40 draw a ray diagram
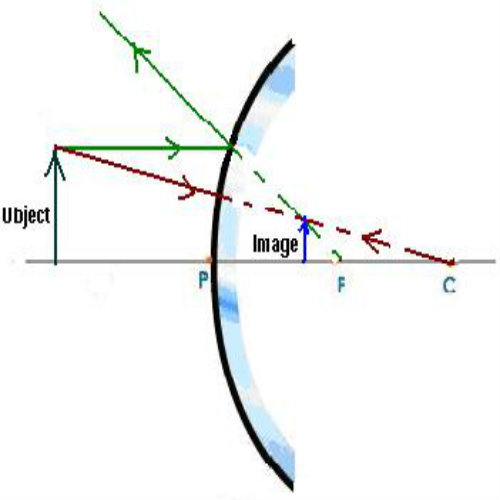
Method for drawing ray diagrams – Concave lens. A concave lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a concave lens. To draw a ray diagram you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as “the two rules of refraction for diverging lenses”. This section of Lesson 2 details and illustrates the procedure for drawing ray diagrams. Let's begin with the task of drawing a ray diagram to show how Suzie will be able to see the image of the green object arrowin the diagram below. For simplicity sake, we will suppose that Suzie is viewing the image with her left eye closed. Thus, we will focus on how light travels from the two extremities of the object arrow (the left and right side) to the mirror and finally to Suzie's right eye as she sights at the image. The four steps of the process for drawing a ray diagram are listed, described and illustrated below. 1. Draw the image of the object. 2. Pick one extreme on the image of the object and draw the reflected ray that will travel to the eye as it sights at this point. 3. Draw the incident ray for light traveling from the corresponding extreme on the object to the mirror. 4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 for all other extremities on the object.
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are:
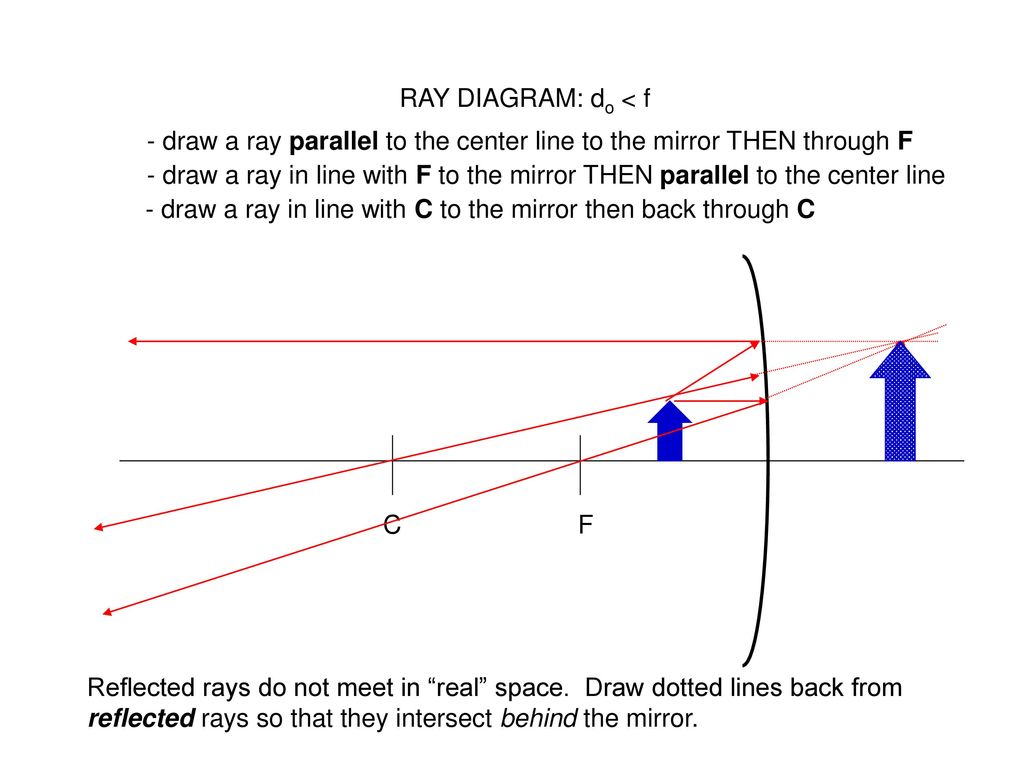
Draw a ray diagram
When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object. Transcribed image text: Ray diagrams: Draw a ray diagram that shows why a convex lens magnifies objects that are closer to it than the focal length. Label the object and image, and indicate if the image is real or virtual. Draw a ray diagram that shows why the image produced by a convex lens is inverted if the object is farther away from the lens than the focal length. Draw a ray diagram to show how such a lens would work. Hint: you need to label both the object and image in your diagram and to think about where the image appears to be. Share. Cite. Improve this answer. Follow answered May 9 '17 at 11:21. user155557 user155557. 1 $\endgroup$
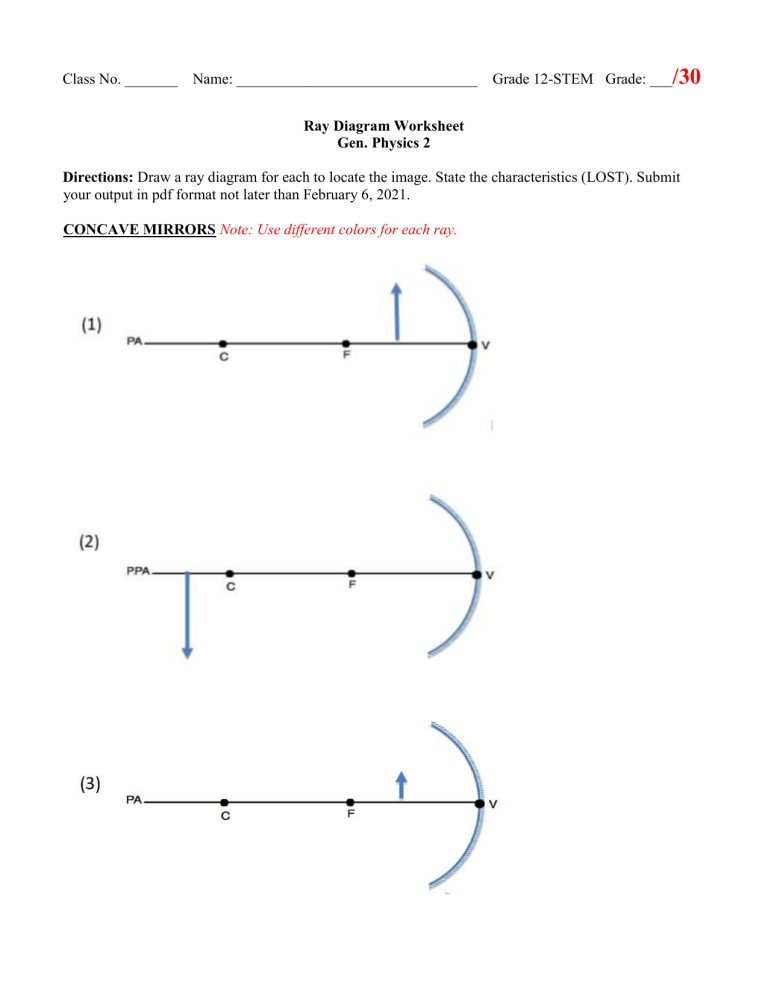
Draw a ray diagram. Some rules for ray diagrams, exemplified by your good practice. When pupils draw ray diagrams in their books you should insist on three things: The diagrams are drawn in pencil. All rays are drawn with a ruler. All rays carry an arrow showing the direction of travel of the light. When you draw ray diagrams on the board or on a transparency: Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The distance from the lens to the screen is 1) the focal length. 2) the object distance. 3) the magnifying power. 4) one-half the radius of curvature of one of the lens faces. . (10) Draw a ray diagram for a cm tall object placed cm from a converging lens having a focal length of cm. It is important to be able to draw ray diagrams to show the refraction of a wave at a boundary. To draw a ray diagram: Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis ... Set your child up for success with Lido, book a class today! Our top 5% students will be awarded a special scholarship to Lido. Q40) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed on the principal axis of a convex mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
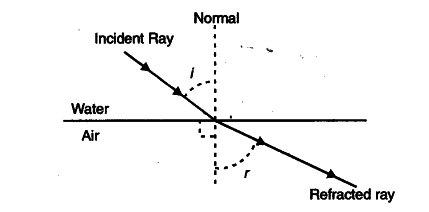
Draw 3 rays of light to make a ray diagram 1 – Draw a line from the top of the object, parallel to the axis. Once the line reaches the lens, refract it through the focal point. 2 – Draw a line from the top of the object, through the centre of the lens. Ray diagrams. A ray diagram shows how light travels, including what happens when it reaches a surface. In a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: a straight line; The Basic Ray Diagram Draw a basic ray diagram and choose a point to mention the object. From the top of the object, draw two rays such that one ray passes through the focal point (if produced), while the other travels straight towards the mirror and is parallel to the principal axis. Draw a ray diagram showing the path of rays of light when it enters with oblique incidence (i) from air into water; (ii) from water into air.
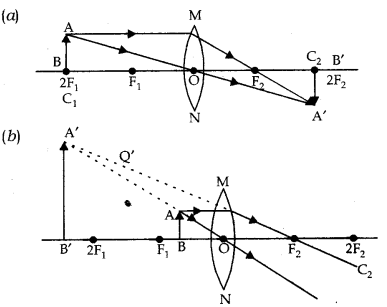
Answer (1 of 2): Accuracy will only come by drawing with calculation. But of course if you know all the rules correct the diagram so formed will be correct. Like you want to draw ray diagram for a convex lens then For lenses, we have — 1. Light coming parallel to the principal axis passes thro... This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. The rays parallel to the principal axis and the ray through the center of the lens are drawn.Locators allow you to drag both the object and the lens. You can change the focal length using a slider. First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. So, it passes through focus after refraction. We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center. So, the ray will go through without any deviation. Where both rays meet is point A'. And the image formed is A'B'. This image is formed between F 2 and 2F 2. We can say that. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in a myopic eye. asked May 15, 2018 in Physics by paayal (147k points) cbse; class-12; 0 votes. 1 answer. With the help of ray diagrams, show the formation of image by (i) a myopic eye (ii) correction of myopic eye by using an appropriate lens.
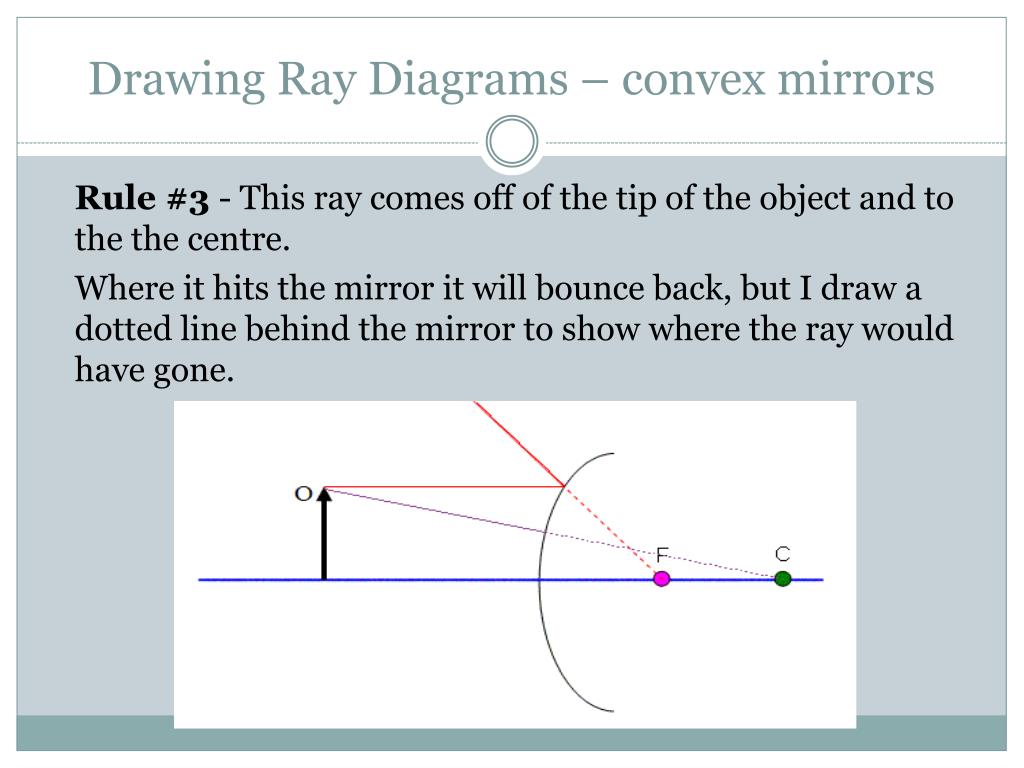
The method for drawing ray diagrams for concave mirror is described below. The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the center of curvature (C) of a concave mirror. Yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two ...
This video covers:- How to draw ray diagrams for convex and concave lenses - How to comment on whether an image is real or virtual, upright or inverted, and ...
