39 photosystem 1 and 2 diagram
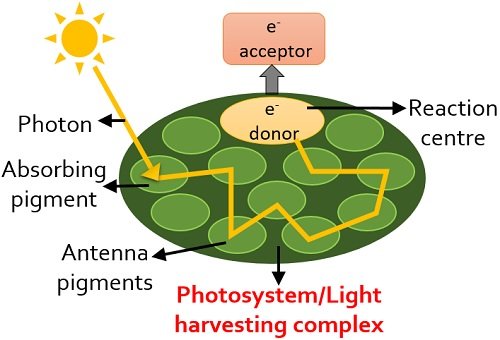
Photosystem 1 and 2 Diagram | Quizlet To get the electron from photosystem 2 to photosystem 1. Where is this photon from. An outside source (sun) What is the function of P700. It absorbs light at 700 nm (red light) What is this. The reaction center. What happens when the photon combines with the electron. Become excited again. PDF BIOL 1020 1. List and differentiate the 4 ... - Auburn 1. there are two types, Photosystem I and Photosystem II 2. antenna complexes are highly organized arrangements of pigments, proteins, and other molecules that capture light energy 3. energy is transferred to a reaction center where electrons are actually moved into electron transport chains
A Comparison Between Plant Photosystem I and Photosystem ... 1.2. Structure of the Core Complexes. Photosynthetic reaction centres are embedded in the so called "core complexes" (Fig. 1B 1B).The core of PSII is a multi-subunit complex composed of about 25-30 subunits.
Photosystem 1 and 2 diagram
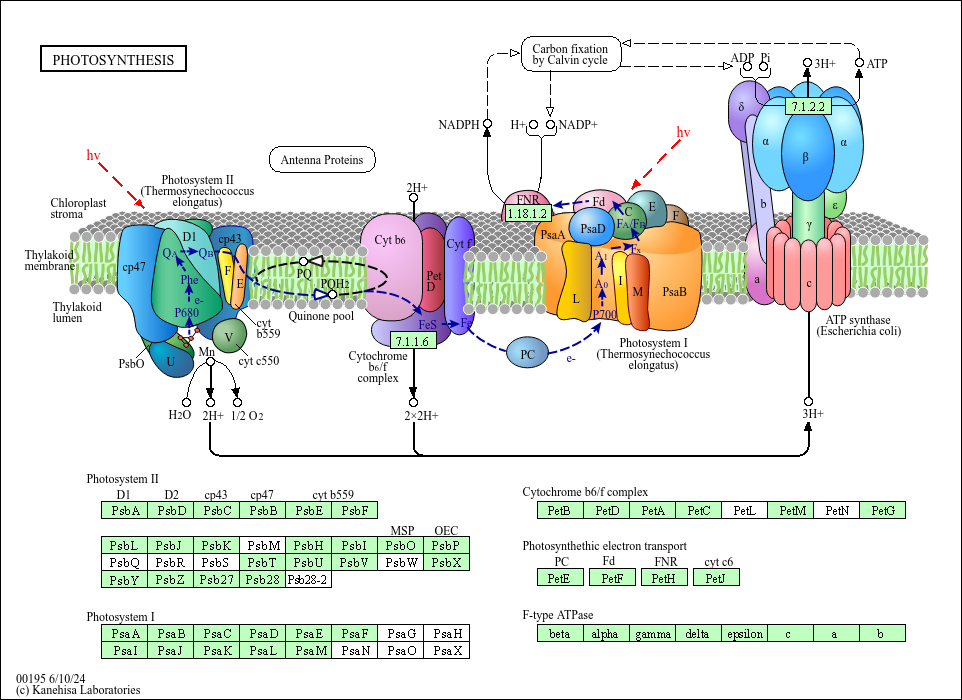
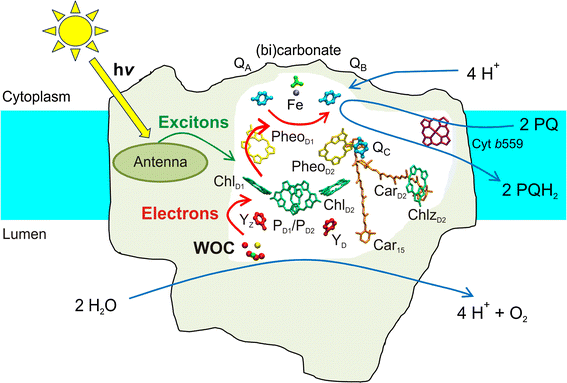
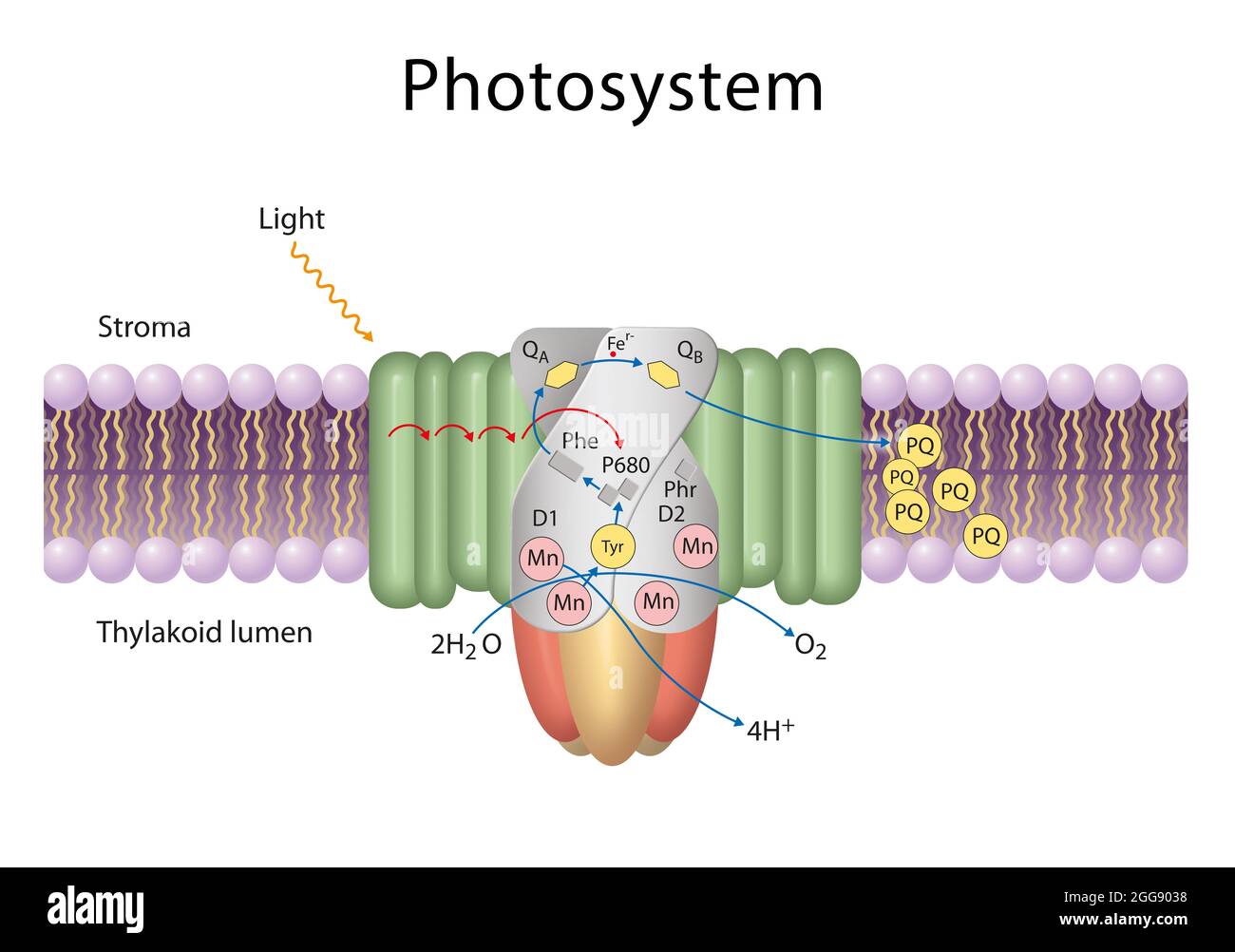
Photosystem II - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Photosystem II particles were prepared from spinach chloroplasts using Triton X-100 (1) and, in most cases, stored in liquid nitrogen with 30% ethylene glycol. Recovery of chlorophyll in the particles by this method was about 30%. The particles had oxygen evolution activity ranging from 250 to 400 μmol O 2 mg −1 chlorophyll h −1. PDF 8.3 The Process of Photosynthesis Photosystem II absorbs light and increases the electrons' energy level. The electrons are passed to the electron transport chain. Enzymes in the thylakoid break up water molecules into 2 electrons, 2 H+ ions, and 1 oxygen atom. The 2 electrons replace the high-energy electrons that have been lost to the electron transport chain. Cytochrome b6f complex - Wikipedia Enzyme structure. The cytochrome b 6 f complex is a dimer, with each monomer composed of eight subunits. These consist of four large subunits: a 32 kDa cytochrome f with a c-type cytochrome, a 25 kDa cytochrome b 6 with a low- and high-potential heme group, a 19 kDa Rieske iron-sulfur protein containing a [2Fe-2S] cluster, and a 17 kDa subunit IV; along with four small subunits (3-4 kDa): PetG ...
