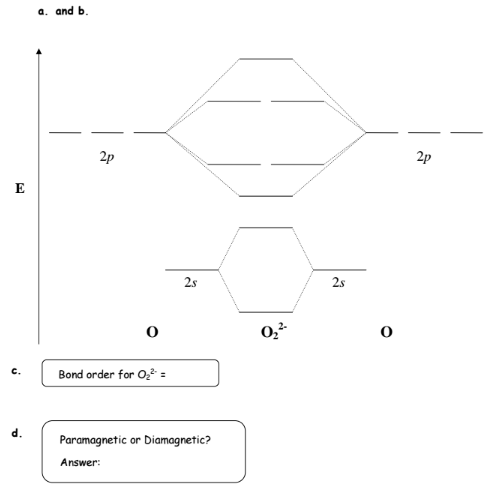
42 complete the energy-level diagram for h2−.
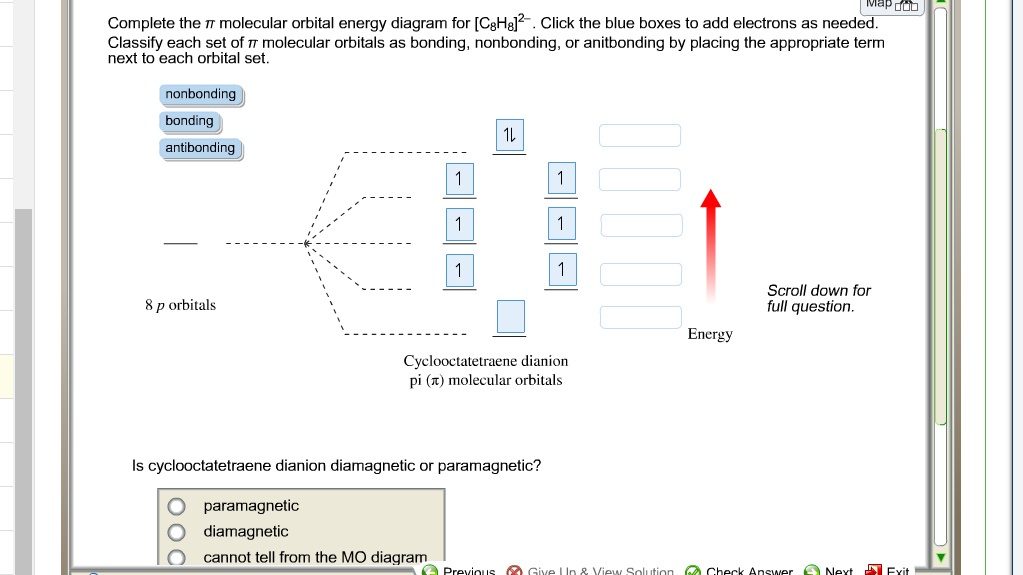
(a) Sketch the molecular orbitals ofthe ion and draw its energy-level diagram. (b) How manyelectrons are there in the H2+ ion? (c) Write the electronconfiguration of the ion in terms of its MOs. (d) What isthe bond order in H2+? (e) Suppose that the ion is excitedby light so that an electron moves from a lower-energy toa higher-energy MO. The energy level diagram for CO2 in Figure 5.25 can be used as a guide, with the orbitals of Be higher in energy than those of C and the orbitals of F lower in energy than those of O. Calculated molecular orbital shapes are below, for comparison for those of CO2 in Figure 5.25.
Insight: The work done by the spring is negative whenever you displace the block away from x = 0, but it is positive when the displacement vector points toward x = 0.. Introduction to Potential Energy . The work energy theorem: WKtotal f i=−K i A) A force acting on a particle over a distance changes the kinetic energy of the particle. B) To calculate the change energy, you must know the ...

Complete the energy-level diagram for h2−.