SmartDraw is the easiest and most powerful way to create diagrams. It runs on any device with an internet connection. Simply start with one of the many included diagram templates and SmartDraw will walk you through the rest with intuitive tools, automation, and lots of included symbols. SmartDraw's powerful automation aligns shapes and objects ...
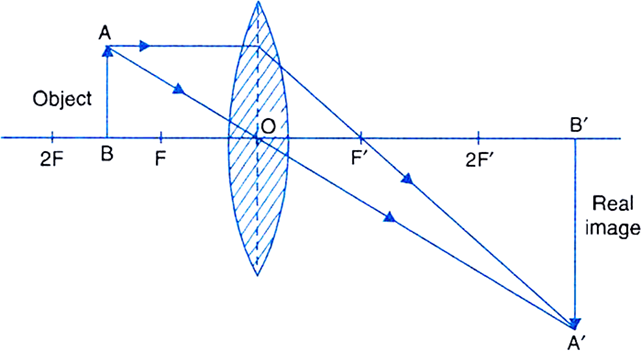
Draw Ray Diagrams To Show The Formation Of A Three Times Magnified I Real Image Ii Virtual Image Of An Object Kept In Front Of A Converging Lens Mark The Positions Of Object
A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens.The ray tacing needs to have the three principal rays.Also draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principle waves converge.. B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram.

Draw The Ray Diagram For Convergent Mirror When Object Is Placed Perpendicular On The Principal Axis Brainly In
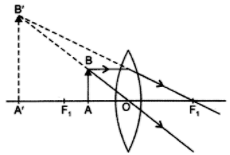
To explain how to draw the diagrams, there are two key things to remember. 1 A converging lens refracts the light so that any ray of light parallel to the principal axis (the thick horizontal line) is turned to pass through the focal point. Rays of light parallel to the principal axis are all refracted through the focal point.
Drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Refraction of light. Total internal reflection. This is a short tutorial on how to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Click on the images to view a larger version. Initially, we have an object in front of a plane mirror.

Draw A Ray Diagram To Show The Formation Of Image By A Concave Mirror For An Object Placed Between Its Pole And Focus State Three Characteristics Of The Image Physics
Answer (1 of 2): General info * Always use a ruler while drawing ray diagrams. never draw free hand ray diagrams. * The distance b/w pole & focus and b/w focus and centre of curvature should be same on both the sides of lens/mirror. * Always draw arrow heads on the ray to show their path. Rul...