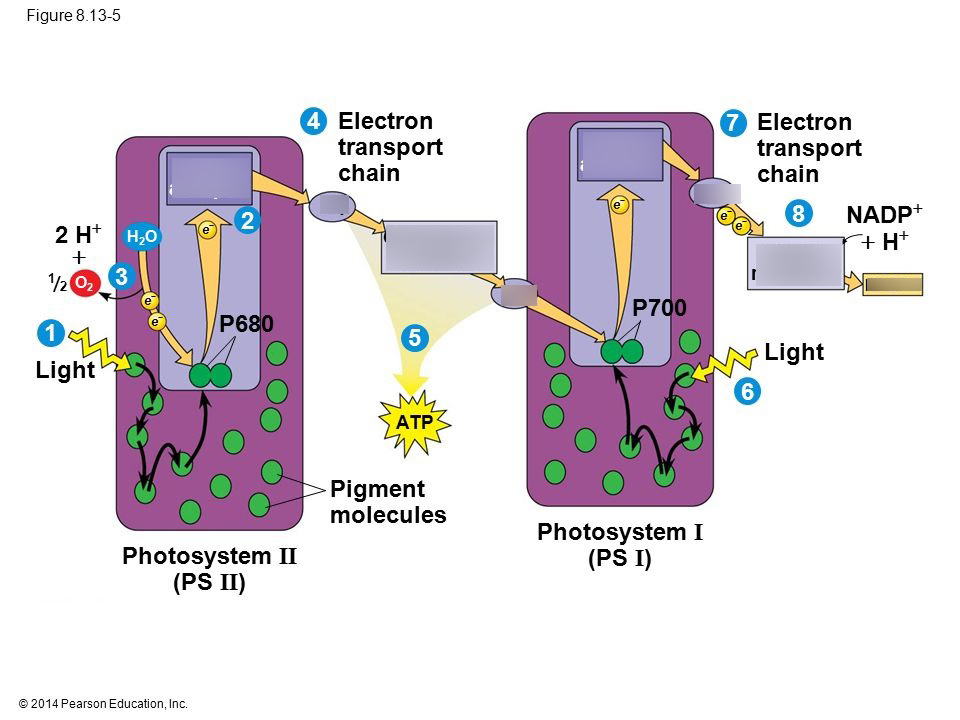
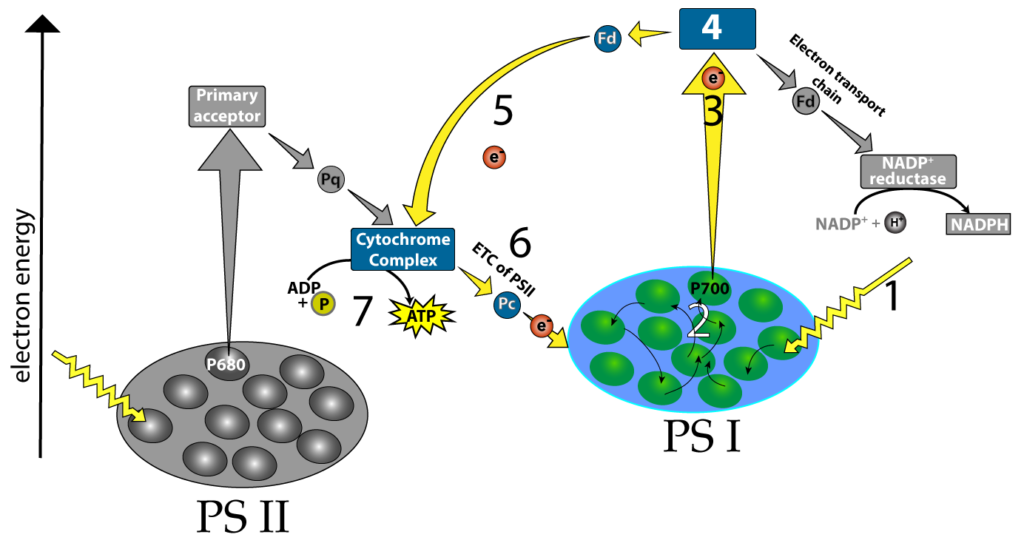
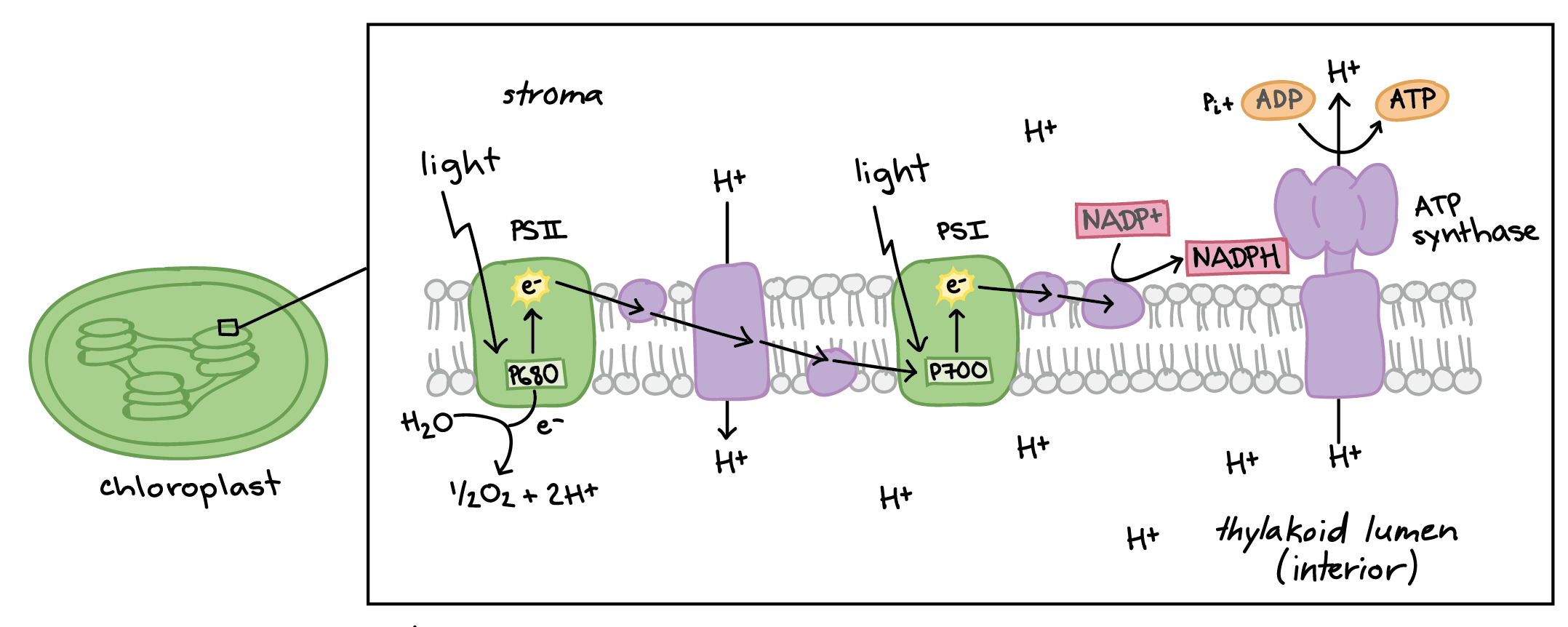
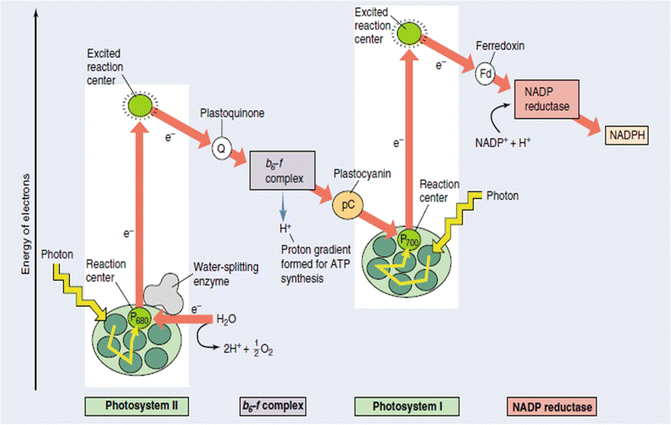
Photosystem 1 and 2 diagram. Photosynthesis Coloring (Chemiosmosis) 1. The thylakoid membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer (color phospholipids "B" light blue) with an interior space and an exterior, called the stroma. Photosynthesis takes place in two systems: photosystem I (P1) and photosystem II (P2). 2. The first event is the capturing of light energy (color E orange) by pigments in the membrane Chlorophyll - Wikipedia This reaction is how photosynthetic organisms such as plants produce O 2 gas, and is the source for practically all the O 2 in Earth's atmosphere. Photosystem I typically works in series with Photosystem II; thus the P700 + of Photosystem I is usually reduced as it accepts the electron, via many intermediates in the thylakoid membrane, by ... Fig. 1 Electron transfer pathway between photosystem 