41 construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify the bond order
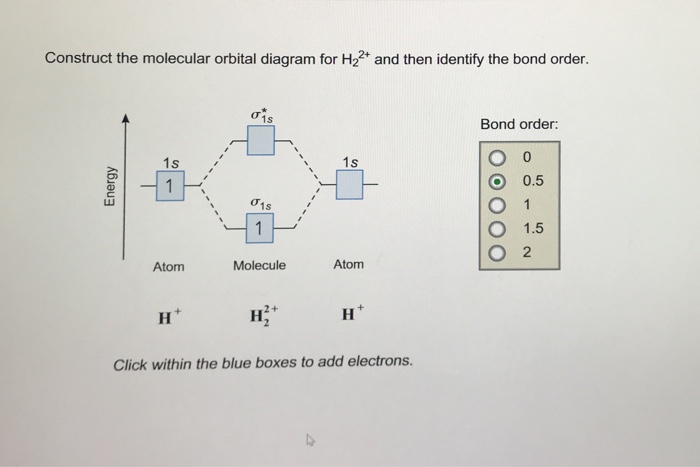
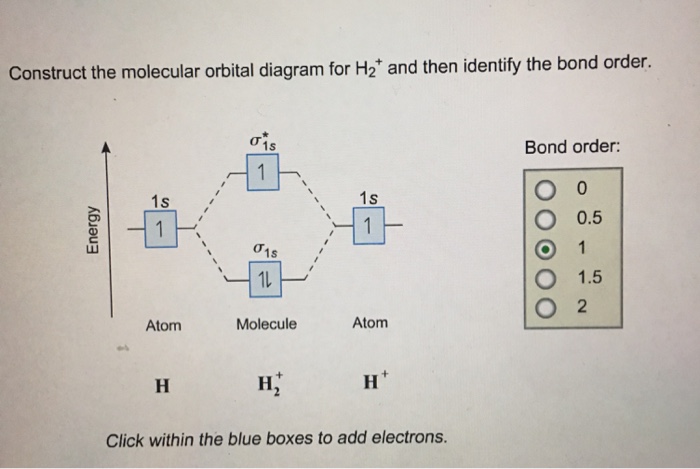
Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one σ1s and one σ* 1s MO by conservation of orbitals. If you calculate their bond order, you get: BOH+ 2 = 1 2(Bonding − Antibonding) = 1 2 (1 − 0) = 1 2 BOH− 2 = 1 2(Bonding − Antibonding) = 1 2 (2 − 1) = 1 2 Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxe. Molecular Orbital Theory - Build He2 Molecular Orbital Theory - Build He2 Watch later Watch on Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order.
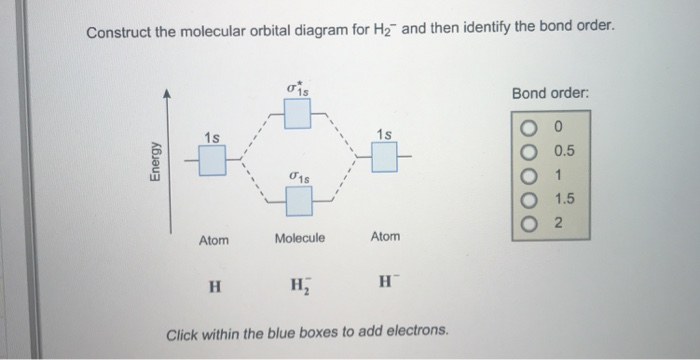
Dec 15, 2018 · Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce {H2}\) is get a sigma (s) bonding orbital, denoted as s1s in the diagram here. Chemical bonding - Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The procedure can ...
Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify the bond order
Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN- then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. To add arrows to the MO diagram, click on the blue boxes.Bond order of CN-00.511.522.53. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Previous question Next question. The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H2 molecule is shown in Figure Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxe.