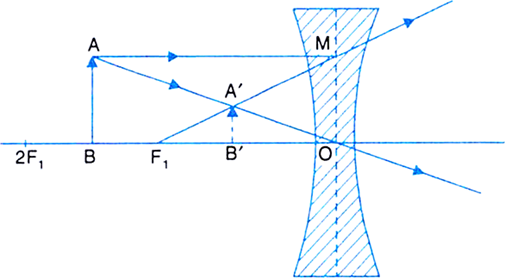
Draw A Ray Diagram To Show The Formation Of The Image Of An Object Placed Between F And 2f Of A Thin Concave Lens Deduce The Relation Between The Object Distance The
Image formation by convex lens ray diagrams. Image formation in a convex lens can be explained with the help of three principal rays shown in the figure. The ray parallel to the principal axis passes through the focal point after refraction by the lens. The ray passing through optical centre passes straight through the lens and remains undeviated.
How to Draw Ray Diagram (POWERPOINT) - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. DRAWING TECHNIQUE (CHAPTER 7 FORM4 SCIENCE)
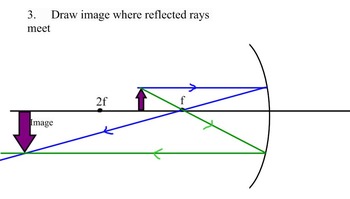
First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. So, it appears to pass through focus after reflection. We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center. So, the ray will go through without any deviation. Where both reflected rays meet is point A'. And the image formed is A'B'. This image is formed between F 1 and Optical Center (O) We ...
www.toppr.com
This physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. It explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging lens, diverging l...
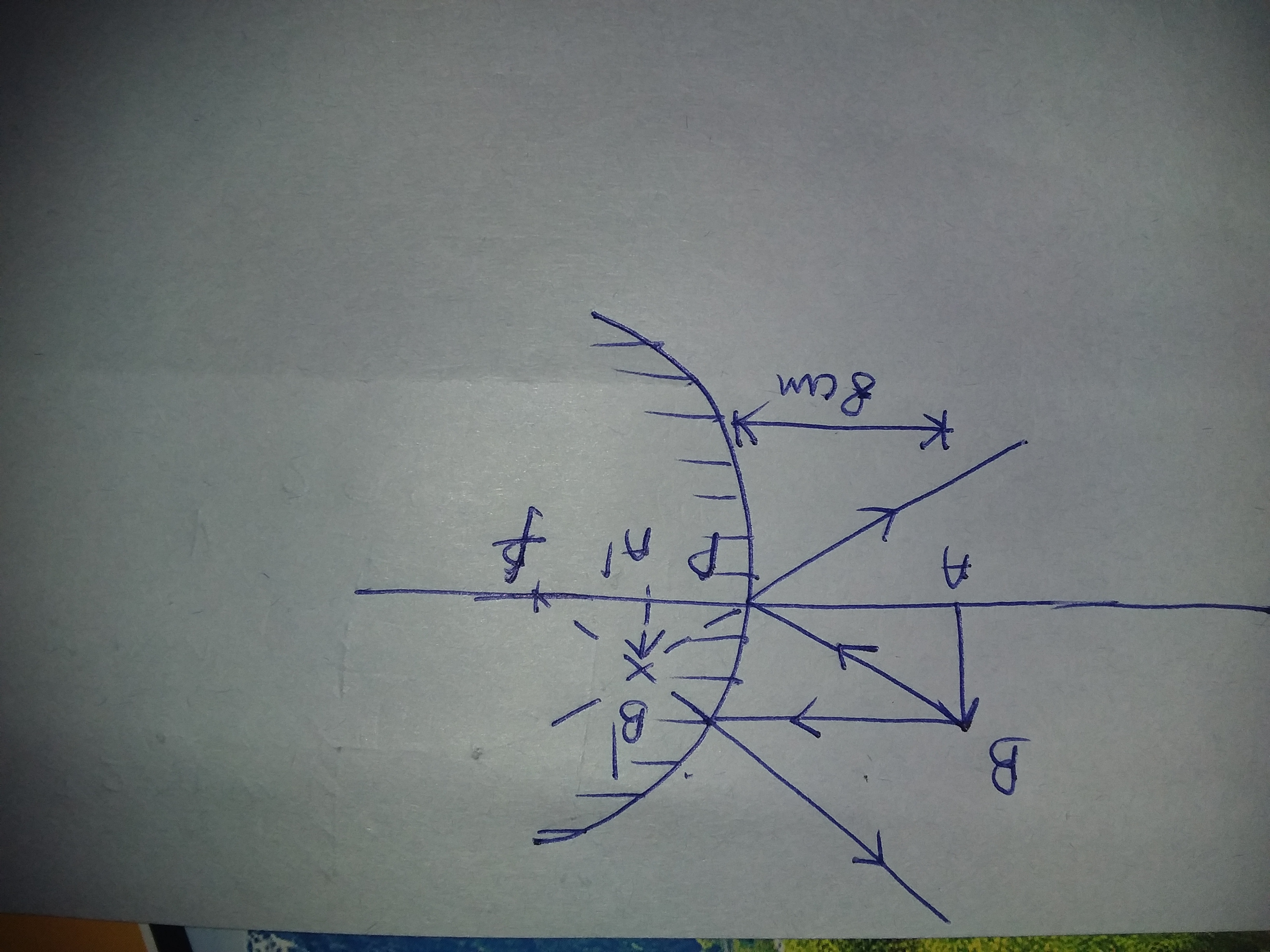
How To Draw A Ray Diagram To Find The Image When Object Kept At 8cm From The Pole For Convex Mirror Physics Topperlearning Com Yy3wxtvv
Ray diagrams help us trace the path of the light for the person to view a point on the image of an object. Ray diagram uses lines with arrows to represent the incident ray and the reflected ray. It also helps us trace the direction in which the light travels. Plane Mirror vs Spherical Mirrors.
Draw A Ray Diagram To Represent The Nature Position And Relative Size Of The Image Cbse Class 10 Science Learn Cbse Forum