2 ... Download scientific diagram | Electron transfer pathway between photosystem 2 (PS2) and photosystem 1 (PS1) via redox polymers. Comparison of the previous system according to Kothe 11 (grey arrows ... 12 Difference Between Photosystem I And Photosystem II ... Light Reaction Process The light reaction of photosynthesis. The light reaction occurs in two photosystems (units of chlorophyll molecules). Light energy (indicated by wavy arrows) absorbed by photosystem II causes the formation of high-energy electrons, which are transferred along a series of acceptor molecules in an electron transport chain to photosystem I. Photosystem II obtains […]
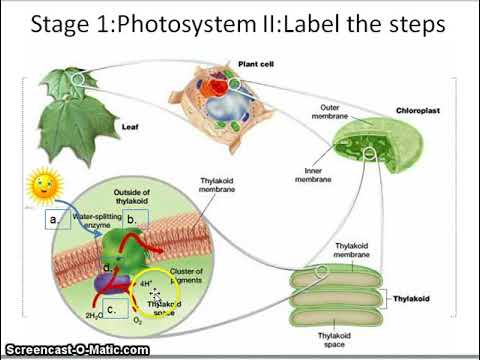
photosynthesis - Photosystems I and II | Britannica photosynthesis - photosynthesis - Photosystems I and II: The structural and photochemical properties of the minimum particles capable of performing light reactions I and II have received much study. Treatment of lamellar fragments with neutral detergents releases these particles, designated photosystem I and photosystem II, respectively. Difference Between Photosystem 1 and Photosystem 2 ... The key difference between photosystem 1 and photosystem 2 is that the photosystem 1 has a reaction centre composing of chlorophyll a molecule of P700 that absorbs light at a wavelength of 700 nm. On the other hand, the photosystem II has a reaction centre comprising chlorophyll a molecule of P680 that absorbs light at a wavelength of 680 nm. Photosystem 1 and 2 Diagram | Quizlet | Cadena de ... 12-oct-2019 - Start studying Photosystem 1 and 2. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Where are photosystem 1 and 2 located? - Theburningofrome.com Photosystem 2: Photosystem 2 is located on the inner surface of the thylakoid membrane. How are the two types of photosystems related? In particular, it carries out the absorption of light photons and the transfer of electrons ( e- in our diagram). There are two photosystems, Photosystem I and Photosystem II.