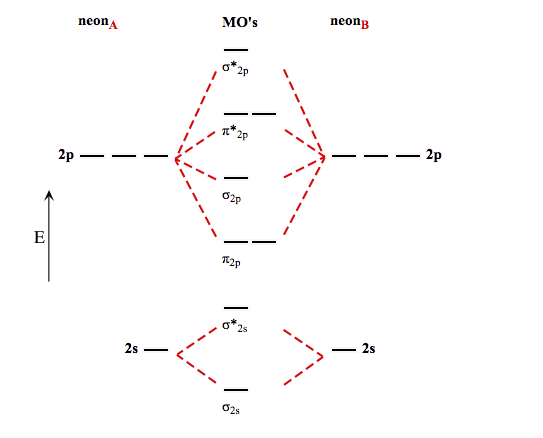
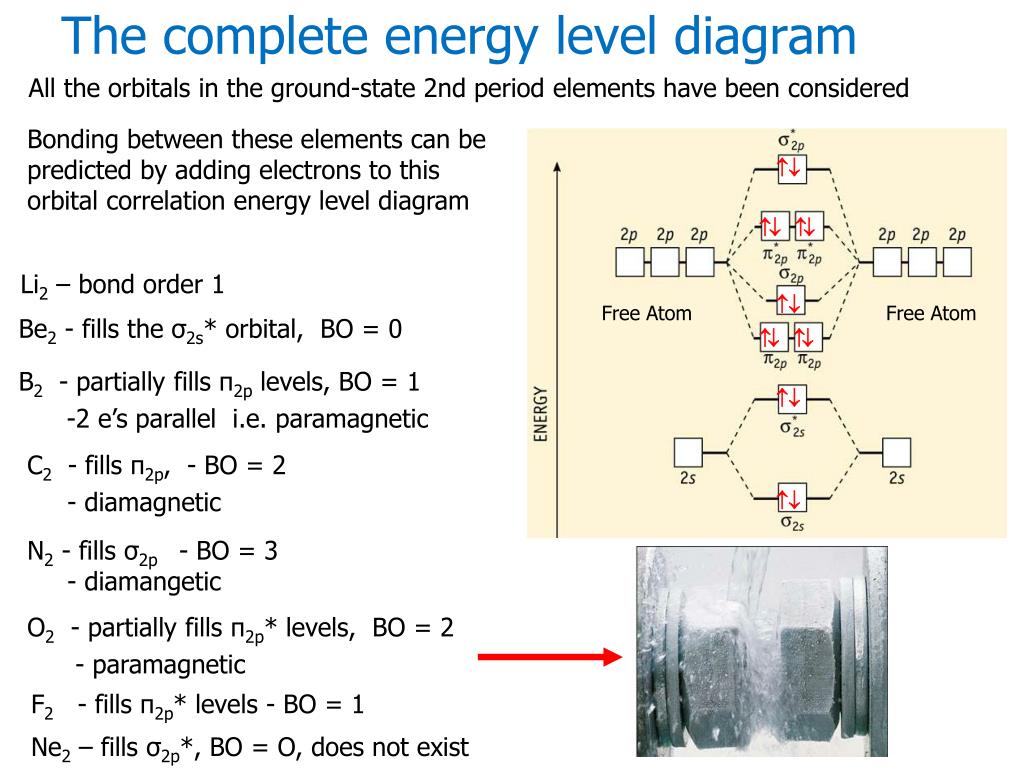
1 The properties of gases. 1A The perfect gas Answers to discussion questions 1A.2 The partial pressure of a gas in a mixture of gases is the pressure the gas would exert if it occupied alone the same container as the mixture at the same temperature. Dalton’s law is a limiting law because it holds exactly only under conditions where the gases have no effect upon each other. The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total of 4 electrons in this molecule. Two are placed in the bonding orbital, the other two in antibonding orbital. The bond order = 1/2 x (Number of Bonding Electrons - Number of Antibonding Electrons) = . Energy level diagrams and the hydrogen atom. It's often helpful to draw a diagram showing the energy levels for the particular element you're interested in. The diagram for hydrogen is shown above. The n = 1 state is known as the ground state, while higher n states are known as excited states. If the electron in the atom makes a transition from ...
