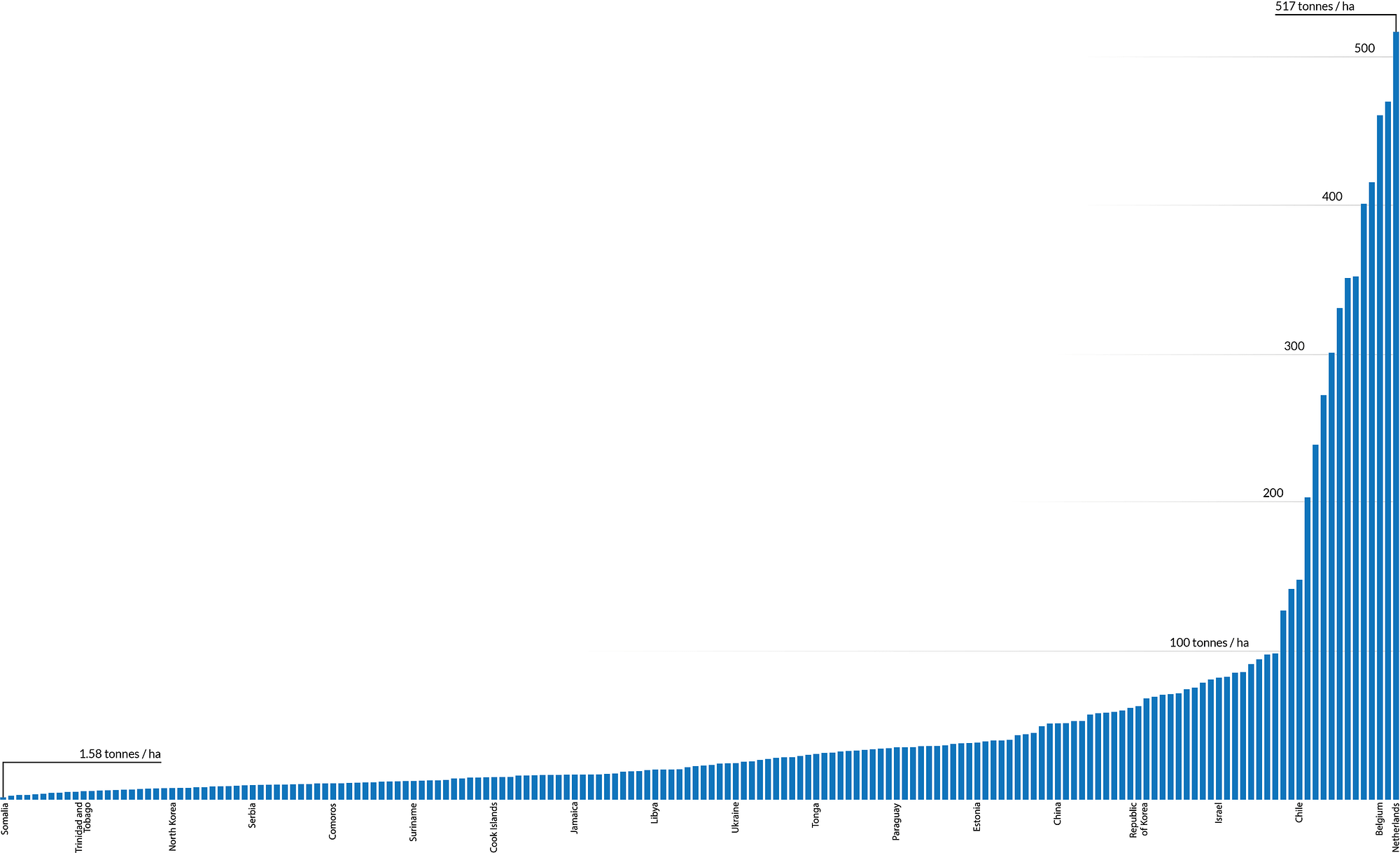
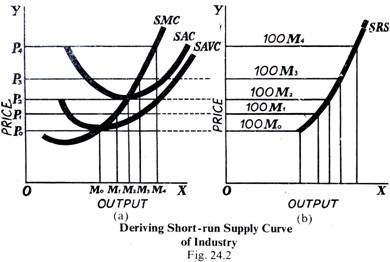
39 line (1) in the diagram reflects the long-run supply curve for
9.3 Perfect Competition in the Long Run - Principles of ... The long-run supply curve for a constant-cost, perfectly competitive industry is a horizontal line, SCC, shown in Panel (a). The long-run curve for an increasing-cost industry is an upward-sloping curve, SIC, as in Panel (b). The downward-sloping long-run supply curve, SDC, for a decreasing cost industry is given in Panel (c). Solved 9. Line (1) in the diagram reflects the long-run ... See the answer 9. Line (1) in the diagram reflects the long-run supply curve for a technologically progressive industry. a decreasing-cost industry. a constant-cost industry. an increasing-cost industry. 10. The operation of the invisible hand means the pursuit of private interests promotes social interests in pure competition. True False
PDF The Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curve Page 1 of 3 The Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curve Page 1 of 3 ... Before I put the short-run supply curve in this diagram, let's think about what would shift the long-run aggregate supply curve. ... run aggregate supply curve reflects the impact that the price level has on output in the short run when people are confused and when there are fixed wages and ...