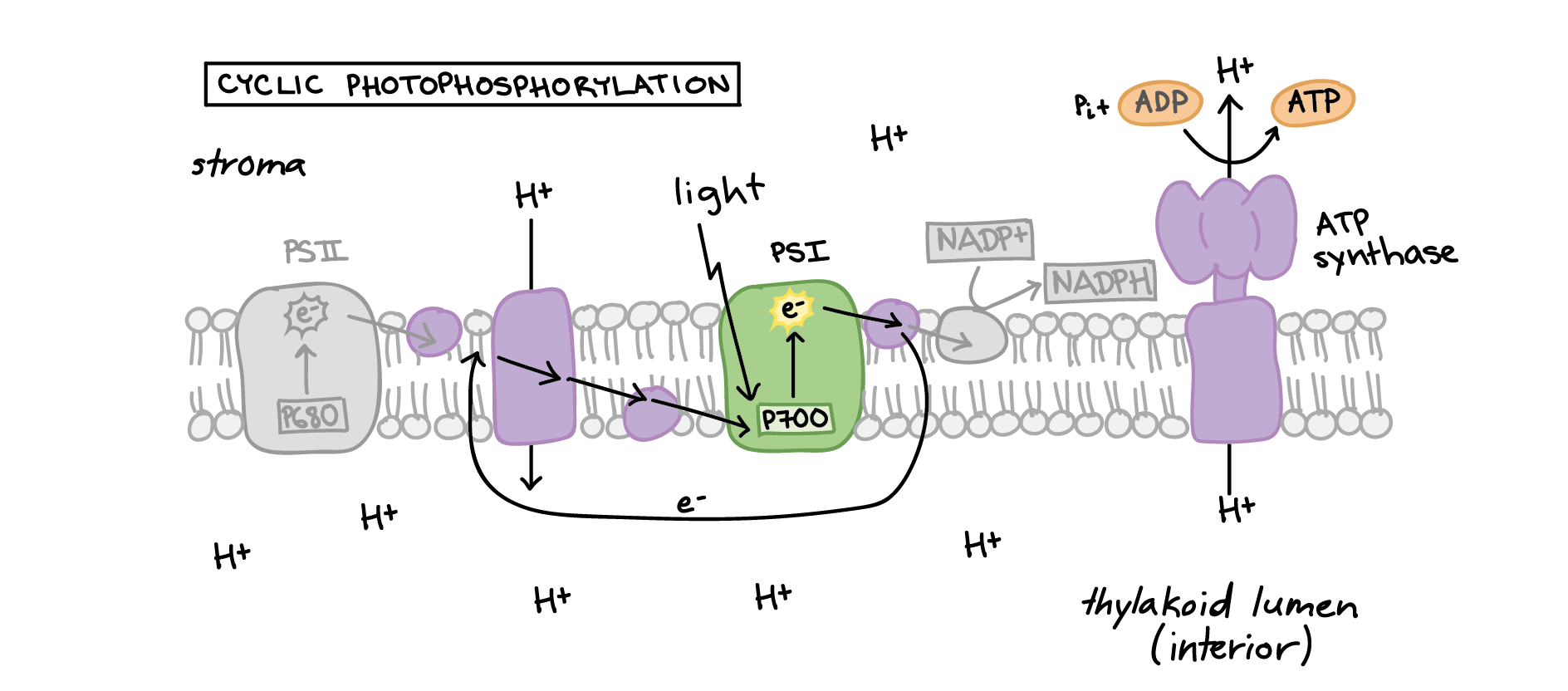
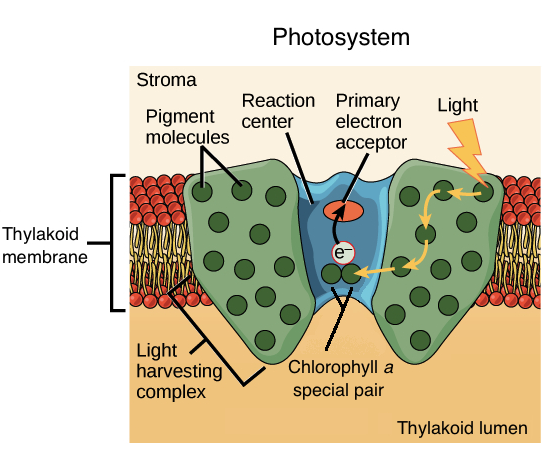
Photosynthesis, the light reactions: (HS Interactive ... Photosystems are complexes of connected proteins which are embedded in the membranes of the thylakoid sacs. In the diagram above, two photosystems are shown: one is at letter "l," and the second is at letter "e." Photosystem I (PS I) and Photosystem II (PS II ... Difference # Photosystem I (PS I): 1. Photosystem I (PS I) is involved in the cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation. 2. Photosystem I (PS I) receives the electrons from photosystem II. This system produces a strong reductant which reduces NADP+ to NADPH 2. 3. Molecular oxygen is not evolved in this system. 4. What is a photosystem? - Biology Q&A - BYJUS A photosystem is a protein complex, a group of two or more proteins, that is essential for the photochemistry of photosynthesis. There are two photosystems, Photosystem I and Photosystem II. Photosystem II is first in the process of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Structure of photosystems I and II - ScienceDirect Photosystem I from the thermophilic cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus is a trimer with a molecular weight of 1 056 000 Da. It is the largest and most complex membrane protein for which the structure has been determined , .It was crystallized by an approach that includes microgravity experiments, the determination of phase diagrams and seeding techniques .
