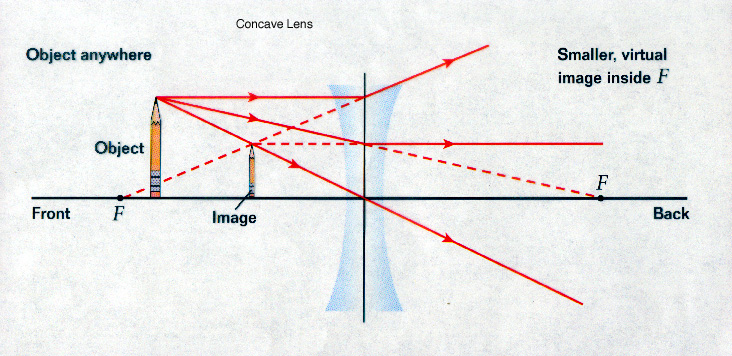
Apr 26, 2020 · NCERT Question 10 - An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed View Answer NCERT Question 11 - A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? For aconvex lens, we draw the ray diagram as follows: Draw a ray from the top of the object straight through the middle of the lens. Its direction is not changed. Draw a ray from the top of the object parallel to the principal axis. It is refracted by the lens to pass through the focal point. F From the diagram we see that the image in this ... Ray diagram for converging lens. Ray 1 is parallel to the axis and refracts as if from F. Ray 2 heads towards F’ before refracting parallel to the axis. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. image is always virtual, upright and reduced O F I F’ Ray diagram for diverging lens
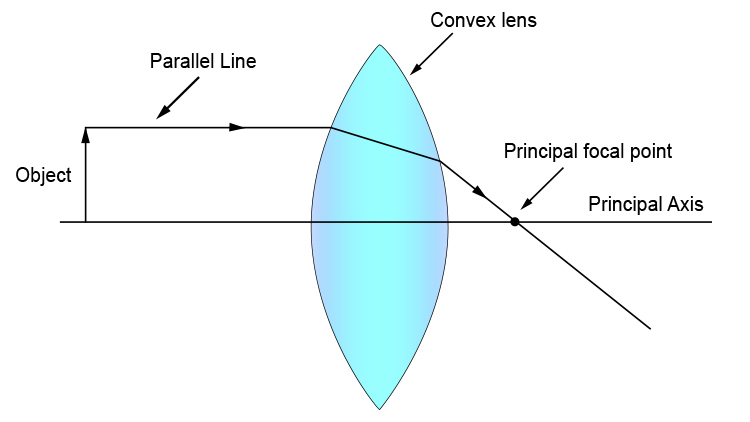
Converging lens ray diagram. A converging lens is an optical lens that converges all rays of light passing through it. The primary purpose of a converging lens is to focus the incoming rays from an object and converge them to form an image. The image can be magnified, diminished, or remain the same depending on the distance of the object from the lens. A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction.A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis.Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a … In the convex lens, the incident ray passing through F goes parallel to the principal axis after refraction. Convex lens. A convex lens is a lens with an outward curve. The thickness at the centre of a convex lens is more than the thickness at the edges of the lens. Convex lenses are converging lenses. To explain how to draw the diagrams, there are two key things to remember. 1 A converging lens refracts the light so that any ray of light parallel to the principal axis (the thick horizontal line) is turned to pass through the focal point. Rays of light parallel to the principal axis are all refracted through the focal point.
