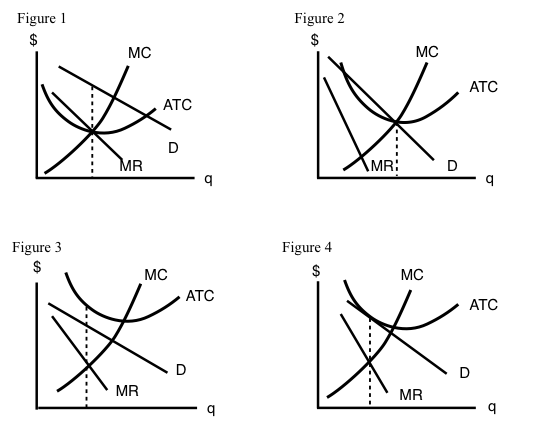
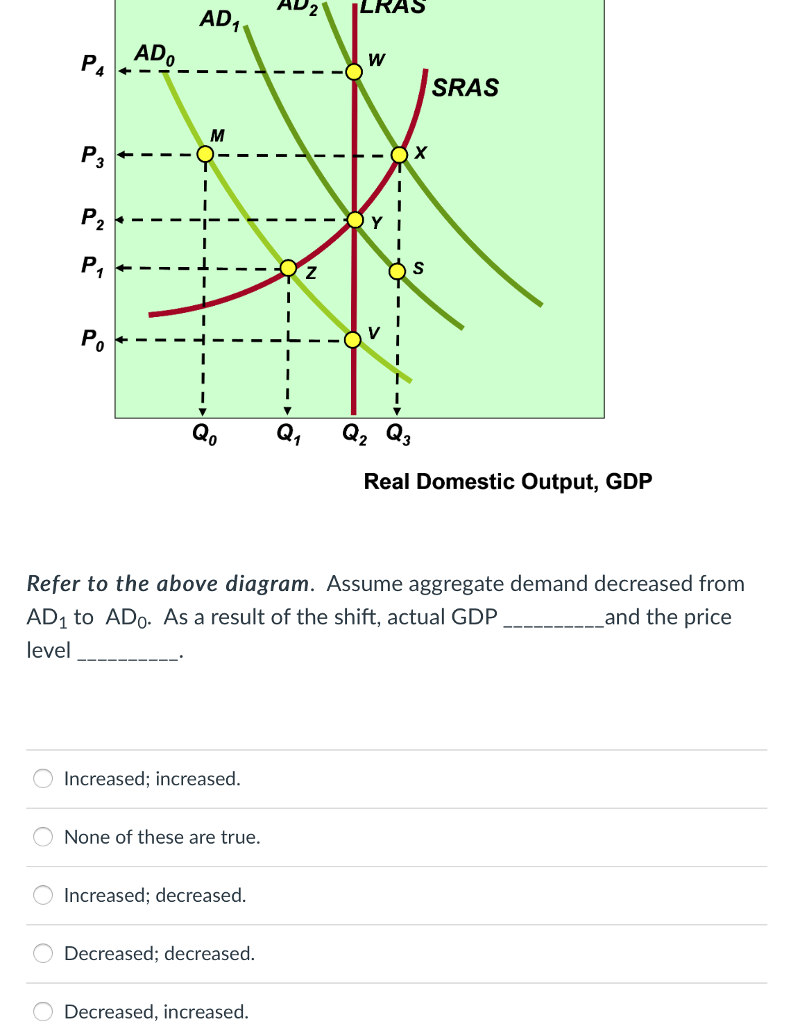
37 the monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of q1 in the diagram is
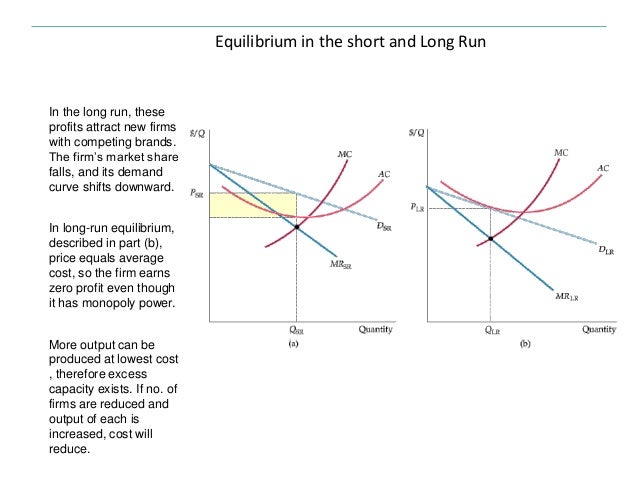
Unlike a perfectly competitive firm, a monopolistically competitive firm ends up choosing a level of output that is below its minimum efficient scale, labeled as point b in Figure . When the firm produces below its minimum efficient scale, it is under‐utilizing its available resources. If a monopolistically competitive firm is earning positive economic profits, entry will occur until economic profits are equal to zero. 5.2.1 Monopolistic Competition in the Short and Long Runs. The demand curve of a monopolistically competitive firm is downward sloping, indicating that the firm has a degree of market power.
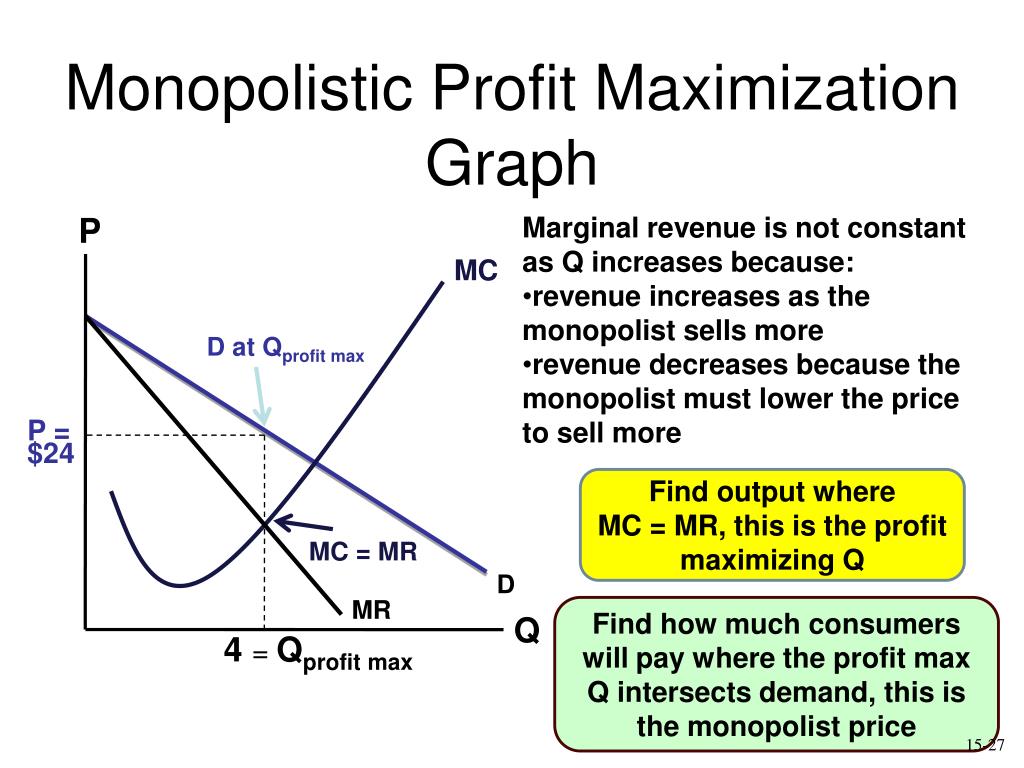
Monopolistic Competition Red=4 largest. Green=5-8 Blue=9-20 The numbers are the HHI. Market Share in Monopolistic Competition Output and Price in Monopolistic Competition The Firm's Short-Run Output and Price Decision Holding quality and marketing constant, profit maximization is achieved by choosing the price/quantity where MR = MC
The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of q1 in the diagram is
22)If a monopolistically competitive firm's marginal cost curve shifts upward, then its level of output A)will decrease. B)could increase, decrease, or stay the same but more information is needed. C)will increase. D)will stay the same. 22) 23)When firms in monopolistic competition incur an economic loss, some firms will This means that the firms in monopolistic competition will suffer from productive inefficiency as their costs are not minimised. The level of productive inefficiency can be expressed as an 'excess capacity,' marked by the difference between Q2 (the maximum output) and Q1 (the output a firm can produce in the long run). 5) In the short run, a firm in a monopolistic competition will produce a level of output where its A)marginal revenue equals marginal cost and takes the market price as given. B)marginal revenue equals marginal cost and will set its price according to the demand for that output level.
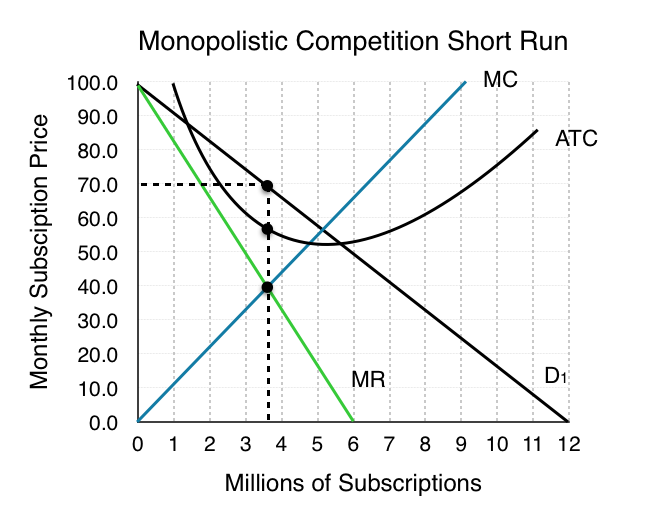
The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of q1 in the diagram is. The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is A. not in long-run equilibrium. B. earning a positive economic profit. C. in long-run equilibrium. D. earning negative economic profits. This is in contrast to competitive, monopolistically competitive,and monopolistic firms, all of which increase output when marginal costs decline. To see why firms competing in a Sweezy oligopoly may not increase outputwhen marginal cost declines, suppose marginal cost decreases from MC0 to MC1 inFigure 9-2. Figure 13 - 14 illustrates a monopolistically competitive firm. 7) Refer to Figure 13 -14. Which of the following statements describes the firm depicted in the diagram? 7) A) The firm is making no economic profit and will exit the industry. B) The firm is in long - run equilibrium and is breaking even. Expert Answer Diagram monopolistic competition short run n the short run, the diagram for the monopolistic competition is the same as for a monopoly. The firm maximizes profit where MR=MC. This is at output Q1 and price P1, leading to supernormal profit Monopolist … View the full answer Previous question Next question
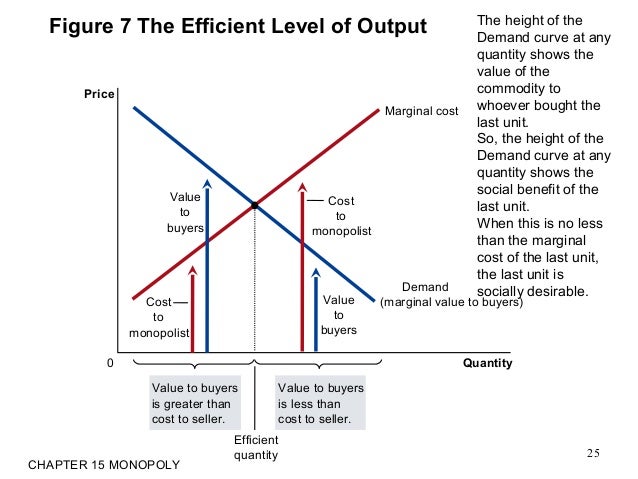
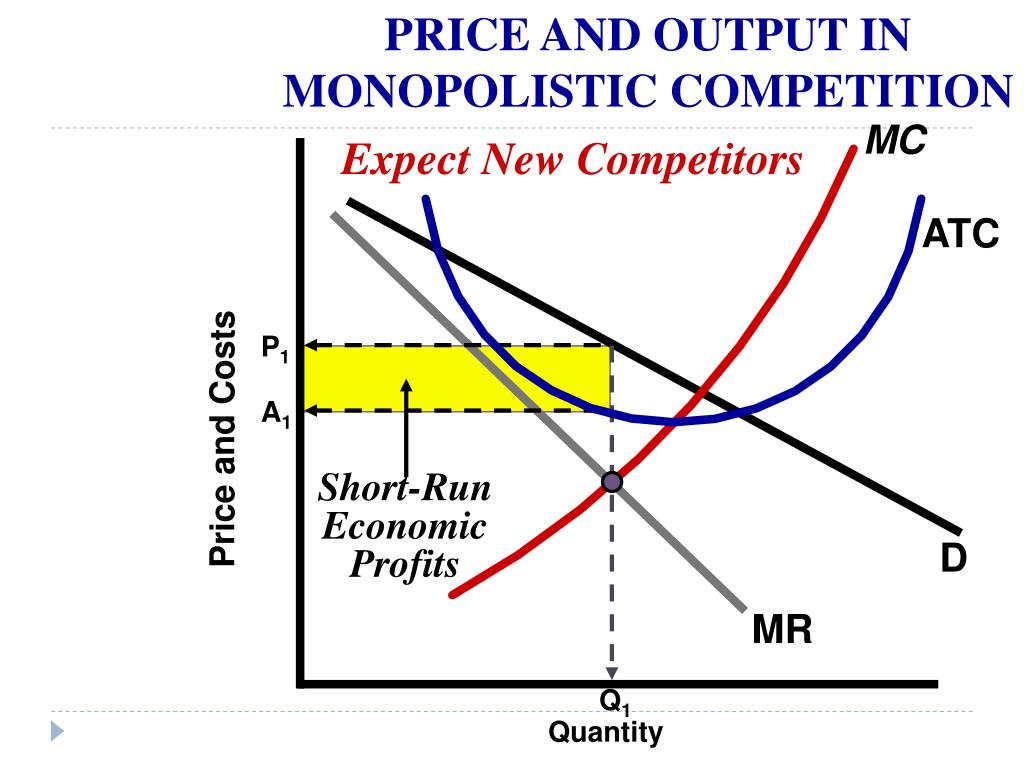
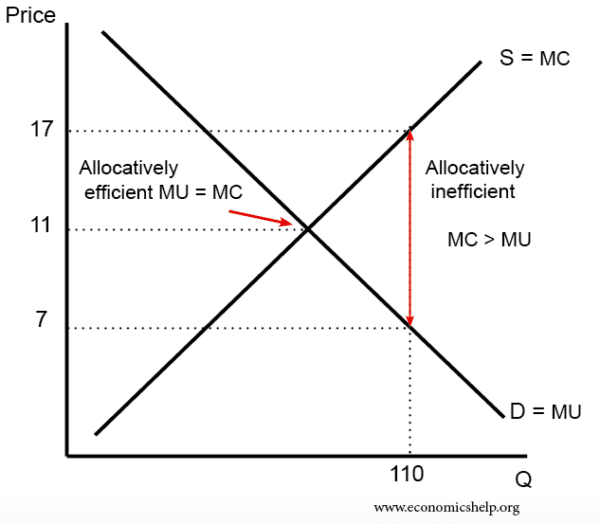
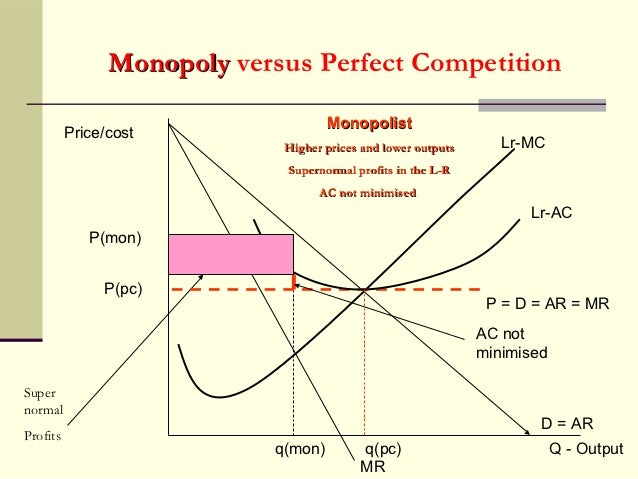
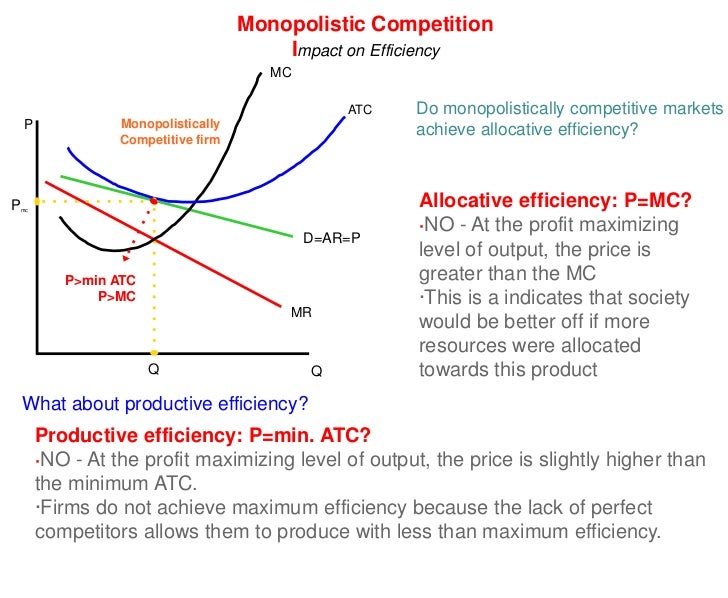
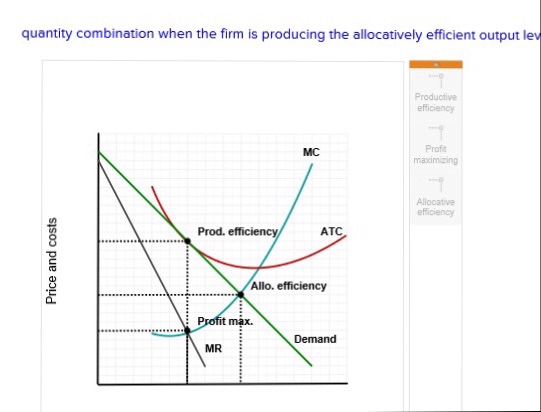
However, monopolistic competition comes with a product mark-up, as the price is always greater than the marginal cost. Inefficiencies in Monopolistic Competition. The equilibrium output at the profit maximization level (MR = MC) for monopolistic competition means consumers pay more since the price is greater than marginal revenue. As the diagram show, productive efficiency is at q1 and allocative efficiency level of output is q2. However, in a monopolistically competitive market, a firm is producing at profit maximising level q does not achieve any of the efficiency. Long Run. In the long run too, a monopolistic competitive firm will not achieve any of the efficiencies. In a monopolistically competitive market each firm makes independent decisions about price and output, based on its product, its market and its costs of production • Monopoly market - pure monopoly where there is only one firm in the market - a sole supplier; OR a cartel, where firms collude as one firm OR where firms have Under monopolistic competition, firms have freedom to enter and exit the industry. In the long run if firms are earning profit new firms are attracted and it will increase the output and consequently prices will fall leading to conversion of profit making situation into normal profit situation.
View CAIE 2018 Oct Q3a.docx from ECN 121 at Kolej Yayasan UEM. 2018 Oct/Nov 42 3. (a) Analyse the factors which determine the price of a firm's product and its output in monopolistic competition. 2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit. The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is in long-run equilibrium. The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is earning positive economic profits. In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms make zero economic profits. At the profit-maximizing output level the firm will A) earn a profit of $176. B) break even. ... Refer to the above figure. Based on the diagram, one can conclude that A) some existing firms will exit the market. B) new firms will enter the market. C) the industry is in long-run equilibrium. ... A monopolistically competitive firm that earns an ...
A. Consider the diagram below depicting the demand and cost conditions faced by a monopolistically competitive firm. a. Use the graph to show how price and output will vary depending upon which point the firm produces. Indicate the levels that will be produced under profit maximization, productive efficiency, and allocative efficiency.
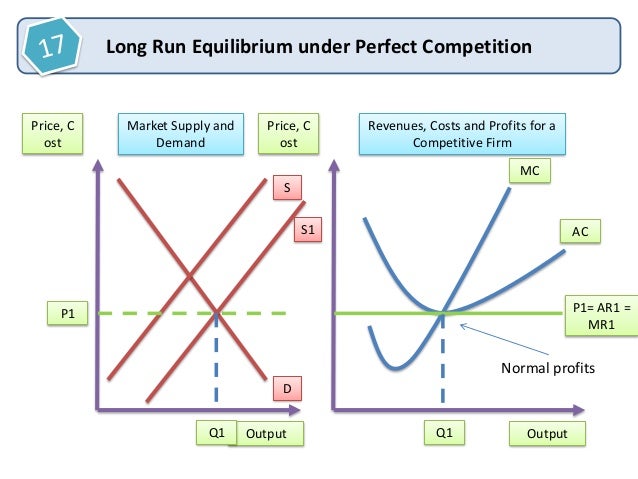
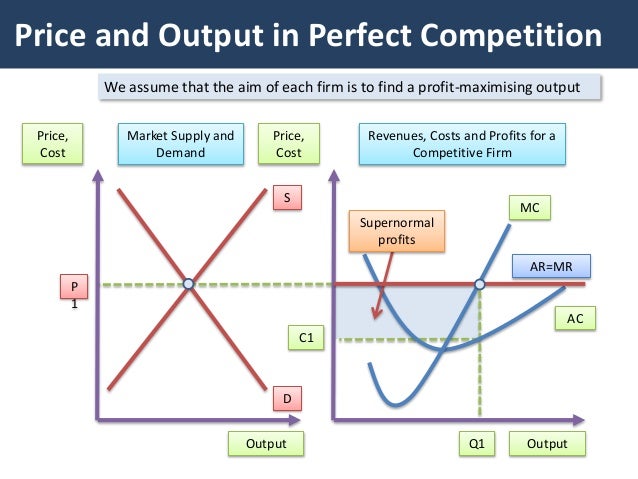
The firm will follow the profit-maximising rule and produce at the output level where MR = MC, and at this output level AR = ATC (shown as AC in the diagram, it means the same thing) which means that it is making a normal profit only. What is of interest here is that the firm is producing at a long-run output level where its ATC is at a minimum ...
The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. FIGURE 11-3 19) Refer to Figure 11-3. A monopolistically competitive firm is allocatively inefficient because in the long-run equilibrium A) MC is greater than price. B) price is greater than LRAC at QL.
The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is in long-run equilibrium 12 The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is earning positive economic profits. 25.3
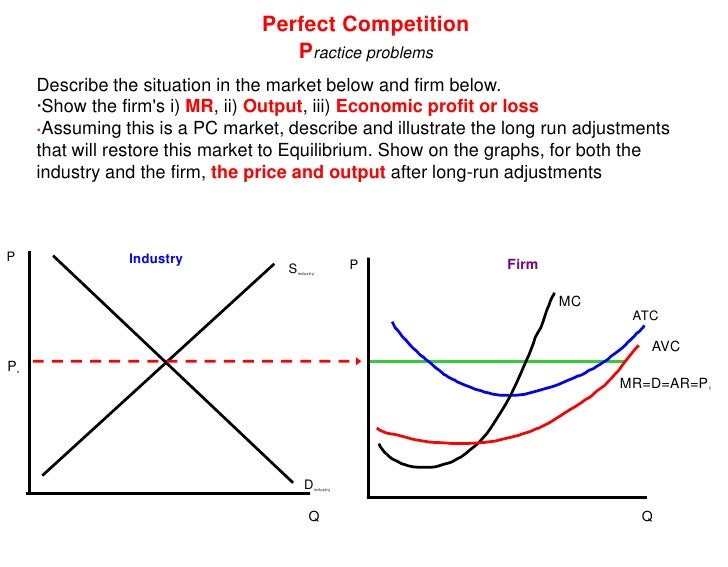
27. In the short run a competitive firm will always choose to shut down if product price is less than the lowest attainable average total cost. True False 28. After all long-run adjustments have been completed, a firm in a competitive industry will produce that level of output where average total cost is at a minimum. True False 29.
The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is A.not in long-run equilibrium. B.in long-run equilibrium. C.earning a positive economic profit. D.earning negative economic profits.