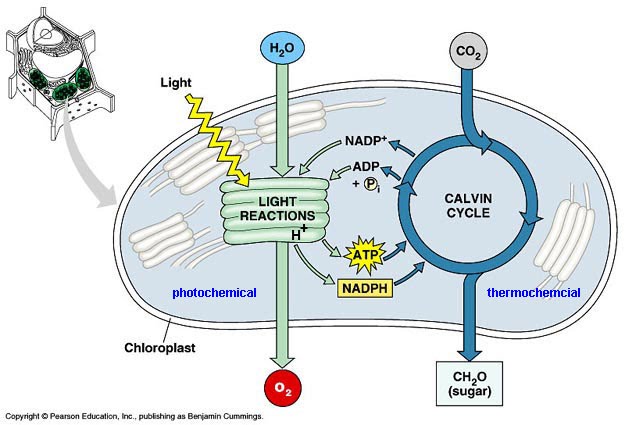
The Process of Photosynthesis in Plants (With Diagram) 1. Excitation of chlorophyll. 2. Photolysis of water. 3. Photophosphorylation. 1. Excitation of Chlorophyll: It is the first step of light reaction. When P 680 or P 700 (special type of chlorophyll a) of two pigment systems receives quantum of light then it becomes excited and releases electrons. 2. Photolysis of Water and Oxygen Evolution ...
Difference Between Photosystem I and Photosystem II (with ... The two main multi-subunit membrane protein complexes differ in their absorbing wavelength, where the photosystem I or PS 1 absorbs the longer wavelength of light which is 700 nm while photosystem II or PS 2 absorbs the shorter wavelength of light 680 nm.
Light-dependent reactions (photosynthesis reaction) (article) ENE‑1.J.4 (EK), ENE‑1.J.5 (EK) How light energy is used to make ATP and NADPH. Photosystems I and II. Reaction center chlorophylls P700 and P680. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Email. Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis. Intro to photosynthesis. Breaking down photosynthesis stages.
Photosystem 1 Diagram - Diagram Sketch Photosystems 1 And 2. Chemiosmosis Is The Source Of The Atp Produced In Photophosphorylation Plasma Membrane Plasma Membrane Membrane Plasma. Photosystem 1 And 2 Diagram Electron Transport Chain Photosynthesis Light Reaction. Photosystem 1 And 2 Diagram Quizlet Cadena De Transporte De Electrones Fotosintesis Ensenanza Biologia.
Photosynthesis 5.2.1 - Coggle Diagram Photosynthesis 5.2.1 - Coggle Diagram: Photosynthesis 5.2.1. Accessory pigments are light absorbing compounds, that work in conjunction with chlorophyll A
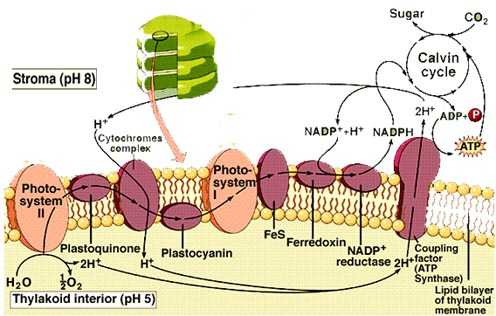
The Z-Scheme Diagram of Photosynthesis Electron Transfer Pathway from Water to NADP in photosynthesis. The Electron Transport Pathway from Water (H 2 O) to NADP+ (the Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate, oxidized form). Many versions of the Z-scheme are available in the literature.This particular diagram was developed by Wilbert Veit and Govindjee, 2000, and can be also found at molecadv.com.
Photosynthesis- Definition, Equation, Steps, Process, Diagram Jun 28, 2021 · Photosystem II. Photosystem II is a group of proteins and pigments that work together to absorb light energy and transfer electrons through a chain of molecules until it finally reaches an electron acceptor. Photosystem II has a pair of chlorophyll molecules, also known as P680 as the molecules best absorb light of the wavelength 680 nm.
1. Diagram of photosystem II (PS II) representing the ... Download scientific diagram | 1. Diagram of photosystem II (PS II) representing the polypeptide composition, electron transport carriers and light-driven ...