Line (1) in the diagram reflects the long-run supply curve for
The Battle of Ideas: Hayek versus Keynes on Aggregate Supply The graph above shows the long-run and short-run perspective on AS in one graph. The long-run representing. 2. Why are there two aggregate supply curves? What is the difference between the two? The curved AS line is for the short-run where the price levels and total output are affected while the straight line is for long-run where the market ... Long-Run Supply - CliffsNotes The long‐run market supply curve is therefore given by the horizontal line at the market price, P 1 Figure (b) depicts demand and supply curves for a market or industry in which firms face increasing costs of production as output increases. Starting from a market price of P 1, an increase in demand from D 1 to D 2 increases the market price to P 2. Elasticity of Demand and Supply (With Diagram) Thus, (P 1 + P 2)/2 is a measure of the average price in the range along the demand curve and (q 1 + q 2) / 2 is the average quantity in this range. Elasticity of Demand and Supply # 9. Short-Run and Long-Run: The P elasticity of demand varies with time in which consumers can adjust their spending patterns which prices change.
Line (1) in the diagram reflects the long-run supply curve for. Microeconomics Exam 2: Chapter 11 Flashcards | Quizlet If the long-run supply curve of a purely competitive industry slopes upward, this implies that the prices of relevant resources: D. rise as the industry expands. 6. . Refer to the diagram. Line (1) reflects the long-run supply curve for: C. an increasing-cost industry. 7. . Refer to the diagram. Line (2) reflects the long-run supply curve for: Philips Curve (With Explanation and Diagram) The vertical long-run Phillips curve relates to steady rate of inflation. But this is not a correct view because the economy is always passing through a series of disequilibrium positions with little tendency to approach a steady state. In such a situation, expectations may be disappointed year after year. 2. quizlet.com › 276070044 › micro-quiz-ch-5-flash-cardsMicro Quiz Ch. 5 Flashcards | Quizlet A demand curve that has constant price elasticity of demand coefficient equals to one at all points is a(n): a. rectangular hyperbola. b. downward-sloping straight line. c. upward-sloping straight line. d. none of these. Refer to the above diagram Line 1 reflects the long run ... 131. Refer to the above diagram. Line (2) reflects the long-run supply curve for: A. a constant-cost industry. B. a decreasing-cost industry. C. an increasing-cost industry. D. a technologically progressive industry. 132.