Draw a ray diagram to show how such a lens would work. Hint: you need to label both the object and image in your diagram and to think about where the image appears to be. Share. Cite. Improve this answer. Follow answered May 9 '17 at 11:21. user155557 user155557. 1 $\endgroup$
Transcribed image text: Ray diagrams: Draw a ray diagram that shows why a convex lens magnifies objects that are closer to it than the focal length. Label the object and image, and indicate if the image is real or virtual. Draw a ray diagram that shows why the image produced by a convex lens is inverted if the object is farther away from the lens than the focal length.
When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object.
Draw A Ray Diagram Showing The Path Of Rays Of Light When It Enters With Oblique Incidence Cbse Class 10 Science Learn Cbse Forum

Concave And Convex Mirror Ray Diagrams By Dcaulf This Hand Drawn Cartoon Video Demonstrates How To Concave Mirrors Convex Mirror How To Memorize Things

Draw Ray Diagrams To Show The Principal Focus Of A I Concave Mirror Ii Convex Mirror Flash Education

Draw A Ray Diagram Of Astronomical Telescope For Distance Object In Normal Adjustment What Is The Expression For Its Magnifying Power Physics Q A
Draw Ray Diagrams To Represent The Nature Position And Relative Size Of The Image Formed By A Convex Lens For The Object Placed A At 2f1 B Between F1 And The Optical

Draw Ray Diagrams To Show The Formation Of Three Times Magnified Virtual Image Of An Object By A Converging Lens Mark The Positions Of O F And 2f In Each Diagram

Draw A Ray Diagram For Image Of Magnification M 1 For Mirror Science Light Reflection And Refraction 14006697 Meritnation Com
Draw Ray Diagram To Show The Formation Of Images When The Object Is Placed In Front Of A Concave Mirror Converging Mirror Between Its Pole And Focus Studyrankersonline















0 Response to "40 draw a ray diagram"
Post a Comment