Complete the energy-level diagram for h2−.. For the following two complexes. A:[NiCl6]4− and [NiCl4]2− the ratio of CFSE will be nearly: Hard. View solution. Other articles where molecular orbital energy-level diagram is discussed: chemical bonding: Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The molecular orbital ... Jan 25, 2020 — A molecular orbital energy level diagram just shows the energy levels in the molecule. Frequently, but not always, energy level diagrams are ...Missing: h2 | Must include: h2 Sep 05, 2016 · Q.5 H2 = h1 + h2 − g V Q.7 ... by the dotted line in the adjoining diagram where I is the current. ... and perpendicular to vibrations twice in its one complete rotation giving rise to maximum ...
Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxe. A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagram s He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. You then pace off the distance from the pole to the base of the building with big, 1-m-long steps, and you get a total of 16 steps or 16 m. S LUTI N Now you draw, to scale, the diagram shown in Fig. l - 9 b using these measurements. You can measure, right on the diagram, the last side of the triangle to be about x = 13 m. Watch the video solution for the question: what is the energy-level diagram for H2−....1 answer · Top answer: Hey there!We are asked to draw the energy-level diagram or the molecular orbital energy diagram for H2-.An H2 molecule has two electrons and a charge ... and the rest energy of the electron is mc2. Then, e2 a 0 = me4 ~2 = mα2~2c2 ~2 = α2 mc2. (2.1.5) This states that the energy scale of hydrogen bound states is a factor of α2 smaller than the rest energy of the electron, that is, about 19000 times smaller. We can thus rewrite the possible energies as: En = −1 2α 2 mc2 1 n. (2.1.6)
e, and therefore µc2 is the rest energy of the electron. Eq. (11.33) shows that the typical scale of the energy levels in the H atom is 10−4 the rest energy of the electron. This justifies the nonrelativistic treatment of the H atom that we have used here. Clearly Hey there! We are asked to draw the energy-level diagram or the molecular orbital energy diagram for H2-. An H2 molecule has two electrons and a charge of -1 means an additional one electron. Let us write the three electrons on H atoms - 1 H atom with 1 electron and 1 H atom with two electrons. 93% (471 ratings) integers between −Jto J. Vibrations With ψ(r) given by Eq. 9 and the Hamiltonian by Eq. 4, the radial part of Eq. 6 becomes " − ¯h2 2µ d2 dr2 + ¯h2 2µr2 J(J+1)+ V(r) # χ(r) = Eχ(r) (10) The term (¯h2/2µr2) J(J+1) gives the rota-tional energy. Because this energy turns out to be small compared to the total energy E, the ... Complete Solutions Manual GENERAL CHEMISTRY NINTH EDITION Ebbing/Gammon. Uploaded by. Sofia Uribe Sanchez. connect to download. Get pdf ..... Preface This Complete Solutions Manual provides worked-out answers to all of the problems that appear in General Chemistry, 9th Edition, by Darrell D. Ebbing and ...
0:15 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Hydrogen Molecule1:39 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Helium Molecule2:54 Molecular Orbital Diagram of ...
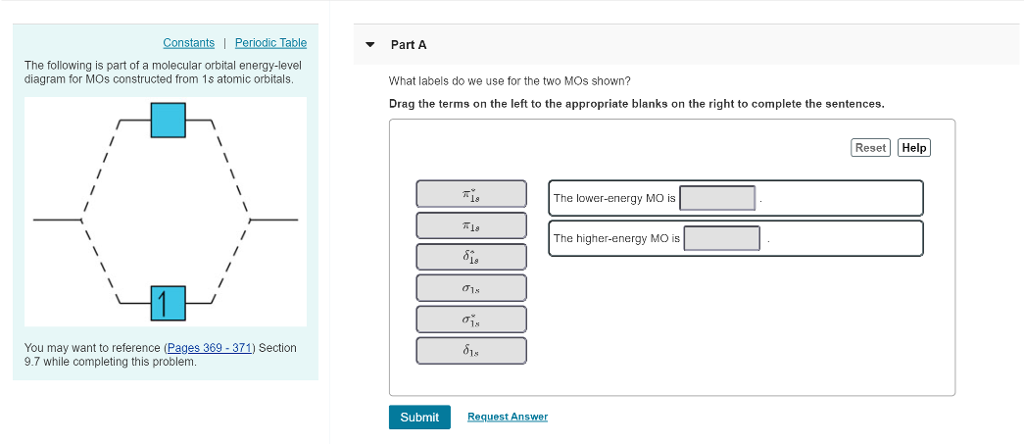
the molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the h 2 molecule is shown in figure on either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms a and b, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding.the …
Here we report our study of the phase diagram of H 2-SiH 4 system to 6.5 GPa at room temperature. Samples with two premixed starting compositions, 5:1 and 1:1 molar H 2 :SiH 4 ratios, were loaded as a well-mixed fluid phase in a diamond anvil cell and were monitored in situ using optical microscopy and Raman spectroscopy.