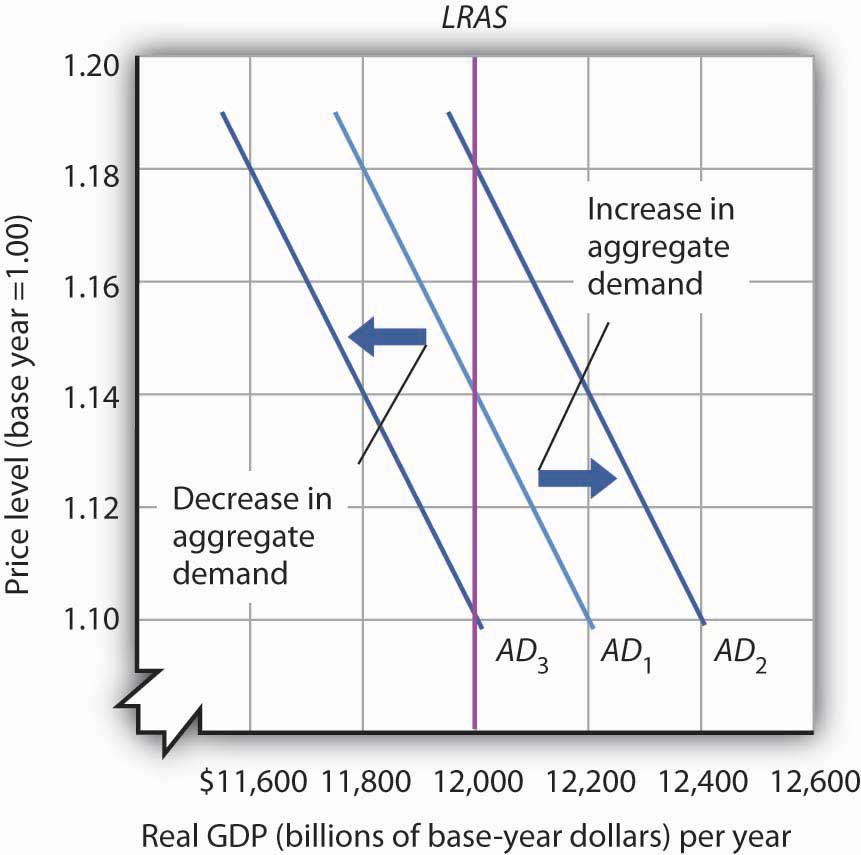
Long-run aggregate supply (video) - Khan Academy All the long run aggregate supply curve is saying is that given any price level, the economy has some level of natural output it can produce. If massive inflation makes prices triple overnight, your country can still produce the same amount in the long run. In essence, you've basically explained the 1973 oil crisis. › class-11-economics-importantClass 11 Economics Important Questions PDF (CBSE & ICSE) Mar 03, 2022 · Q. What is the price elasticity of supply, when: (a) Supply curve passes through the origin; (b) Supply curve is a vertical straight line; (c) Supply curve is a horizontal straight line. Ans. The price elasticity of supply in the following cases will be: (i) Unitary elastic Supply (ii) Perfectly Inelastic Supply (iii) Perfectly Elastic Supply. Q. PDF Expectations and the Phillips Curve Page 1 of 2 The green line in the diagram represents the speed limit of the economy. The long run aggregate supply tells us how much we can produce if all resources are employed. And if we try to produce more, that means pushing unemployment below the natural rate. ... The long run Phillips Curve is vertical and the short run Phillips Curve reflects a ... 22.2 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply: The Long Run ... The long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve relates the level of output produced by firms to the price level in the long run. In Panel (b) of Figure 22.5 "Natural Employment and Long-Run Aggregate Supply", the long-run aggregate supply curve is a vertical line at the economy's potential level of output.
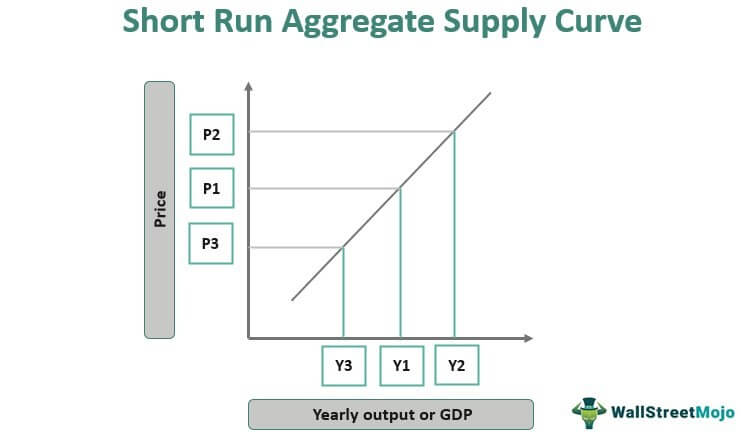
Short Run and Long Run Cost Curves (With Graphs) Long run average cost is long-run total cost divided by the level of output. Long run average cost curve depicts the least cost possible average cost for producing various levels of output. As shown in the figure 4.3a the short run average cost curves which are also known as plant curves. essaysassignment.comEssays Assignment - One assignment at a time, we will help ... Our writers can complete a standard essay for you within 1-3 hours and a part of a dissertation – in 2-5 days. High Quality All the papers we deliver to clients are based on credible sources and are quality-approved by our editors. Chapter 11 | Business Quiz - Quizizz The long-run supply curve for a purely competitive industry will be less elastic than the industry's short-run supply curve. The long-run supply curve for a purely competitive decreasing-cost industry will be upsloping. Question 13 120 seconds Q. A constant-cost industry is one in which answer choices Shape of aggregate supply curves (AS) - Economics Help The aggregate supply curve shows the total supply in an economy at different price levels. Generally, the aggregate supply curve slopes upwards - a higher price level encourages firms to supply more. However, there are different possible slopes for the aggregate supply curve. It could be highly inelastic (vertical) to very elastic.
