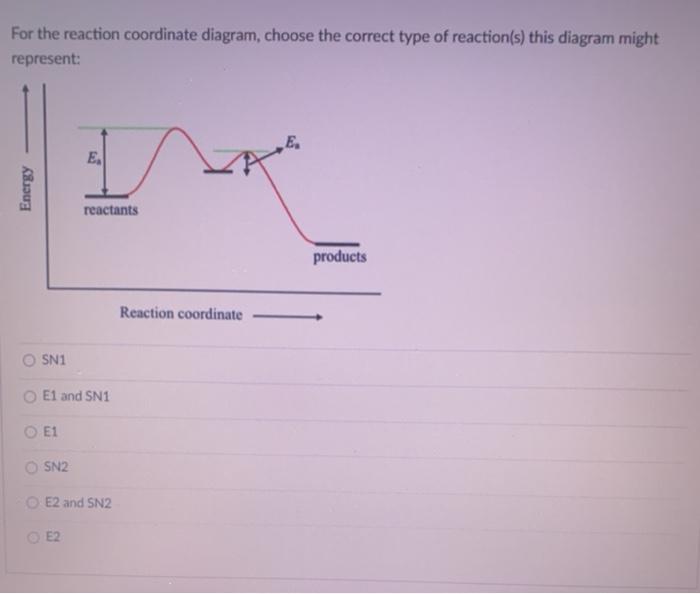
42 sn2 reaction coordinate diagram
PDF Reactions SN2 and SN1 Reactivity via is the highest energy state along the reaction coordinate. The SN2 reaction is said to be concerted because the attack by the nucleophile and the departure of the leaving group occur in concert (simultaneously); there are no intermediates. Although the reaction coordinate energy diagram 8.2. Physical chemistry for SN2 and SN1 reactions | Organic Chemistry 1: An open textbook The S N 2 reaction. There are two mechanistic models for how a nucleophilic substitution reaction can proceed at an alkyl halide (or similar) - S N 2 and S N 1. In the first picture, S N 2, the reaction takes place in a single step, and bond-forming and bond-breaking occur simultaneously. This is called an ' associative', or ' SN2 ...
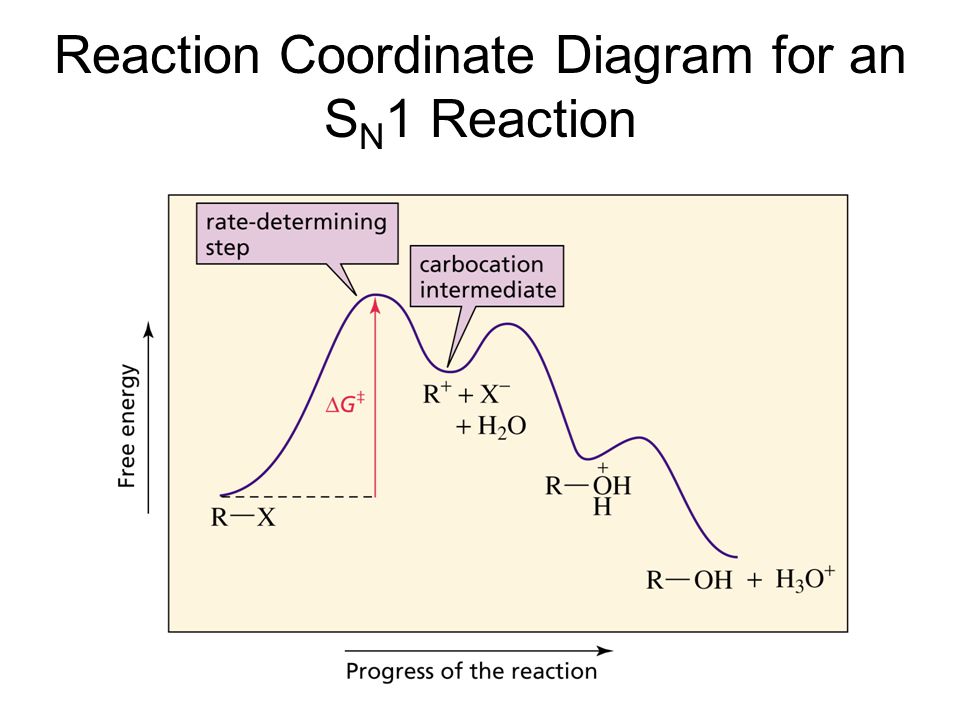
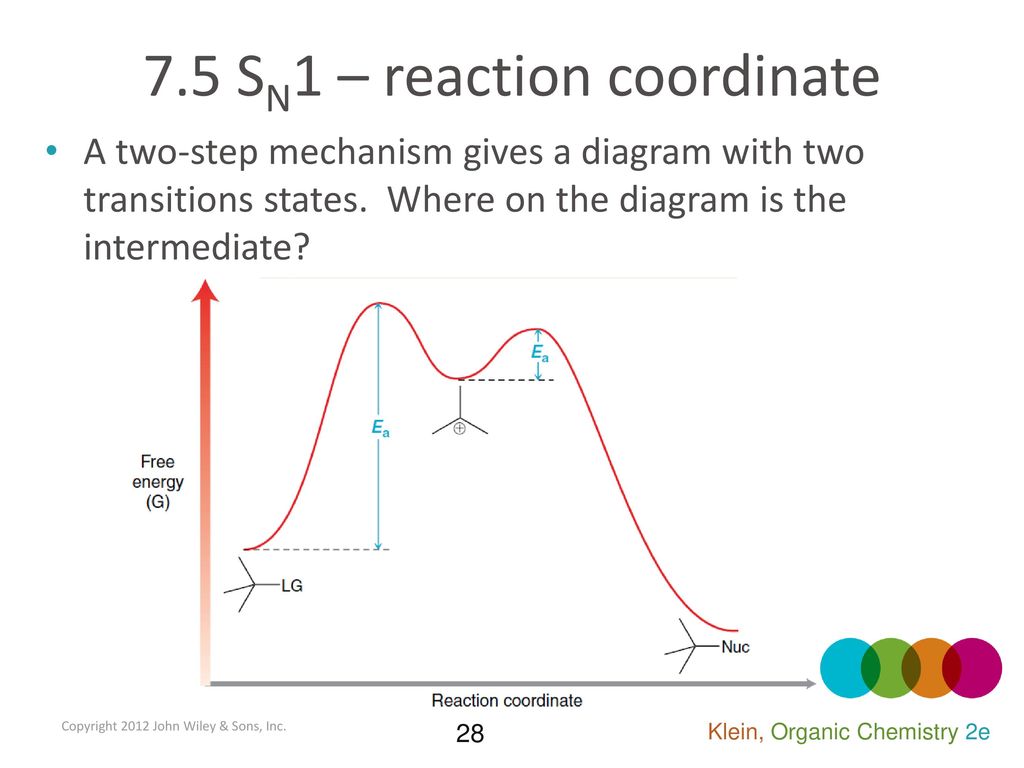
PDF 9.6 THE SN1 AND E1 REACTIONS - Macmillan Learning reaction coordinate Br Figure 9.11 Reaction free-energy diagram for the S N1-E1 solvolysis reaction of (CH 3) 3CBr with ethanol.The rate-limiting step,ionization of the alkyl halide (red curve),has the transition state of highest standard free energy.The
Sn2 reaction coordinate diagram
UIUC CHEM 232 - Worksheet 12 - SN2 - D3130231 - GradeBuddy Unformatted text preview: ! 1 CHEM 232 Worksheet SN2 1. Draw the reaction coordinate diagram for the SN2 reaction of 1-iodopropane with -NH2 to form a neutral organic product. Be sure to include the starting materials, any intermediates, and products on the diagram. Draw the transition state for the rate-determining step. Ch 8 : SN2 mechanism - Faculty of Science SN2 indicates a substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecularreaction, described by the expression rate = k [Nu][R-LG]. This implies that the rate determining step involves an interaction between two species, the nucleophile and the organic substrate. This pathway is a concerted process (single step) as shown Chapter 7: Alkyl Halides Flashcards | Quizlet A reaction coordinate diagram for the SN2 reaction shown would have _____ transition state(s) and _____ reactive intermediates. D Select the statement that correctly explains why backside attack by the nucleophile is preferred in SN2 reactions.