Aug 15, 2020 ... The 1s orbital energy level is -13.6 eV for hydrogen atoms, measured as the ionization ... Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule.
Line diagrams for the energy levels of NO(−) and superoxide. The states and values for superoxide are given in the introduction. The nine X-E doublet states are shown sequentially on the right ...
Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, H− 2 has three electrons while H+ 2 has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one σ1s and one σ* 1s MO by conservation of orbitals. If you calculate their bond order, you get: BOH+ 2 = 1 2(Bonding − ...
The potential is non-zero and equal to −V H in the region −a ≤ x ≤ a. For a quantum mechanical particle we want instead to solve the Schrodinger equation. We consider two cases. In the first case, the kinetic energy is always positive: −. 1 2 d ψ(x) 2 2m dx 2 = Eψ(x) in Region I − 1 2H. d ψ(x) 2m dx. 22 = (E + V. H
Chemical bonding - Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The procedure can be The molecular orbital energy- level diagram that results is constructed by putting .May 20, · Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order? i know the answer im just posting it for whoever may need it. (check picture)Status: Open.
Transcribed Image Textfrom this Question. Complete the energy-level diagram for H2 Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets Reset Help σ1s 1s 1s 14 1s H2.
Complete Solutions Manual GENERAL CHEMISTRY NINTH EDITION Ebbing/Gammon. Sofia Uribe Sanchez. Download Download PDF. Full PDF Package Download Full PDF Package. This Paper. A short summary of this paper. 15 Full PDFs related to this paper. Read Paper. Download Download PDF.
Consider three parts to Δxscreen = 34 cm the electron’s motion and see the diagram, which is a Δ x field = 2.6 cm top view. First, during the horizontal acceleration phase, energy will be ...
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
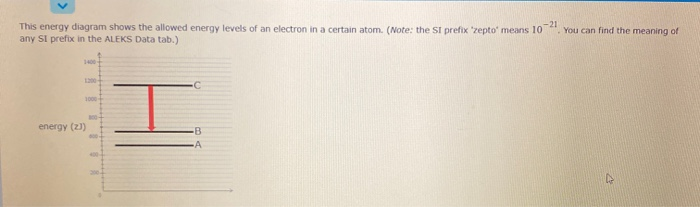
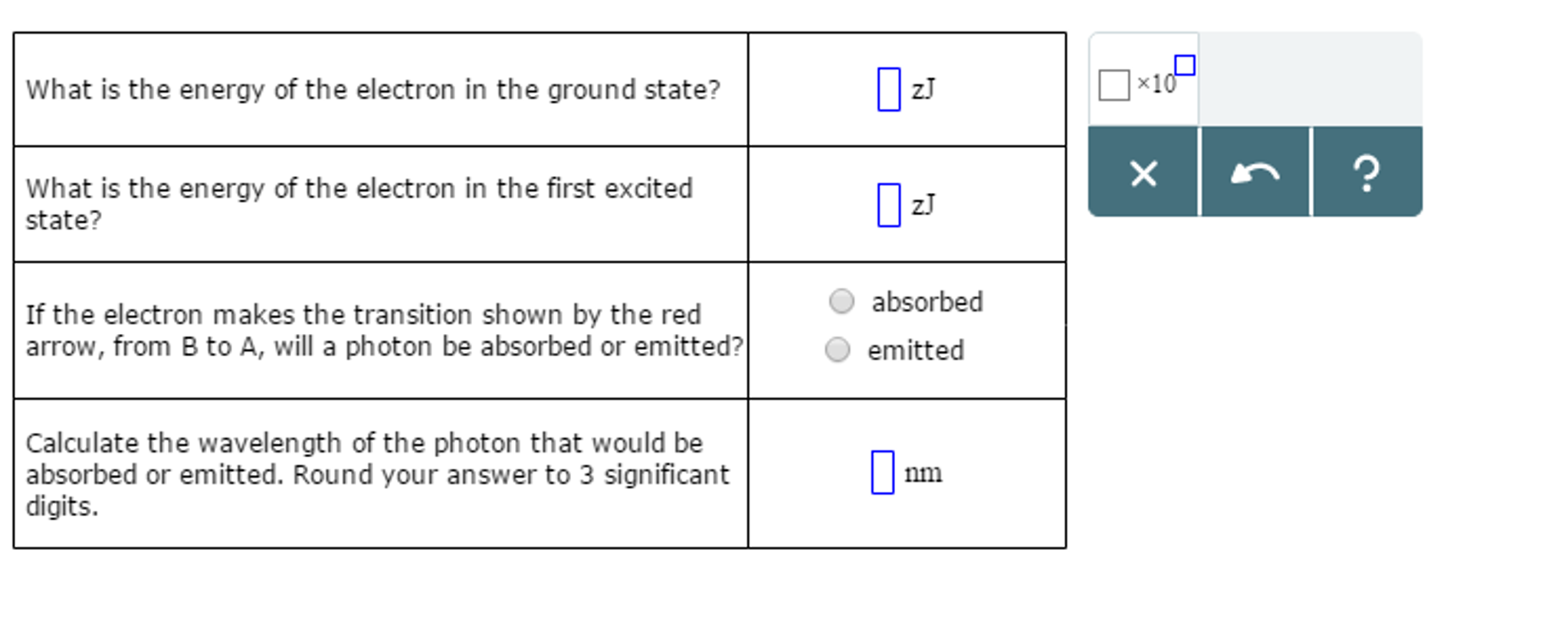
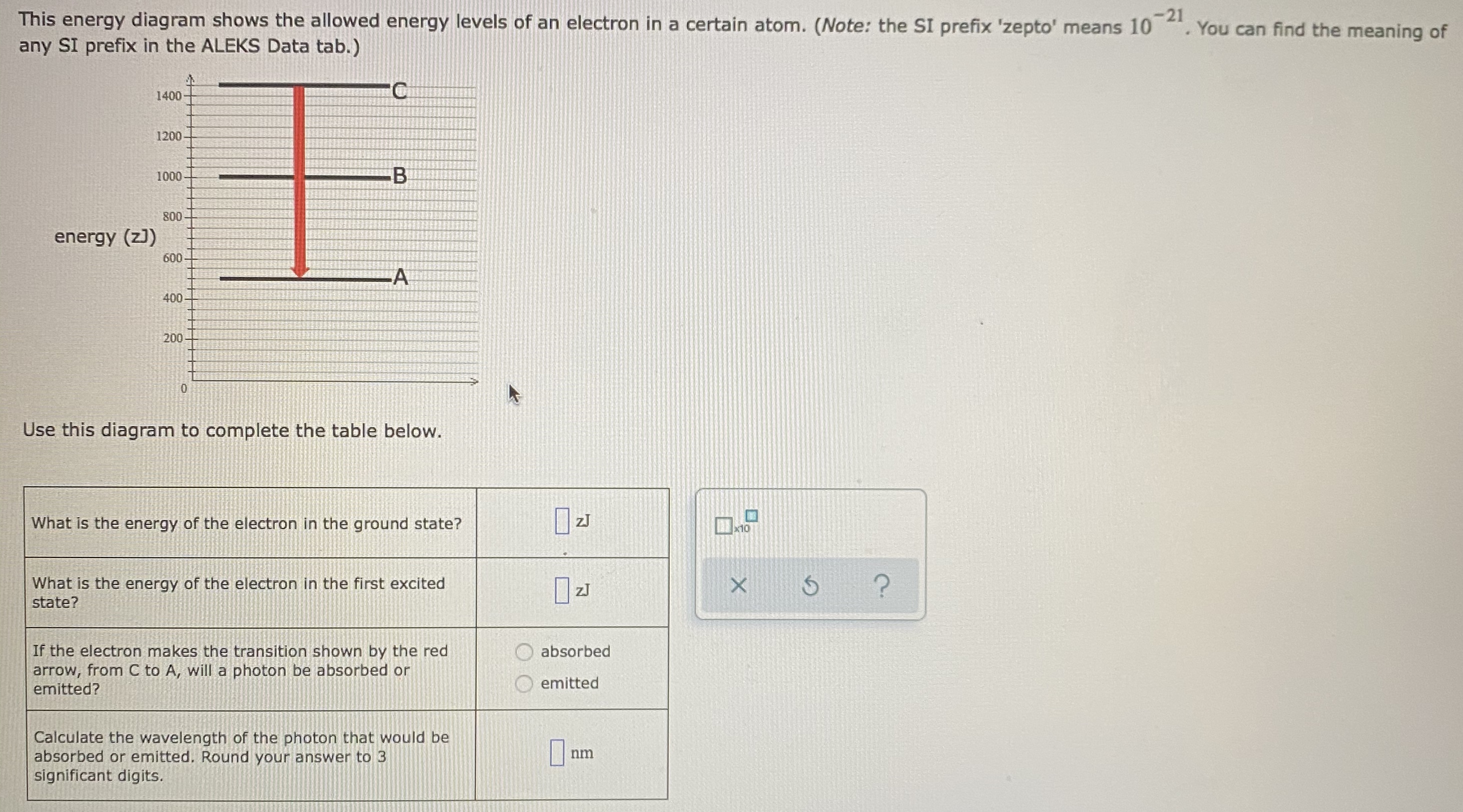
Complete step by step answer: The energy level diagram of the hydrogen atom is given below. When the electron transits from a higher ... 1λ=Z2R(1n2f−1n2i).1 answer · Top answer: Hint: The electrons are transited from higher energy level to the lower energy levels. This causes the spectral lines of different wavelengths. The ...
A simple harmonic potential ( i.e. V(r) ∝ r2) would yield equally spaced energy levels and we would not see the shell structure and hence the magic numbers. It turns out that once again the Saxon-Woods model is a reasonable guess, i.e. V(r) = − V 0 1+exp((( r−R)/δ )) 37
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
The free-energy change, ΔG, for this reaction varies with temperature as shown in. G / kJT / K Δ mol− 1 298 −592.5 288 −594.2 273 −596.7 260 −598.8 240 −602.2 Use these data to plot a graph of free-energy change against temperature on the grid below. Calculate the gradient of the line on your graph and hence calculate the