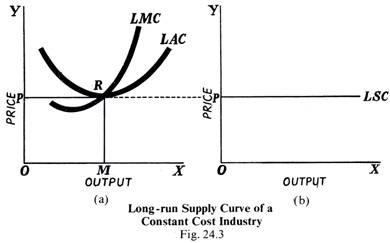
Long Run Average Cost Curve: Derivation, Example, Solved ... From Fig. 2, you can see that the LAC curve (long run average cost curve) is a U-shaped curve. This shape depends on the returns to scale. We know that, as a firm expands, the returns to scale increase. Then they remain constant for some time and eventually decrease. On the same lines, the LAC curve first declines and eventually rises.
Use the... - Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - Facebook A) There will be economic losses in the long run because of cut-throat competition. B) Economic profits will persist in the long run if consumer demand is strong and stable. C) In the short run, firms may incur economic losses or earn economic profits, but in the long run they earn normal profits.
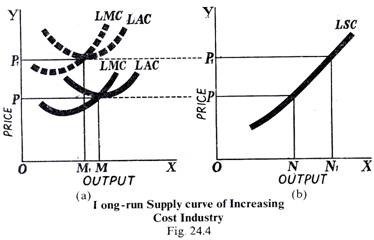
Short-run and Long-run Supply Curves (Explained With Diagram) Corresponding to OP price, the long-run supply curve is LSC, which is a horizontal straight line parallel to the X-axis. This means that whatever the output along the X-axis, price is the same OP where the marginal cost and average cost are equal. The cost remains the same, because it is a constant cost industry. ADVERTISEMENTS:
Chapter 11 Study Questions ( Flashcards - Quizlet Assume a purely competitive, increasing-cost industry is in long-run equilibrium. If a decline in demand occurs, firms will: a. leave the industry, price will decrease, and quantity produced will increase. b. enter the industry and price and quantity will both increase. c. leave the industry and price and output will both increase.
Chapter 8 Tutorial Answers - auknotes - Google Search C. The production possibilities curve would shift outward and the long-run aggregate supply curve would shift leftward D. The production possibilities curve would shift inward and the long-run aggregate supply curve would shift rightward 24. The knowledge and skills that make a productive worker are referred to by economists as:
Aggregate Supply Curve and Definition | Short and Long Run The Long-Run Curve. The Long-Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS) curve is completely vertical. You're probably asking why. It's because the real GDP in the long-run is dependent on the supply of capital, labor, raw materials, and other factors outside of price.
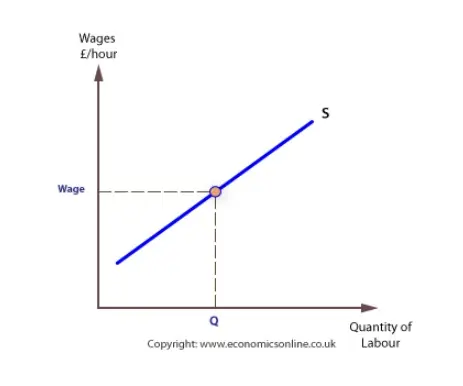
The Supply Curve of Labour (Explained With Diagram) In Fig. 33.3 (b) supply curve of labour is drawn with K-axis representing the hourly wage rate and X-axis representing number of hours worked per week at various wage rates. It will be seen from Fig. 33.3 (b) as the wage rate rises from P 1 to P 4 the supply of labour (i.e., number of hours worked per week) decreases from OL 1 to OL 4.
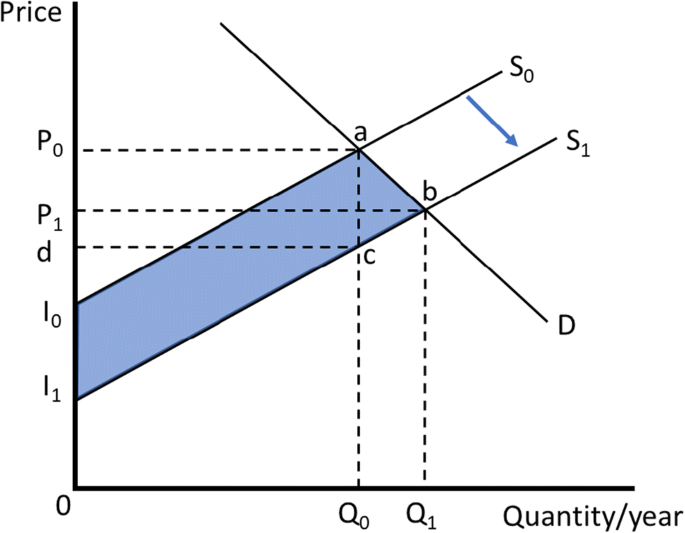
Movement along a Supply Curve and Shifts in Supply Curve This has caused the supply curve rightwards and new supply curve S 2 S 2 has formed. In the same, due to unfavorable changes in non-price factors of the commodity, the production and supply have fallen to Q 1 amount. Accordingly, the supply curve has shifted leftwards and new supply curve S 1 S 1 has formed. Reasons for rightward shift of ...
Teaching economics behind the global COVID-19 pandemic - PMC During 'normal' economic times, a long-term equilibrium exists and is represented by the intersection between three curves: the short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS), the aggregate demand curve (AD), and the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS), as illustrated in Fig. 4 a below. The LRAS curve represents the long-run potential output in ...
Aggregate supply - Wikipedia In economics, aggregate supply ( AS) or domestic final supply ( DFS) is the total supply of goods and services that firms in a national economy plan on selling during a specific time period. It is the total amount of goods and services that firms are willing and able to sell at a given price level in an economy. Contents 1 Analysis
Refer to the above diagram Line 1 reflects the long run ... 41. Refer to the above diagram. Line (1) reflects the long-run supply curve for: A. a constant-cost industry. B. a decreasing-cost industry. C. an increasing-cost industry. D. a technologically progressive industry.
Solved Refer to the diagram below. Line (1) reflects the ... View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Refer to the diagram below. Line (1) reflects the long-run supply curve for: (1) Long-run supply Unit costs (2) Long-run supply Select one: a. an increasing-cost industry, b. technologically progressive industry, c. a constant-cost industry. d. a decreasing-cost industry.
quizlet.com › 280027159 › chapter-24-macroeconomicsChapter 24 Macroeconomics Flashcards - Quizlet When an economy's output increases and the price level decreases, the _____ curve has shifted to the _____. AS; right The graph refers to a significant increase in individual income taxes, taking them to their highest level in 50 years.
3.1 Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium in Markets for Goods ... The demand curve (D) is identical to Figure 1. The supply curve (S) is identical to Figure 2. Table 3 contains the same information in tabular form. Figure 3. Demand and Supply for Gasoline. The demand curve (D) and the supply curve (S) intersect at the equilibrium point E, with a price of $1.40 and a quantity of 600.
Aggregate Supply (AS) Curve The LAS curve—depicted in Figure (b)—is a vertical line, reflecting the fact that long‐run aggregate supply is not affected by changes in the price level. Note that the LAS curve is vertical at the point labeled as the natural level of real GDP.
Elasticity of Demand and Supply (With Diagram) Thus, (P 1 + P 2)/2 is a measure of the average price in the range along the demand curve and (q 1 + q 2) / 2 is the average quantity in this range. Elasticity of Demand and Supply # 9. Short-Run and Long-Run: The P elasticity of demand varies with time in which consumers can adjust their spending patterns which prices change.
Long-Run Supply - CliffsNotes The long‐run market supply curve is therefore given by the horizontal line at the market price, P 1 Figure (b) depicts demand and supply curves for a market or industry in which firms face increasing costs of production as output increases. Starting from a market price of P 1, an increase in demand from D 1 to D 2 increases the market price to P 2.
The Battle of Ideas: Hayek versus Keynes on Aggregate Supply The graph above shows the long-run and short-run perspective on AS in one graph. The long-run representing. 2. Why are there two aggregate supply curves? What is the difference between the two? The curved AS line is for the short-run where the price levels and total output are affected while the straight line is for long-run where the market ...


















0 Response to "39 line (1) in the diagram reflects the long-run supply curve for"
Post a Comment