Sn2 reaction coordinate diagram. Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram. SN1 reaction is a two step reaction as mentioned below: 1. Leaving group leaves first being solvolysed by solvent creating a carbocation intermediate. This is. whose proposed mechanism and free energy diagram are depicted Figures 1 and 2. Figure 2: Reaction coordinate diagram for an SN1 reaction1. 1. Identify the . Sn2 Energy Diagram - Wiring Diagrams SN2 reaction coordinate diagram. In this diagram, there are really only three parts: the reagents, the transition state, and the products. The transition state is the point in the reaction with the highest energy level, and the difference in energy between the reagents and transition state is called the activation energy (often abbreviated as Ea). PDF SN2 REACTIONS - Anugrah Narayan College, Patna SN2 REACTIONS Introduction ... Transition state represents an energy maximum on the reaction coordinate and can't be measured directly due to their extremely short lifetime interval. ... An energy diagram of the SN2 reaction Kinetics of SN2 Reactions SN2 Mechanism - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Figure 9.3 shows the reaction coordinate diagram in the S N 2 reaction of hydroxide ion with chloromethane to give methanol and chloride ion. We see that the transition state contains both hydroxide ion and the substrate. As the reaction proceeds through the transition state, a bond forms between carbon and hydroxide ion, and the bond between carbon and chlorine breaks.
Solved Draw the reaction coordinate diagram for an SN2 - Chegg Draw the reaction coordinate diagram for an SN2 reaction with ethyl bromide and sodium hydroxide with a solid line. Then superimpose on the same diagram the coordinate of the SN2 reaction for isopropyl bromide and sodium hydroxide. Make sure to clearly label which curve is which, and don't forget to label your axes. Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram Substitution Reactions (SN2 versus SN1). Substrate: Sterics reaction coordinate (SN1) en er g y en erg Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams. Predicting the. SN1 indicates a substitution, nucleophilic, unimolecular reaction, described by the expression rate = k reaction coordinate diagram for a two step process. SN1 reaction The S1 reaction is a ... Energy Diagram For Sn2 Oct 24, 2018 · SN2 reaction coordinate diagram. In this diagram, there are really only three parts: the reagents, the transition state, and the products. The transition state is the point in the reaction with the highest energy level, and the difference in energy between the reagents and transition state is called the activation energy (often abbreviated as Ea). Physics Page - This diagram illustrates the reaction coordinate diagram for the ... This diagram illustrates the reaction coordinate diagram for the bimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN2) reaction between bromomethane and the hydroxide anion. Transition state theory (TST)...
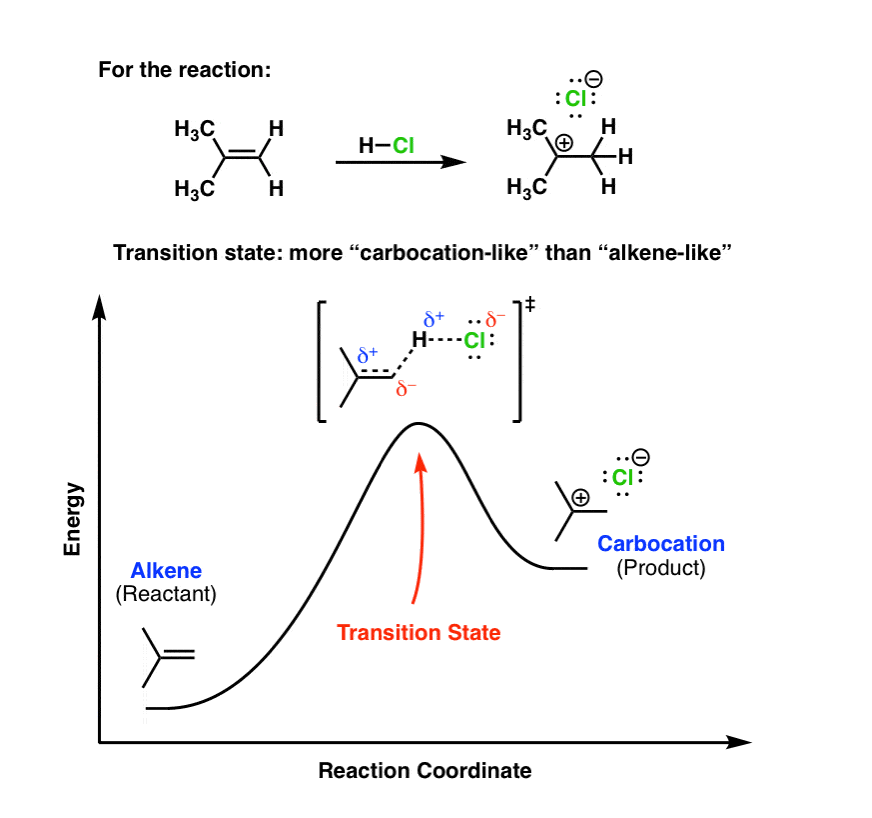
PDF Thermodynamics vs Kinetics - Columbia University Construct the gas phase Reaction Coordinate Diagram for the Cl + CH3Cl SN2 reaction by plotting the relative energy in kJmol 1 versus Cl + C | {z} Distance H3 Cl. Place the Reaction Coordinate Diagram on the graph provided below and plot the energies on a relative energy scale. Label the various species along the reaction pathway. 0 5 10 15 20 ... SN2 Reaction - Organic Chemistry Video | Clutch Prep The SN2 mechanism proceeds through a concerted mechanism. All that means is that it proceeds in one step and there’s no intermediate. As the nucleophile (Nu–) performs a “backside attack,” the leaving group (LG) dissociates. In other words, the nucleophile makes a bond and breaks the bond of the leaving group to the carbon holding it. SN2 generic mechanism In this generic reaction, the nucleophile is attacking the carbon holding the leaving group, which causes the nucleophile to dissociate. Notice that the net charge of the reaction stays the same. There’s no intermediate in this reaction; it goes straight from reagents to products. SN2 transition state As the nucleophile forms a bond to the carbon, the leaving group’s bond is broken. This is called the transition state, and it’s indicated from the double dagger (≠) that’s generally placed at the top right of the box it’s included in. Notice that both the nucleophile and leaving group have partial negative charges. That makes sen... SN2 Arrow Pushing Tutorial and Reaction Coordinate Diagram ... The SN2 reaction mechanism stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular and is a fundamental mechanism in organic chemistry. In an SN2 mechanism, a nucle... Solved SN2 Energy Diagram For the following SN2 reaction, | Chegg.com SN2 Energy Diagram For the following SN2 reaction, please fill in the reaction-coordinate diagram below. On your diagram, include the structures of the starting materials, the transition state, and the products. You can assume that the reaction is exothermic. 5. a. OMs + OMs Reaction Coordinate b.
PDF SN1 and SN2 Reactions - Illinois Institute of Technology The S N 2 Reaction Notes: In the SN2 reaction, the nucleophile attacks from the most δ+ region: behind the leaving group. This is called a back-side attack. This back-side attack causes an inversion (study the previous slide): after the leaving group leaves, the other substituents shift to make room for the newly-bonded nucleophile, changing the stereochemistry of the molecule.
PDF SN2 S 1 - Massachusetts Institute of Technology Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams Predicting the Products: Substitution versus Elimination Is Nuc/Base strong? no Unimolecular Reaction Bimolecular yes Reaction Is Nuc/Base bulky? E2 yes no What kind of substrate? methyl or 1° S N2 3° yes mostly E1* 2° no mostly S N1* What kind of substrate? 2°, 3°, or stabilized 1° 1° S N2 + E2 Is Nuc ...
Answered: Identify the energy diagram which… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: Identify the energy diagram which represents exothermic SN2 reaction. B Cheistry s Reaction coordinate D Chemist Select one: О а. С O b.
Ch4 : SN2 mechanism - Faculty of Science S N 2 mechanism. S N 2 indicates a substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecular reaction, described by the kinetic expression : rate = k [Nu][R-LG] . This pathway is a concerted mechanism (single step) as shown by the following reaction coordinate diagrams, where there is simultaneous attack of the nucleophile and displacement of the leaving group.
SN1/SN2, Sn1 and Sn2, E1 and E2, Organic Chemistry Sn1 vs Sn2 Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram. Sn2 Reaction Coordinate Diagram. Why is R-I better for Sn1? the rate determine step involves C+ formation and the breaking of the R-X bond, the weaker the R-X (C-X) bond the easier it is to break. R-I is the most reactive because it is the weakest R-X bond.
Sn2 Energy Diagram - schematron.org Sn2 Energy Diagram. You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram. SN2 Reaction follows second order rate kinetics. It forms a product via one transition state. Transition state is the state at which it posses. SN2 Reaction follows second order rate ...
PDF 201 Nucleophilic Substitution - La Salle University This pathway is a concerted process (single step) as shown by the following reaction coordinate diagrams, where there is simultaneous attack of the nucleophile and ... nucleophile is very important in an SN2 reaction. The more reactive the nucleophile, the more likely the reaction will be SN2 rather than SN1.
SN2 Reaction Mechanism - Detailed Explanation with Examples SN1 is a two-stage system, while SN2 is a one-stage process. The carbocation can form as an intermediate during SN1 reactions, while it is not formed during SN2 reactions. 3. What determines sn1 or sn2? Ans: In the rate of reaction, Sn1 reactions are unimolecular and have a step-wise mechanism.
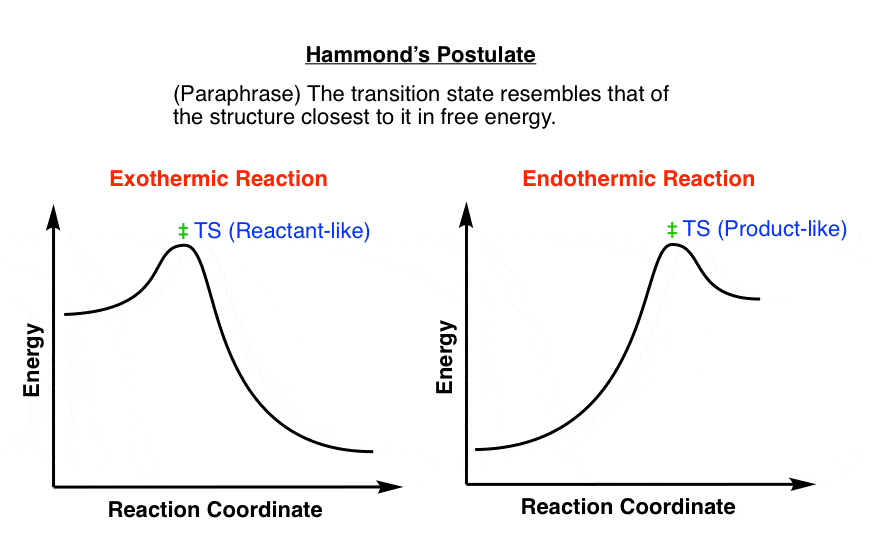
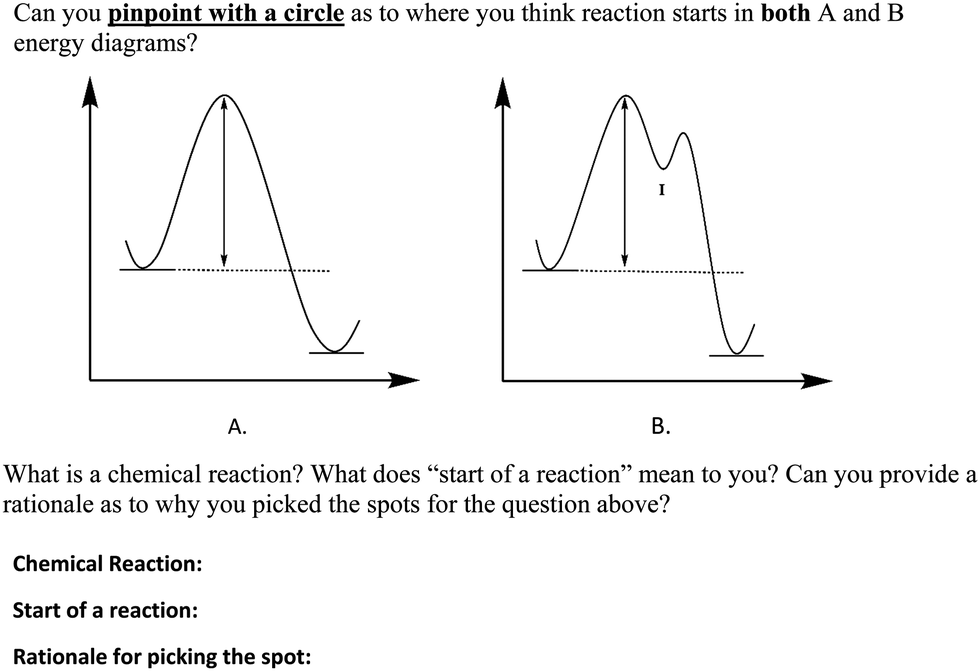
nucleophilic substitution - How to draw a reaction coordinate diagram for SN1 ... It is also typical of SN1 reactions for the first step to be rate-limiting, as carbocation formation from a neutral reactant is thermodynamically unfavorable unless specific reaction conditions are present. The three general rules for reaction coordinate diagrams are as follows:
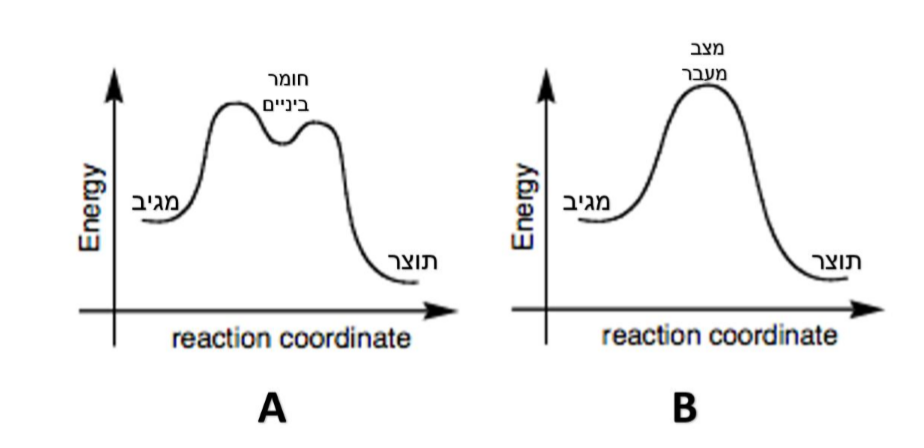
SN2 - Second-order Nucleophilic Substitution - Chemgapedia The reaction coordinate is the direct connection of starting products, transition state (mountain pass), and products on the mountain's surface (the red line in the illustration). A mountain pass that is relatively broad in cross direction represents a reaction with a lower free energy of activation ΔG ‡ than a narrow mountain pass does.