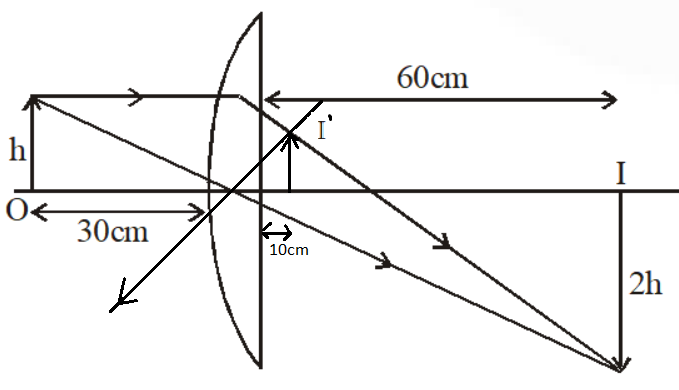
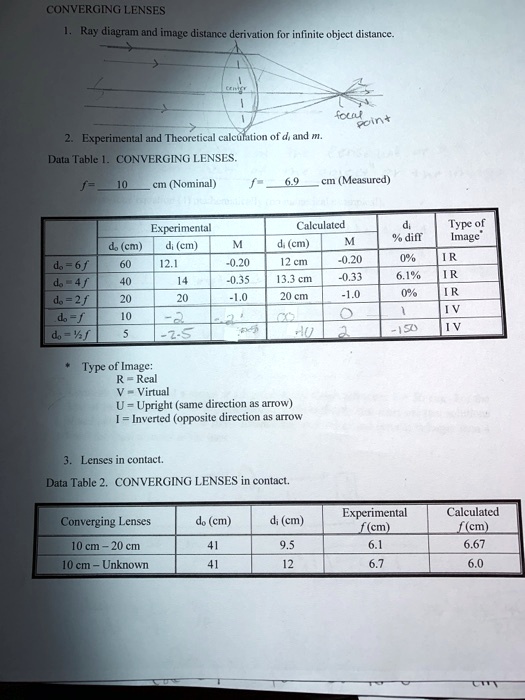
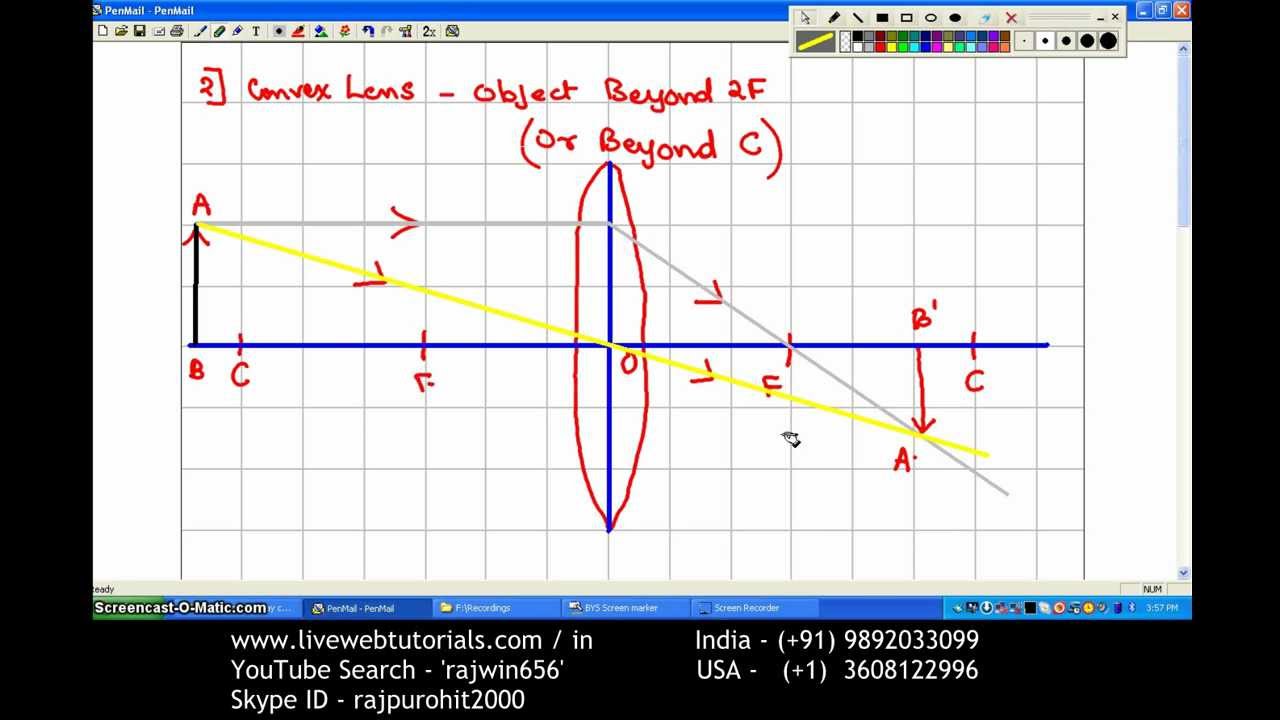
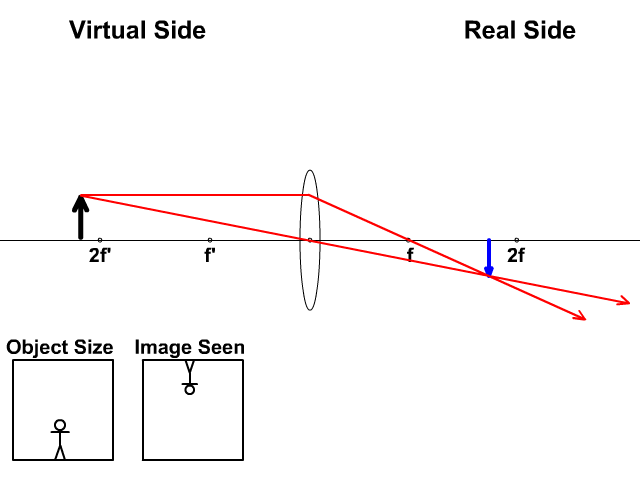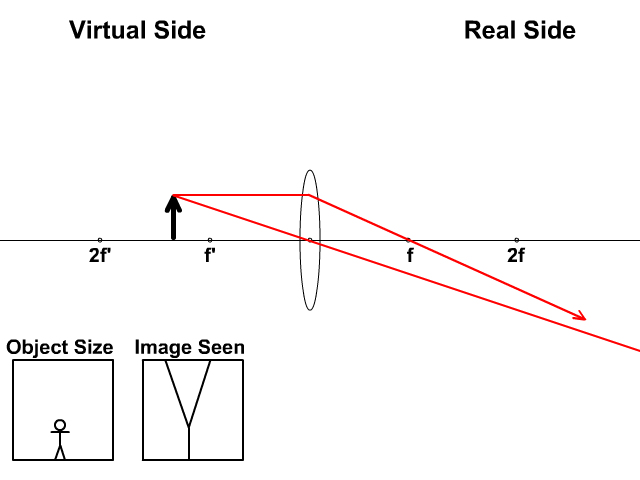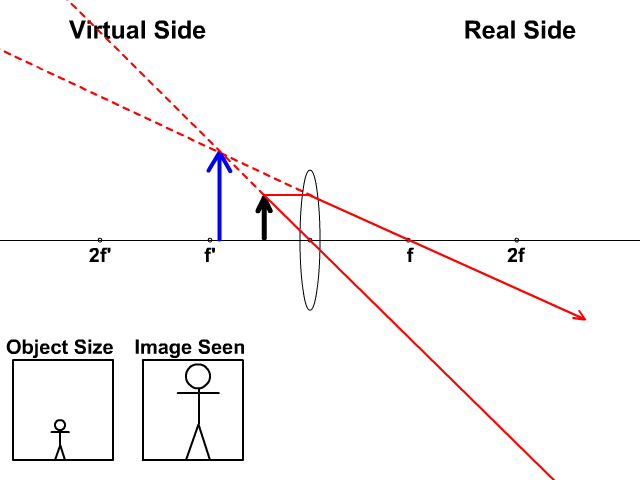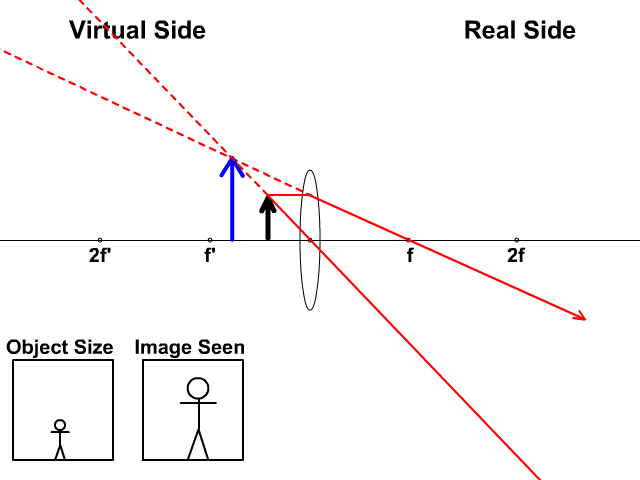
1. Converging Lenses The pre-lab notes described how ray diagrams involving the drawing of three principal rays can be used to determine image location, size, orientation, and whether the image is real or virtual. For each of the following cases, draw the ray diagrams and answer the related questions. All drawings and responses to the questions ... Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ An object is placed 50 cm from a lens produces a virtual image at a distance of 10 cm in front of the lens. Draw a diagram to show the formation of image and calculate the focal length of the lens. Ray Diagram for Object Located in Front of the Focal Point. In the three cases described above - the case of the object being located beyond 2F, the case of the object being located at 2F, and the case of the object being located between 2F and F - light rays are converging to a point after refracting through the lens. In such cases, a real image is formed. Apr 26, 2020 · For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa
The Physics Classroom » Curriculum Corner » Refraction and Lenses » Ray Diagrams for Converging Lenses. The document shown below can be downloaded and printed. Teachers are granted permission to use them freely with their students and to use it as part of their curriculum. Visit the Usage Policy page for additional information. Show/Hide Sub-topics (Converging Lens | O Level)Thin converging lensesRay diagrams for converging lensApplication of converging lens. There is one ray of light passing through the center of the lens. Always. 2 rays are enough to determine the position of image/object. The other ray of light ALWAYS passes through the focal point of the lens. Ray tracing diagram for a converging lens, with the object beyond twice the focal length. (yes, the light actually bends at both surfaces, not the middle of ... Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray.
Nov 25, 2021 · The image formation by convex lenses using ray diagram depiction can be briefly explained as follows, When the object is placed at infinity: When the object is placed at infinity, the image formed by the convex lens will be at the second focus, F2. The nature of the image obtained will be a real image and it will be in inverted form.
Ray diagram for converging lens. Ray 1 is parallel to the axis and refracts as if from F. Ray 2 heads towards F’ before refracting parallel to the axis. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. image is always virtual, upright and reduced O F I F’ Ray diagram for diverging lens
For aconvex lens, we draw the ray diagram as follows: Draw a ray from the top of the object straight through the middle of the lens. Its direction is not changed. Draw a ray from the top of the object parallel to the principal axis. It is refracted by the lens to pass through the focal point. F From the diagram we see that the image in this ...
Apr 26, 2020 · NCERT Question 10 - An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed View Answer NCERT Question 11 - A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens?











---teachoo.png)


0 Response to "37 converging lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment