39 fatty acid structure diagram
Lipid Structures And Functions | A-Level Biology Revision ... Lipid structures. The structure of the fatty acids influences the structure of the lipid. In the fatty acid chains, the carbon atoms could have single bonds between them making the lipid "saturated".This generates fats that are usually solid at room temperature.. Alternatively, if one or more of the bonds between the carbon atoms are double bonds, the lipid is said to be "unsaturated". PDF Fatty Acids: Structures and Introductory article Properties forms. The cis fatty acids have lower melting points than the trans fatty acids or their saturated counterparts. In polyunsaturatedfattyacids(PUFAs)thefirst double bond may be found between the third and the fourth car-bon atom from the o carbon; these are called o-3 fatty acids. If the first double bond is between the sixth and
microbenotes.com › animal-cell-definitionAnimal Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled ... Feb 17, 2022 · Figure: Diagram of Mitochondria, created with biorender.com Structure of Mitochondria. They are rod-shaped or oval or spherically shaped, with a size of 0.5 to 10 μm. Mitochondria have two special membranes – outer and inner membrane. They have a mitochondrial gel-matric in the central mass. The membranes bend into folds known as cristae.

Fatty acid structure diagram
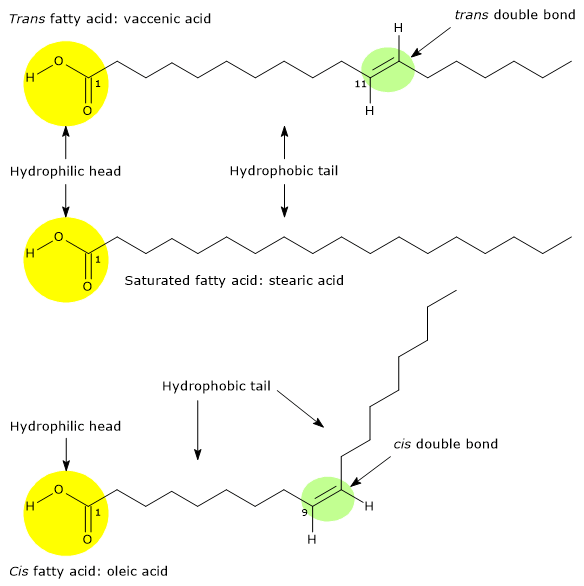
Trans fatty acids: definition, structure, health effects ... Trans fatty acids (TFA) or trans-unsaturated fatty acids or trans fats are unsaturated fatty acids, a subclass of lipids, with at least one a double bond in the trans configuration. Carbon-carbon double bonds show planar conformation, and so they can be considered as planes from whose opposite sides carbon chain attaches and continues. Fatty Acids And Triglycerides | Structure, Functions & Facts Fatty acids are made up of two components; An alkyl or hydrocarbon chain A carboxylic group The carboxylic group is present at the terminal of the hydrocarbon chain. The hydrocarbon chain is hydrophobic and non-polar while the carboxylic group is polar. The carboxylic group of fatty acids has a pK a of around 4.8. PDF Fatty Acid Biosynthesis - California State University ... Fatty Acid Biosynthesis 4 Fatty Acid Synthase (FAS) • FAS is a polypeptide chain with multiple domains, each with distinct enzyme activities required for fatty acid biosynthesis. •ACP: Recall that CoA is used as an activator for β-oxidation. For fatty acid biosynthesis, the activator is a protein called the acyl carrier protein (ACP).
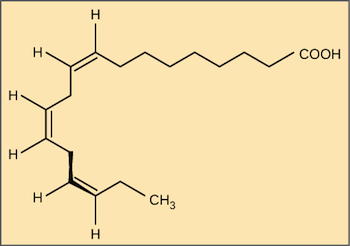
Fatty acid structure diagram. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid - an overview | ScienceDirect ... 5.2.1 PUFA structure. Polyunsaturated fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains containing two or more double bonds. The characterisation of PUFAs as either an n-3 PUFA or n-6 PUFA refers to the position of the first double bond relative to the methyl end of the fatty acid. In nature, double bonds are usually in the cis (bent) format. Fatty Acids -- Overview - University of Utah Overview The elements of fatty acid structure are quite simple. There are two essential features: A long hydrocarbon chain The chain length ranges from 4 to 30 carbons; 12-24 is most common. The chain is typically linear, and usually contains an even number of carbons. A carboxylic acid group A.1.6 Outline the variation in the molecular structure of ... Fatty acids have 3 parts to their structure: '-COOH' carboxyl group, '-CH3' methyl group (or omega group) and the hydrocarbon chain in the middle.Saturated V... DOCX It is made by attaching fatty acids, by condensation, to a sucrose molecule. The diagram shows the structure of olestra. The letter R shows where a fatty acid molecule has attached. (i) Name bond X (1) (ii) A triglyceride does not contain sucrose or bond X Give one
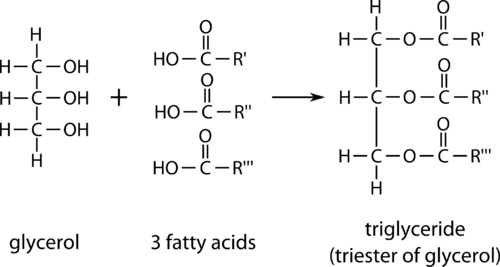
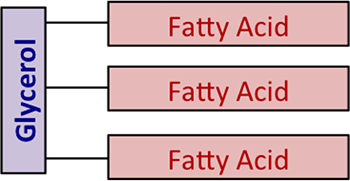