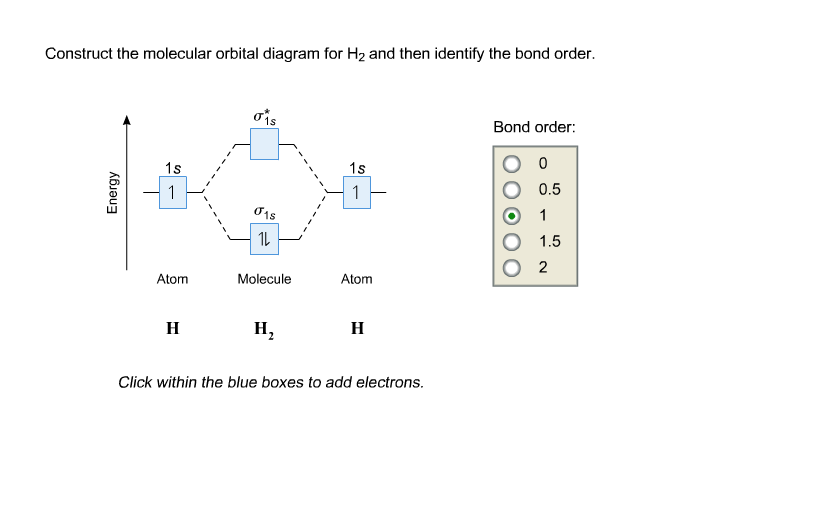
Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify the bond order. A dihydrogen molecule contains two bonding electrons and no antibonding electrons so we have. bond order in H2 = (2−0) 2 = 1 bond order in H 2 = ( 2 − 0) 2 = 1. Because the bond order for the H-H bond is equal to 1, the bond is a single bond. A helium atom has two electrons, both of which are in its 1 s orbital. Problem: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Click thin the blue boxes to add electrons.Bond order: a) 0 b) 0.5c) 1 d) 1.5e) 2. FREE Expert Solution. Show answer. Answer: 80% (433 ratings) play-rounded-fill. play-rounded-outline. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes to add electrons. Question: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes to add electrons. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2 and then identify the bond order. Make sure you add electrons to the boxes corresponding to the MOs for the molecule and to the boxes corresponding to the AOs for the two atomic species. Bond order: 1s o 0.5 O 1.5 2 Atom Molecule Atom Click within the blue boxes to add electrons.
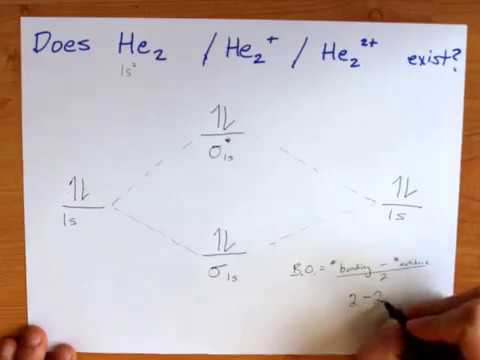
We can therefore use a molecular orbital energy-level diagram and the calculated bond order to predict the relative stability of species such as H 2+. With a bond order of only 1/2 the bond in H 2+ should be weaker than in the H 2 molecule, and the H–H bond should be longer. Solution for construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2− and then identify the bond order. close. Start your trial now! First week only $4.99! arrow_forward. learn. write. tutor. study resourcesexpand_more. Study Resources. We've got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments. ... Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For He2 And Then Identify The Bond Order. Calculate the bond order by subtracting the number of antibonding electrons from bonding electrons and then dividing the difference by two. 4. Assign the para just now. servantes. Molecular Orbital Diagram For He2. MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
We will do the following steps. Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons present. Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram. Step 3: Calculate the bond order of the molecule/ion. Recall that the formula for bond order is: Bond Order = 1 2[# of e - in bonding MO - # of e - in antibonding MO] 84% (394 ratings) Problem Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He 2 + and then identify the bond order. Since both molecular ions have a bond order of 1/2, they are approximately equally stable. Problem: Surprisingly, the hybridization of the starred oxygen in the following molecule is sp 2, not sp 3. ChemistryHelper2024. Since 1s shell of bonding orbital can accommodate only two electrons. So, next one electron will go into 1 s shell of anti-bonding orbital. - Bond order = (Bonding electrons - antibonding electrons) / 2. = (2 - 1) / 2 = 0.5. search. rotate. apsiganocj and 20 more users found this answer helpful. heart outlined. Bond order XXXXXXXXXXClick within the blue boxes to add electrons. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2 and then identify the bond order. Nov 11, 2021
Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes to add electrons. Outline a separation scheme for isolating benzoic acid from a reaction mixture if mixing a Grignard reagent...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Solution We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in .
Construct the molecular orbit diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Shortcut order: Click slim the blue box to include electrons. The concept used to settle this problem is based on molecular orbit diagram.
Oct 13, 2020 · Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2 and then identify the bond order. Make sure you add electrons to the boxes corresponding to the MOs for the molecule and to the boxes corresponding to the AOs for the two atomic species. Bond order: 1s o 0.5 O 1.5 2 Atom Molecule Atom Click within the blue boxes to add electrons.
Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer.
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H2 molecule is shown in Figure Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxe.
View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Previous question Next question.
Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN- then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. To add arrows to the MO diagram, click on the blue boxes.Bond order of CN-00.511.522.53. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He.