How would the dx2−y2 orbital in the n=5 shell compare to the dx2−y2 orbital in the n=3 subshell? A. The contour of the orbital would extend further out along the x and y axes. B. The value of ℓ would increase by 2. C. The radial probability function would include two more nodes. D.
-iE jt/h-, the average value of the energy does not vary with time but the expectation values of other properties do vary with time. 3. A particle is confined to a one-dimensional box of length L having infinitely high walls and is in its lowest quantum state. Calculate: < x>, < x2>, < p>, and < p2>. Using the 2> − < A > 2)1/2, to define the
N b = 2 , Na =0. Bond order = 1. Positive value of bond order indicates that H 2 molecule is stable.. Bond order value of 1 means that two hydrogen atoms are connected by a single bond.. Greater value of bond order for H 2 molecule than H 2 + ion shows that two H 2 molecule is more stable than H 2 +.. Bond length of H 2 is smaller than that of H 2 + ion.. As no unpaired electron is present ...
2 (electrons in bonding orbitals - electrons in antibonding orbitals) Draw a complete MO diagram for all the bonds in ethene.The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total of 4 electrons in this molecule. Two are placed in the bonding orbital, the other two in antibonding orbital.
Figure 5.3.2 Molecular Orbital Energy-Level DiagramforH 2 Thetwo available electrons (one from each H atom) in this diagramfill thebonding σ 1 s molecular orbital. Because theenergyof theσ 1 s molecular orbital is lower than that of thetwo H 1 s atomic orbitals, theH 2 molecule is more stable (at a lower energy) than thetwo ...