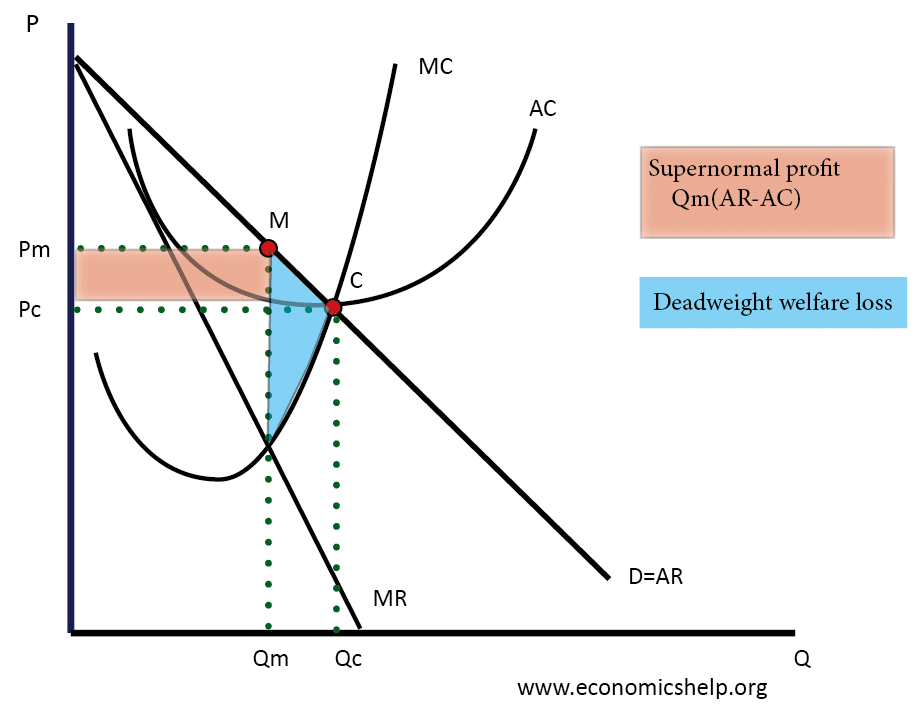
The diagram above shows a firm in a monopolistically competitive industry making super normal profits in the short run. The diagram is exactly the same as the one for the monopolist; the firm maximises profit by setting MC = MR giving price P 1 and quantity Q 1.
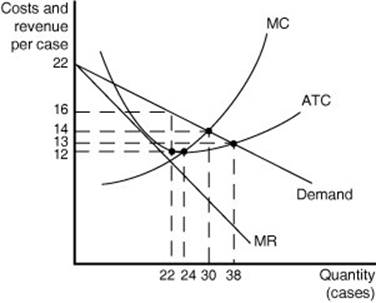
In this example, MR and MC intersect at a quantity of 40, which is the profit-maximizing level of output for the firm. The profit maximizing price is $16. The volume of profits = Total Revenue - Total Cost =$60 . A firm under Monopolistic Competition like a firm under monopoly can have both profit and loss in the short run.
The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is A. not in long-run equilibrium. B. earning a positive economic profit. C. in long-run equilibrium. D. earning negative economic profits.
5) In the short run, a firm in a monopolistic competition will produce a level of output where its A)marginal revenue equals marginal cost and takes the market price as given. B)marginal revenue equals marginal cost and will set its price according to the demand for that output level.
This means that the firms in monopolistic competition will suffer from productive inefficiency as their costs are not minimised. The level of productive inefficiency can be expressed as an 'excess capacity,' marked by the difference between Q2 (the maximum output) and Q1 (the output a firm can produce in the long run).
22)If a monopolistically competitive firm's marginal cost curve shifts upward, then its level of output A)will decrease. B)could increase, decrease, or stay the same but more information is needed. C)will increase. D)will stay the same. 22) 23)When firms in monopolistic competition incur an economic loss, some firms will











![Monopolistic Competition [HL Topic]](https://www.dineshbakshi.com/images/economics_diagrams/monopolistic-competition-7.jpg)




![Monopolistic Competition [A Levels]](https://www.dineshbakshi.com/images/economics_diagrams/monopolistic-competition-6.jpg)

0 Response to "37 the monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of q1 in the diagram is"
Post a Comment