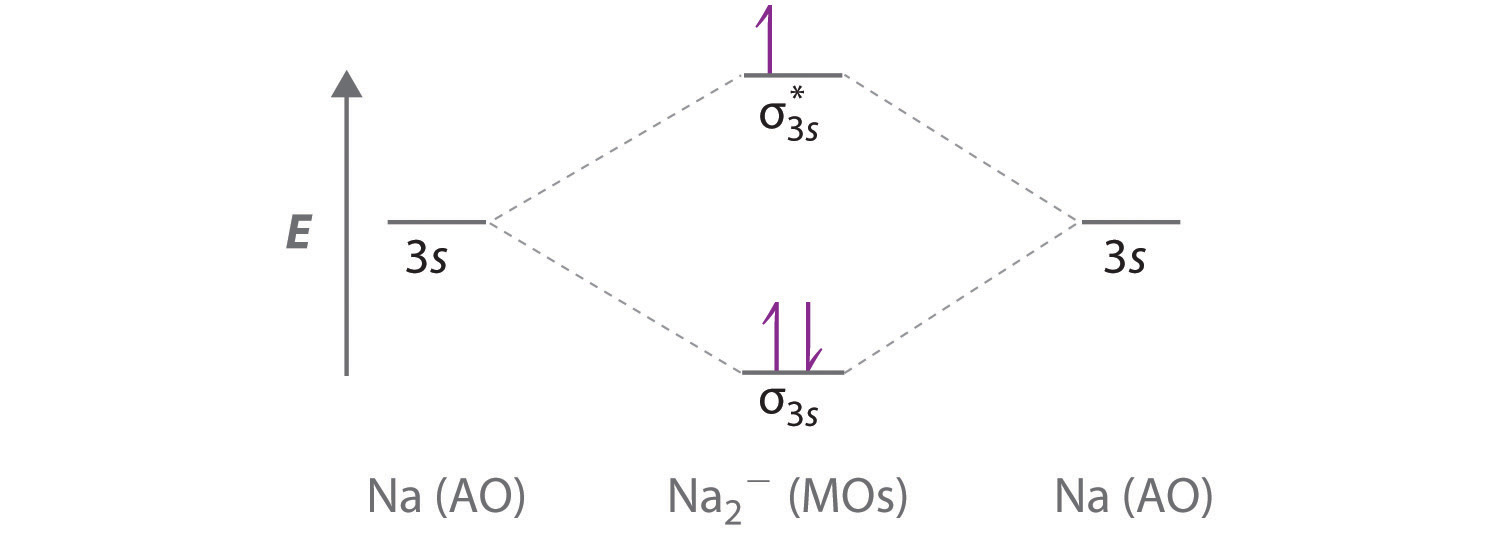

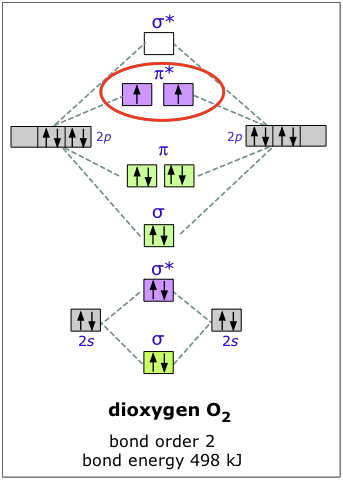
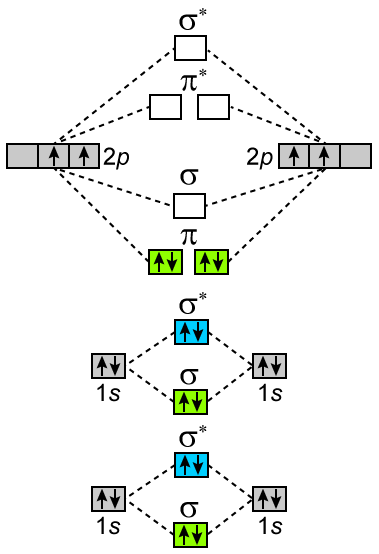








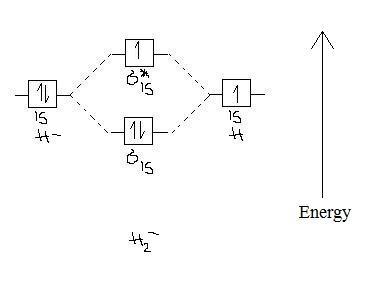








0 Response to "41 construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify the bond order"
Post a Comment