ΔG298D = −34 kJ mol−1 12.0 g H2 × 2 2 1 mol H 2.0 g H × 2 1 mol reaction 3 mol H × 34 kJ 1 mol reaction-= -68 kJ One point is earned for the correct stoichiometry. One point is earned for the correct answer. (c) Given that ΔH298D for the reaction is −92.2 kJ mol−1, which is larger, the total bond dissociation energy
Molecular orbital energy level diagrams for HS − and H 2 S. ... we found that 64% contained only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO formulas) while the ...
10. [8.10(b)] For a certain harmonic oscillator of effective mass 2.88 × 10−25 kg, the difference in adjacent energy levels is 3.17 zJ. Calculate the force constant of the oscillator. 11. [8.14(b)] Confirm that the wavefunction for the first excited state of a one-dimensional linear
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hydrogen Gas (H2).Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total.Bonding Order is 1, ...
The C −Br bond is weaker than the C−Cl bond. The H −Cl bond is weaker than the H−Br bond. Chlorine is more reactive than bromine. (1) (Total 15 marks) Q3.A student investigated the rate of reaction of magnesium and hydrochloric acid. Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) MgCl 2 (aq) + H 2 (g)
Hydrogen atom's valence orbitals, before bonding, include every orbital, and all are the same energy for a specific n. At that point, there is only one electron. HAVING MORE THAN ONE ELECTRON SPLITS ENERGY LEVELS When introducing more electrons into the system, i.e. with another hydrogen wanting to bond, the repulsion splits the energy levels of the AOs of hydrogen. They start out where each n ...