Biology Ch. 2-3 "Lipids Structure" Diagram Diagram | Quizlet A lipid made from fatty acids that have no double bonds between carbon atoms. A kind of fat often found in plant products that contains numerous double bonds between the carbons in the hydrocarbon tails of the fatty acids. A lipid that forms an essential component of animal cell membranes and acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of ... Structure of a Triglyceride Molecule | Healthfully Structure. The main molecule that starts the structure of a triglyceride is glycerol. Glycerol is a three-carbon molecule with three hydroxyl groups on them. These hydroxyl groups are the site of an ester reaction with three fatty acid molecules. The fatty acids can be different types, and the fatty acid structure defines the type of triglyceride. The Molecular Structure of Essential Fatty Acids ... The Molecular Structure of Essential Fatty Acids By Gad Cohen Molecular diagrams illustrate the structural differences between saturated fats and the essential dietary oils. The bent shape of the essential fatty acids keeps them from dissolving into each other. They are slippery and will not clog arteries like the sticky straight shaped saturated fats and the… Unsaturated fatty acids: structure, classification, examples Structure and classification of unsaturated fatty acids. Unsaturated fatty acids are fatty acids that contain one or more double/triple carbon-carbon bonds in the carbon chain. On this basis this class of lipids can be divided into: monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), if only one double bond is present; polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), if at ...
Structure of unsaturated fatty acids in 2D system The behaviour of Langmuir monolayers corresponding to unsaturated fatty acids belonging to the omega-9 (oleic acid), omega-3 (α-linolenic and stearidonic acids) and omega-6 (linoleic, γ-linolenic and eicosadienoic acids) series was studied in order to get insight into the influence of various factors (such as subphase temperature, length, degree of unsaturation and position of the double bonds in the aliphatic chains) on the molecular conformation of these fatty acids spread at the A/W ... Fatty Acids -- Classification of Fatty Acids One system of fatty acid classification is based on the number of double bonds. 0 double bonds: saturated fatty acids. Stearic acid is a typical long chain saturated fatty acid. 1 double bond: monounsaturated fatty acids. Oleic acid is a typical monounsaturated fatty acid. 2 or more double bonds: polyunsaturated fatty acids. Saturated Fatty Acid: Structure, Formula & Example - Video ... Lauric Acid Another way to draw the fatty acid above - lauric acid - is illustrated below. Instead of writing each carbon and hydrogen atom, they are replaced with a zigzag line. Each edge of the... Fatty Acid Structure | Examples | Types | Physical ... Fatty acids are composed of long hydrocarbon chains terminated by carboxylic acid groups. Fatty acids are basically the primary derivative of lipids. Chain length from 4 to usually 24C atoms. They contain even number of C atoms majority of fatty acids are those containing 16 and 18 C atoms. Fatty Acid Structure Described Below. Fatty Acid Structure
Chemical structure of fatty acid ethoxylates | Download ... Download scientific diagram | Chemical structure of fatty acid ethoxylates from publication: Synthesis, Properties and Applications of Anionic Phosphate Ester Surfactants: A Review | This paper ...
Trans Fatty Acid Molecule - World of Molecules Trans Fatty Acid Molecule -- Elaidic Acid-- Space Fill Model To View the Trans Fatty Acid Molecule in 3D using Jsmol What are Trans Fatty Acids? A trans fatty acid (commonly shortened to trans fat) is an unsaturated fatty acid molecule that contains a trans double bond between carbon atoms, which makes the molecule kinked.Research suggests a correlation between diets high in trans fats and ...
Notes on Fatty Acids (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion In unsaturated fatty acids, at least two but usually no more than six of the carbon atoms of the hydrocarbon chain are linked together by double bonds. The two most common unsaturated fatty acids are oleic acid and linoleic acid, depicted in Figure 6-1 along with the saturated fatty acid stearic acid. In all the common saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, the long hydrocarbon chain is unbranched.
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids (With Diagram) Another turn of the helix will produce a chain of fatty acid lengthened by two carbon atoms (i.e. a chain in C 6) and so on. When the fatty acid formed has a particular length, it is liberated from the polyenzymatic complex by the action of deacylase, present in the acylsynthetase complex. The main fatty acid generally formed is palmitic acid (C 16). The synthesized fatty acids can either be used for the synthesis of glycerides or other lipids, or carried into the mitochondria to be ...