Photosynthesis.pdf - Photosynthesis 1 The steps of ... Photosynthesis 1. The steps of photosynthesis are outlined in the diagram. For each of the steps below, identify what starts the reaction, what is created, and where it takes place. a. Light Dependent Reactions - chloroplast and within the thylakoid membrane. Light enters photosystem 2, water
(PDF) Difference Between Photosystem 1 and 2 Photosystem I (PS I) and photosystem II (PS II) are two multi subunit membrane protein complexes involved in oxygenic photosynthesis . Chlorophyll is the pigment involved in capturing light energy...
why do plants have two photosystems? - Lisbdnet.com similarities between photosystem 1 and 2 photosystem 1 and 2 diagram photosystem 1 and 2 notes photosystem 1 and 2 pdf difference between photosystem 1 and 2 photosystem ii does not have a reaction center. See more articles in category: FAQ. admin Send an email December 23, 2021. 6 minutes read.
chloroplast | Definition, Function, Structure, Location ... Chloroplasts are roughly 1–2 μm (1 μm = 0.001 mm) thick and 5–7 μm in diameter.They are enclosed in a chloroplast envelope, which consists of a double membrane with outer and inner layers, between which is a gap called the intermembrane space.
Photosystem Diagram - Diagram Sketch Photosystem Diagram. Ap Biology Unit 3 Energy And Metabolism Cheat Sheet By Hlewsey Download Free From Cheatography Chea Photosynthesis Electron Transport Chain Light Reaction. Photosystem 1 And 2 Diagram Quizlet Cadena De Transporte De Electrones Fotosintesis Ensenanza Biologia.
Metabolism of Carbohydrates: 10 Cycles (With Diagram) Photosystem II produces a strong oxidant that forms O 2 from H 2 O. Further, the generation of ATP occurs as electrons flow from photosystem II to photosystem I (Fig. 67.8). Thus, light is responsible for the flow of electrons from H 2 O to NADPH with a concomitant generation of ATP. The Calvin cycle:
Difference Between Photosystem 1 and 2 | Definition ... Main Difference - Photosystem 1 vs 2. Photosystem I (PS I) and photosystem II (PS II) are two multi-subunit membrane-protein complexes involved in oxygenic photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is the pigment involved in capturing light energy. PS 1 contains chlorophyll B, chlorophyll A-670, Chlorophyll A-680, chlorophyll A-695, chlorophyll A-700 and carotenoids.
Photosystems I and II and the Light Reactions of ... Photosystem I can be excited by light of wavelengths shorter than 700 nm, but photosystem II requires light of wavelengths shorter than 680 nm for excitation. Both photosystems must operate for the chloroplast to produce NADPH, ATP, and O 2 , because the two photosystems are connected by the electron transport chain.
IB Biology Notes - 8.2 Photosynthesis 8.2.1 Draw and label a diagram showing the structure of a chloroplast as seen in electron micrographs. Figure 8.2.1 - Chloroplast. 8.2.2 State that photosynthesis consists of light-dependent and light- independent reactions. Photosynthesis consists of light-dependent and light-independent reactions. 8.2.3 Explain the light-dependent reactions.
Cytochrome b6f complex - Wikipedia Enzyme structure. The cytochrome b 6 f complex is a dimer, with each monomer composed of eight subunits. These consist of four large subunits: a 32 kDa cytochrome f with a c-type cytochrome, a 25 kDa cytochrome b 6 with a low- and high-potential heme group, a 19 kDa Rieske iron-sulfur protein containing a [2Fe-2S] cluster, and a 17 kDa subunit IV; along with four small subunits (3-4 kDa): PetG ...
PDF 8.3 The Process of Photosynthesis Photosystem II absorbs light and increases the electrons' energy level. The electrons are passed to the electron transport chain. Enzymes in the thylakoid break up water molecules into 2 electrons, 2 H+ ions, and 1 oxygen atom. The 2 electrons replace the high-energy electrons that have been lost to the electron transport chain.
Photosystem II - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Photosystem II particles were prepared from spinach chloroplasts using Triton X-100 (1) and, in most cases, stored in liquid nitrogen with 30% ethylene glycol. Recovery of chlorophyll in the particles by this method was about 30%. The particles had oxygen evolution activity ranging from 250 to 400 μmol O 2 mg −1 chlorophyll h −1.















0 Response to "39 photosystem 1 and 2 diagram"
Post a Comment