42 cellular respiration electron transport chain diagram
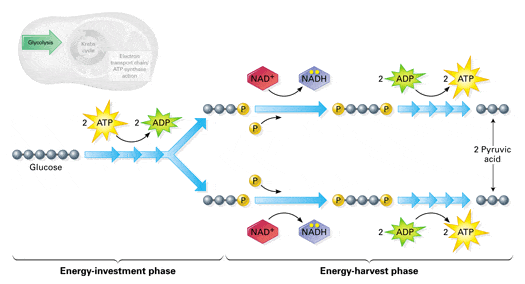
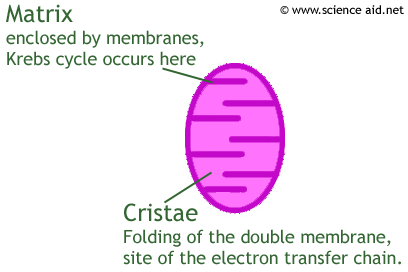
Cellular Respiration 38 ATP (maximum per glucose) Glucose Glycolysis 2ATP 4ATP 6ATP 18ATP 4ATP 2ATP 2 ATP 2NADH 2NADH 6NADH Krebs Cycle 2FADH 2 2 ATP 2 Pyruvate 2 Acetyl CoA Electron Transport Chain Cytoplasm Mitochondria Cellular respiration that uses glycolysis and fermentation when no oxygen is present, producing about 2 ATP per molecule of glucose Inner mitochondrial membrane The location of electron transport chains and ATP synthase, folded many times to increase surface area
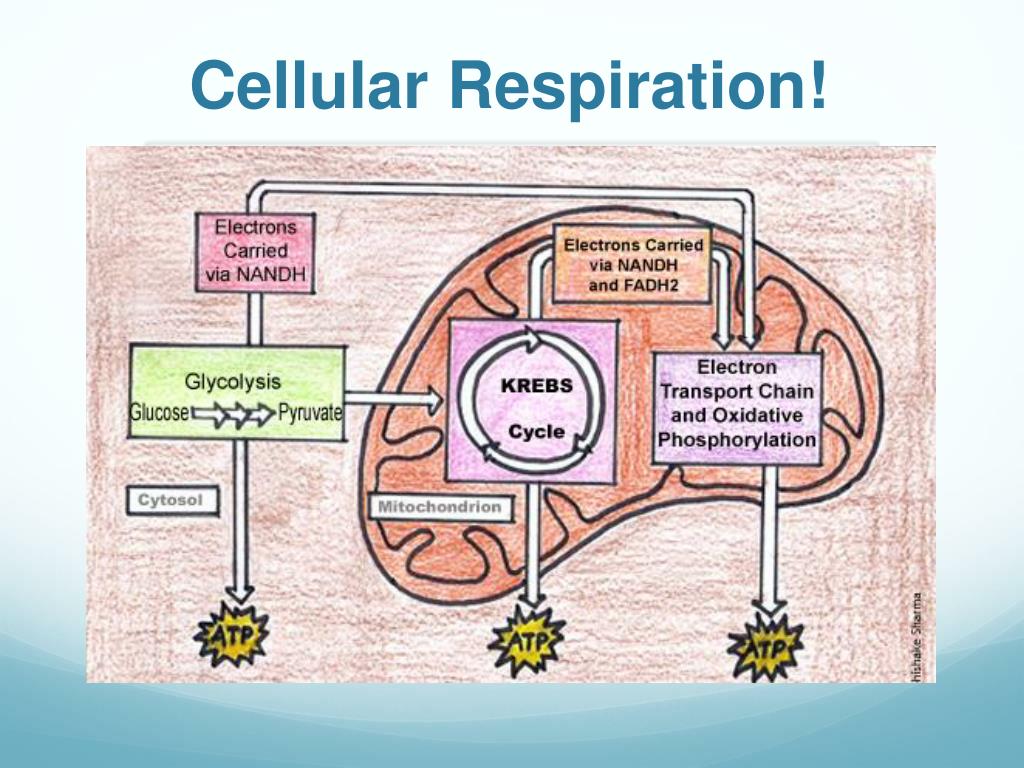
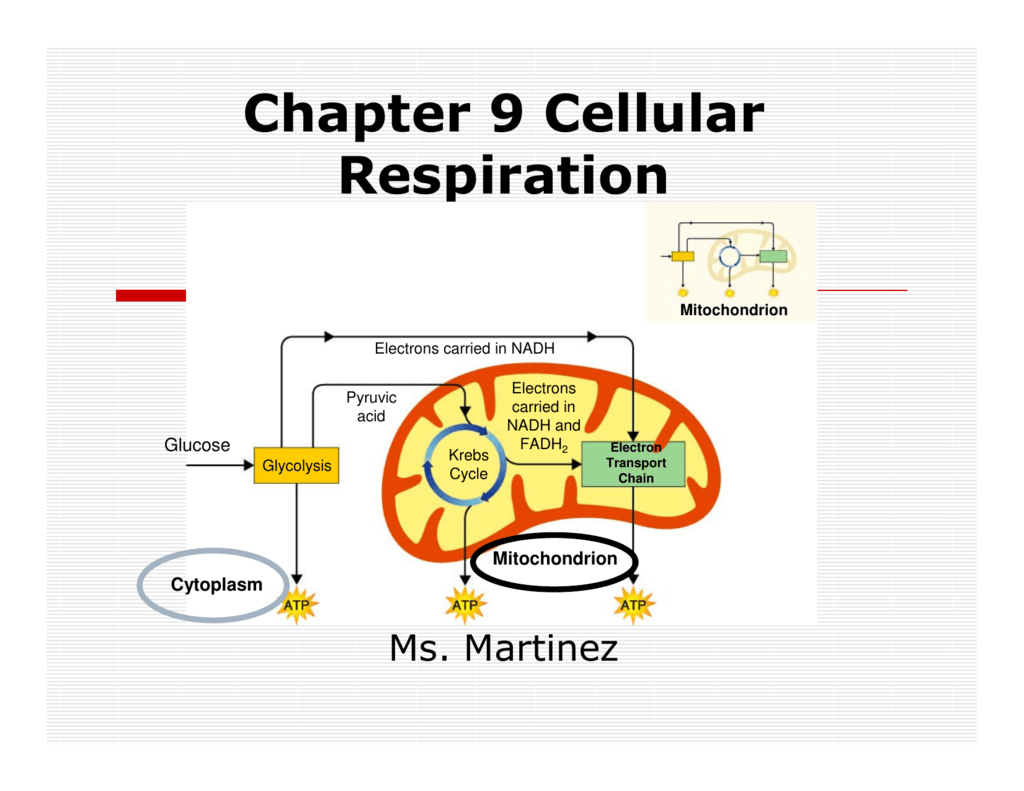
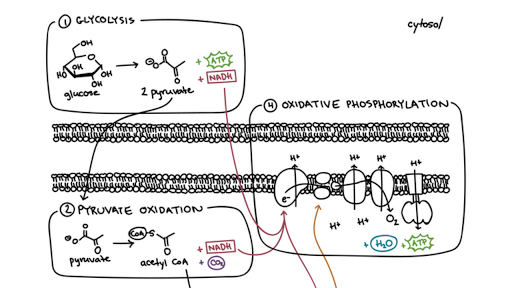
Steps of cellular respiration. Overview of the steps of cellular respiration. Glycolysis. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). ATP and NADH are made. These reactions take place in the cytosol. Pyruvate oxidation. Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a two-carbon molecule bound to ...
Cellular respiration electron transport chain diagram
More About Cellular Respiration So now we know that cellular respiration is a three stage process that converts glucose and oxygen to ATP and releases carbon dioxide and water. What are the 3 phases that do this? 1) Glycolysis 2) Krebs Cycle 3) The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) This is a very simple overview of these 3 stages: Glycolysis (Stage 1) 3. Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation Electron Transport Chain (Source: Wikimedia) The final pathway in the cellular respiration is comprised of the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation which both occur in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. Thus, the total ATP yield in the cellular respiration process is 36 or 38 ATP molecules. Hope this article on simple cellular respiration diagram has helped you understand the process well. The process of cellular respiration is a very complex reaction that involves many enzymes, coenzyme, and molecules. 10.9.2015 · Mitochondrial respiration involves the carbon balance in the whole plant ...