SN2 Reaction Energy Diagram - YouTube presents: SN2 Energy Diagram Need help with Orgo? Download my free guide '10 Secrets to Acing Organic Chemistry'...
Chapter 7: Alkyl Halides Flashcards | Quizlet A reaction coordinate diagram for the SN2 reaction shown would have _____ transition state(s) and _____ reactive intermediates. D Select the statement that correctly explains why backside attack by the nucleophile is preferred in SN2 reactions.
Ch 8 : SN2 mechanism - Faculty of Science SN2 indicates a substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecularreaction, described by the expression rate = k [Nu][R-LG]. This implies that the rate determining step involves an interaction between two species, the nucleophile and the organic substrate. This pathway is a concerted process (single step) as shown
UIUC CHEM 232 - Worksheet 12 - SN2 - D3130231 - GradeBuddy Unformatted text preview: ! 1 CHEM 232 Worksheet SN2 1. Draw the reaction coordinate diagram for the SN2 reaction of 1-iodopropane with -NH2 to form a neutral organic product. Be sure to include the starting materials, any intermediates, and products on the diagram. Draw the transition state for the rate-determining step.
/chapter7/pages5and6/page5and6_files/sn2phenoxyenergy.png)
















![Comparing the [SN1] and [SN2] Substitution Pathways](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/nHjwyT307tU/hqdefault.jpg)
![Solved] Draw a hypothetical free-energy diagram for the SN2 ...](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.question.images/image/images11/877-C-O-S(403).png)




0 Response to "42 sn2 reaction coordinate diagram"
Post a Comment