Fatty acid - Wikipedia In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and choleste
Fatty Acids: Definition, Structure, Function & Types ... Moreover, while short-chain fatty acids are formed from various precursors by anaerobic micro-organisms, carbohydrates are the most common progenitors of short-chain fatty acids. Fatty Acid Structure. Fatty acids are composed of carbon chains containing a methyl group at one end and a carboxyl group at the other. The methyl group is termed the omega (ω) and the carbon atom situated next to the carboxyl group is termed the "α" carbon, followed by the "β" carbon, etc. Fatty acid ...
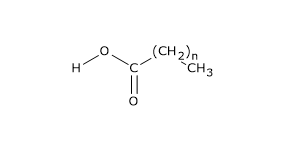
fatty acid | Definition, Structure, Functions, Properties ... Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with hydrogen atoms along the length of the chain and at one end of the chain and a carboxyl group (―COOH) at the other end. It is that carboxyl group that makes it an acid ( carboxylic acid ).
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Revisited: Structure Elucidation ... The dotted arrow in the bottom right corner represent diffusion of fatty acids into the cell, as well as active FadL-mediated transport. Fatty acid catabolism (blue circle): FadD, CoA-ligase; FadE, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; FadB, dual-function enoyl-CoA hydratase and hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase; FadA, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase. FadR and FabR are the master regulators of fatty acid degradation and fatty acid biosynthesis, whereas ppGpp is an alarmone.
Structure of the human fatty acid synthase KS-MAT didomain ... The human fatty acid synthase (FAS) is a key enzyme in the metabolism of fatty acids and a target for antineoplastic and antiobesity drug development. Due to its size and flexibility, structural studies of mammalian FAS have been limited to individual domains or intermediate-resolution studies of th …
Chemical Structure of Omega Fatty Acids. | Download ... Chemical Structure of Omega Fatty Acids. | Download Scientific Diagram. Download scientific diagram | Chemical Structure of Omega Fatty Acids. from publication: Food for Eye Health: Carotenoids ...
Fatty Acid Structure and Function Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying Fatty Acid Structure and Function. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
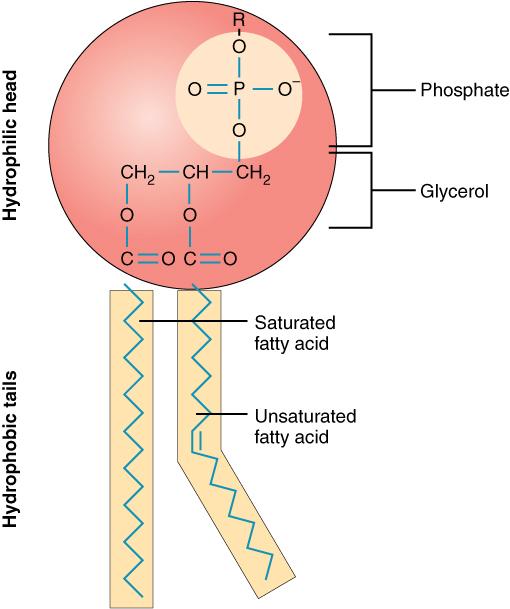
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Biological_membraneBiological membrane - Wikipedia The hydrophobic tails are usually fatty acids that differ in lengths. The interactions of lipids, especially the hydrophobic tails, determine the lipid bilayer physical properties such as fluidity. Membranes in cells typically define enclosed spaces or compartments in which cells may maintain a chemical or biochemical environment that differs ...
Fatty Acids - What Are Fatty Acids - Structure Of Fatty ... In this video we cover the structure of fatty acids and the different types of fatty acids.Fatty acids are made up of long chains of carbon atoms and hydroge...
PDF Fatty Acid Biosynthesis - California State University ... Fatty Acid Biosynthesis 4 Fatty Acid Synthase (FAS) • FAS is a polypeptide chain with multiple domains, each with distinct enzyme activities required for fatty acid biosynthesis. •ACP: Recall that CoA is used as an activator for β-oxidation. For fatty acid biosynthesis, the activator is a protein called the acyl carrier protein (ACP).
Fatty Acids And Triglycerides | Structure, Functions & Facts Fatty acids are made up of two components; An alkyl or hydrocarbon chain A carboxylic group The carboxylic group is present at the terminal of the hydrocarbon chain. The hydrocarbon chain is hydrophobic and non-polar while the carboxylic group is polar. The carboxylic group of fatty acids has a pK a of around 4.8.
Trans fatty acids: definition, structure, health effects ... Trans fatty acids (TFA) or trans-unsaturated fatty acids or trans fats are unsaturated fatty acids, a subclass of lipids, with at least one a double bond in the trans configuration. Carbon-carbon double bonds show planar conformation, and so they can be considered as planes from whose opposite sides carbon chain attaches and continues.





/carboxylic_acid-56a12b445f9b58b7d0bcb431.jpg)





















0 Response to "39 fatty acid structure diagram"
Post a Comment