Cellular respiration electron transport chain diagram. Cellular respiration diagram biologywise after successful pletion of the krebs cycle begins the electron transport chain as you can see in the diagram this stage is where energy is released in bulk in the process of cellular respiration it requires direct use of oxygen molecules this is also known as the oxidative phosphorylation process cellular. The electron transport chain; the last stage of cellular 4 3 cellular respiration diagram quizlet the krebs cycle harnessing chemical energy for cellular easy krebs cycle diagram get rid of wiring diagram problem glycolysis and krebs cycle diagram biology projects tricarboxylic acid cycle biochemistry britannica krebs cycle and link reaction ... Electron transport is defined as a series of redox reaction that is similar to the relay race. It is a part of aerobic respiration. It is the only phase in glucose metabolism that makes use of atmospheric oxygen. When electrons are passed from one component to another until the end of the chain the electrons reduce molecular oxygen thus ... Drag and drop the pins to their correct place on the image.. In Cytoplasm, In Mitochondria, Glucose, ATP, Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain, Glycolysis.
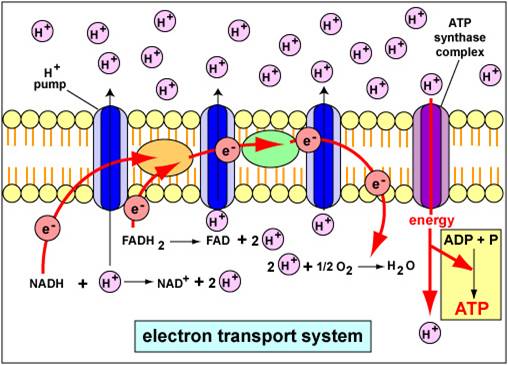
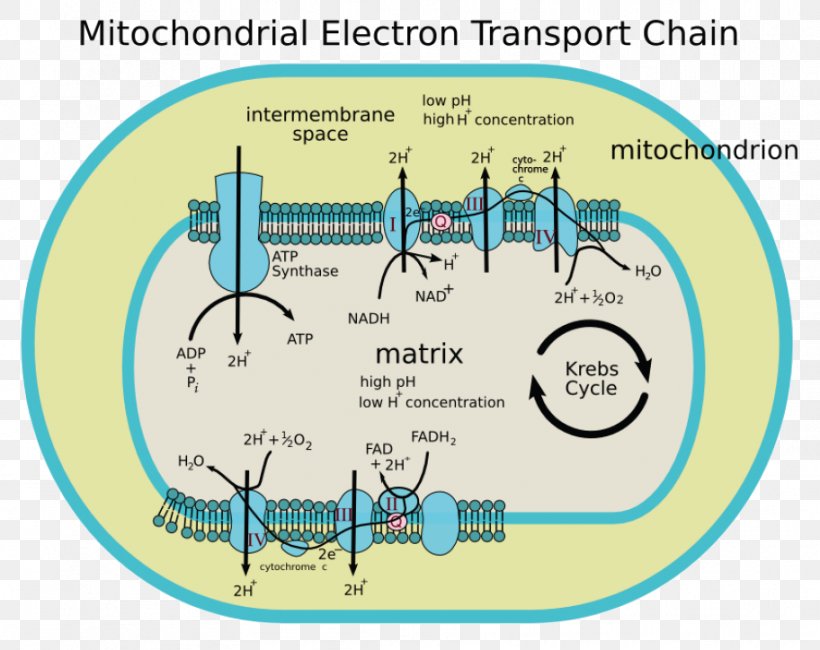
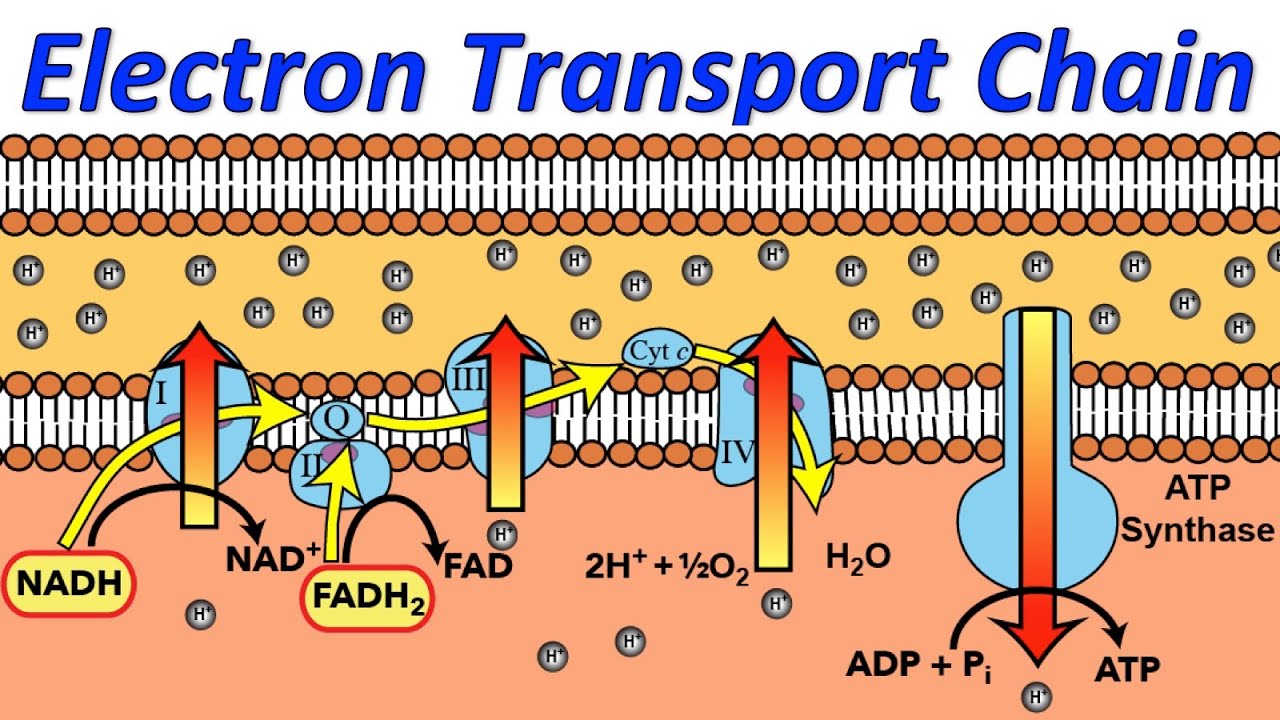
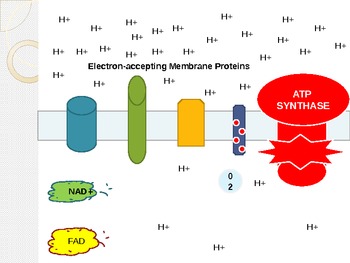
Electron Transport Chain Steps Explained with Diagram. The electron transport chain is an essential metabolic pathway that produces energy by carrying out a series of redox reactions. This BiologyWise article provides a simple explanation of this pathway. Summary Of Cellular Respiration: This video covers all the steps of cellular respiration from start to finish! Organisms perform respiration to create ATP. T... The catabolic pathways of aerobic and anaerobic respiration, which break down organic molecules and use an electron transport chain for the production of ATP. Chemiosmosis An energy-coupling mechanism that uses energy stored in the form of a hydrogen ion gradient across a membrane to drive cellular work, such as the synthesis of ATP. The electron transport chain has two essential functions in the cell: Regeneration of electron carriers: Reduced electron carriers NADH and FADH 2 pass their electrons to the chain, turning them back into NAD + and FAD. This function is vital because the oxidized forms are reused in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) during cellular respiration.