The rotational spectrum of the CO-para-H2 van der Waals complex, produced using a molecular jet expansion, was observed with two different techniques: OROTRON ...
Energy level diagrams and the hydrogen atom. It's often helpful to draw a diagram showing the energy levels for the particular element you're interested in. The diagram for hydrogen is shown above. The n = 1 state is known as the ground state, while higher n states are known as excited states. If the electron in the atom makes a transition from ...
The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total of 4 electrons in this molecule. Two are placed in the bonding orbital, the other two in antibonding orbital. The bond order = 1/2 x (Number of Bonding Electrons - Number of Antibonding Electrons) = .
1 The properties of gases. 1A The perfect gas Answers to discussion questions 1A.2 The partial pressure of a gas in a mixture of gases is the pressure the gas would exert if it occupied alone the same container as the mixture at the same temperature. Dalton’s law is a limiting law because it holds exactly only under conditions where the gases have no effect upon each other.










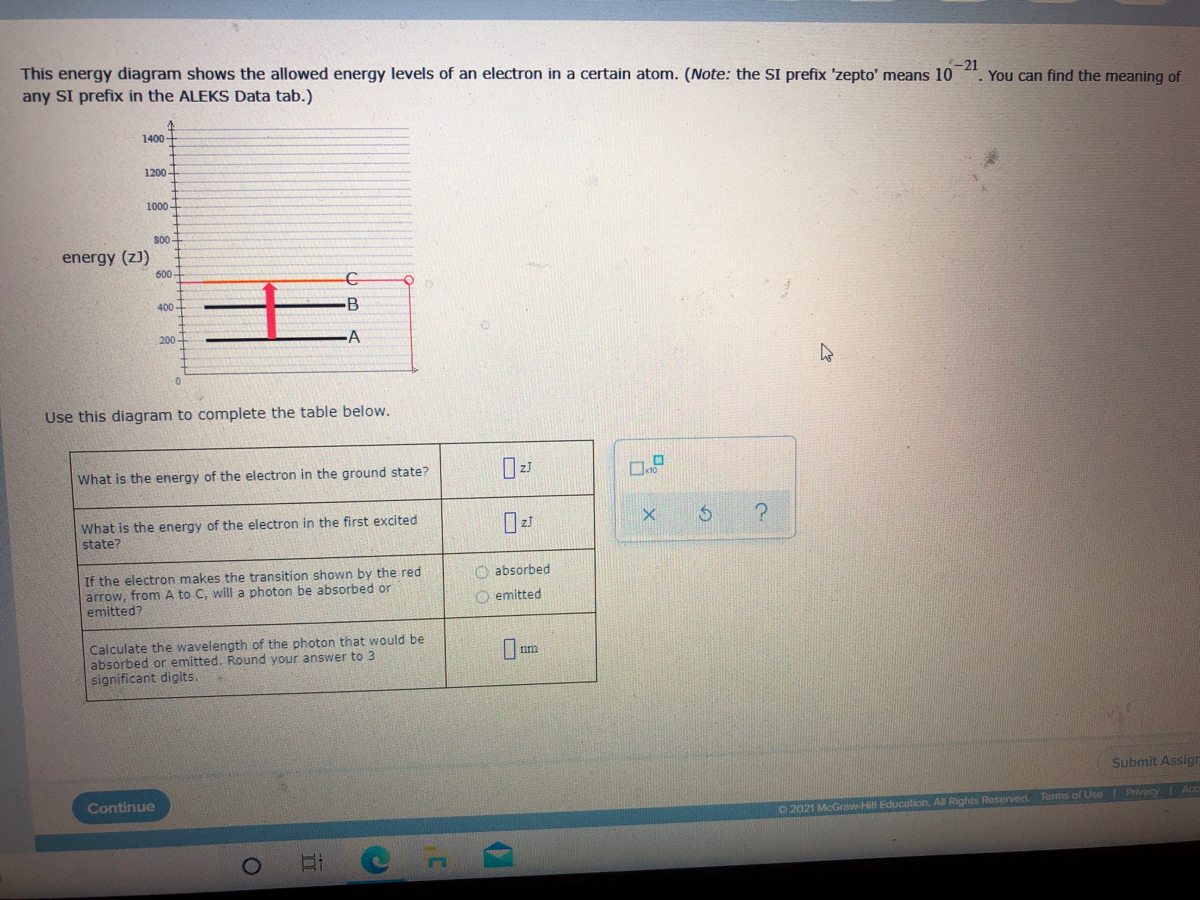












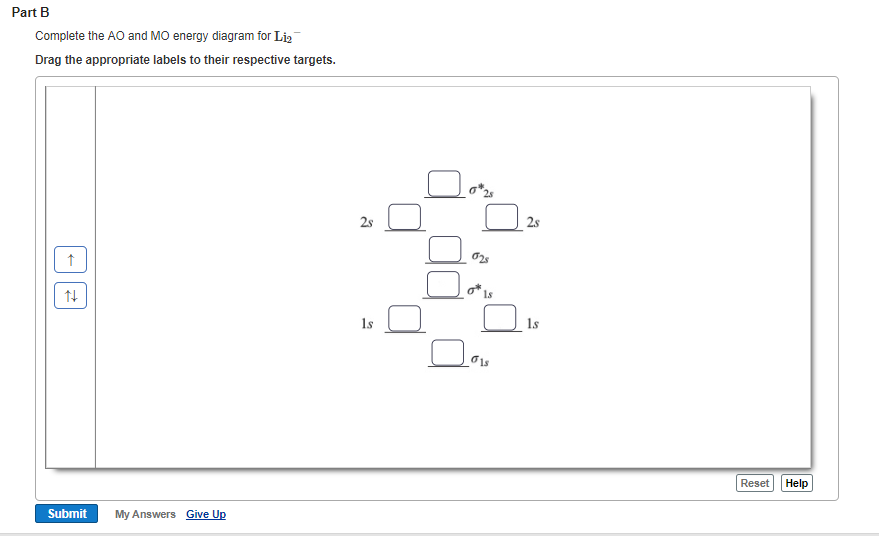


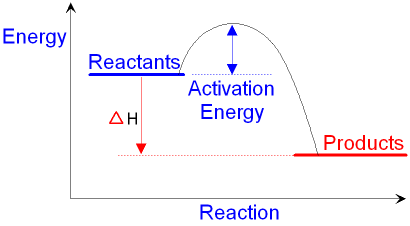
0 Response to "42 complete the energy-level diagram for h2−."
Post a Comment