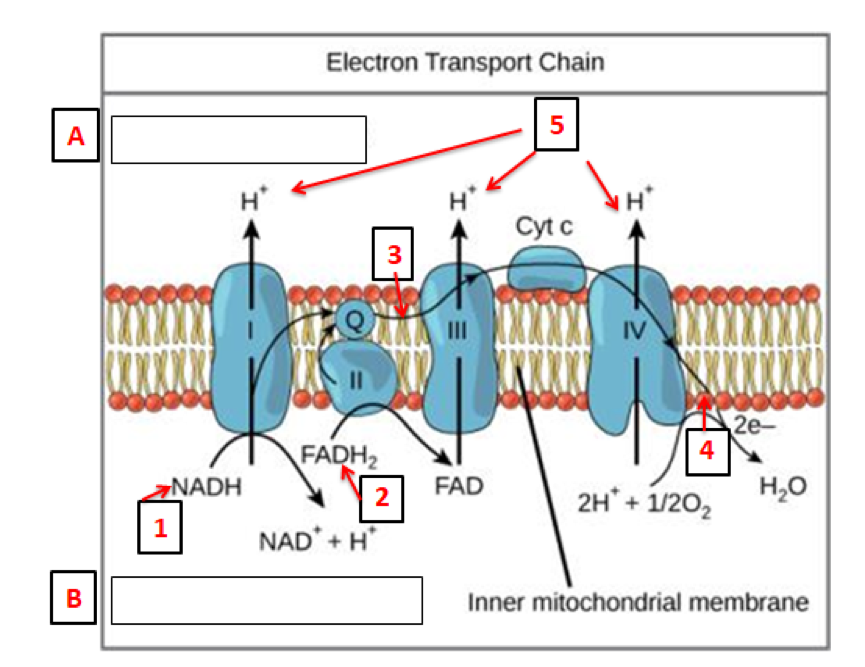
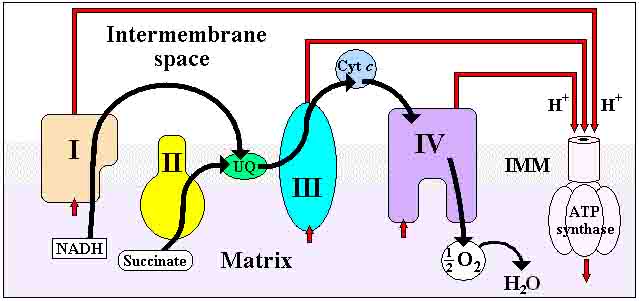
The Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation (Interactive Tutorial) 1. Introduction. In the previous tutorials in this series about cellular respiration, we've seen how glycolysis, the link reaction, and the Krebs cycle oxidize food so that the mobile electron carriers NAD + and FAD can be reduced to NADH and FADH 2, respectively. SBI 4U7 Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration-The Details The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) • Although the Kreb's Cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix, under aerobic conditions, oxygen is not utilized. • The reactions of the ETC, however, MUST be conducted in the presence of oxygen. General Overview of ETC • This is a series of redox reactions in which high energy ... Which of the following happens as electrons pass down the electron transport chain? (type letter) a. energy from the moving electrons transports H+ ions into the intermembrane space b. carbon dioxide is released c. energy from H+ ions crossing back into the matrix causes ATP synthase to make ATP d. water is produced Electron transport chain. The last phase of the cellular respiration is the electron transport chain. Here, the NADH and FADH2 produced in the previous phases enter the electron transport chain. Each NADH molecule that enter the chain results in the production of three ATP molecules while each FADH2 can produce two ATP molecules.
Electron Transport Chain • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration
second step of cellular respiration, occurs in the matrix, yields 2 ATP, 6NADH, 2 FADH2 Electron Transport Chain third step of cellular respiration, occurs in the inner membrane between the intermembrane space and the matrix, can yield 34 ATP
How the ETC Works. ( eukaryotes ). It is easiest to understand how electron transport works by dividing this process into three main events: In the electron transport chain, these electron carriers are oxidized, transferring their electrons to the carrier molecules embedded in the ETC membrane. In aerobic respiration, these electrons are passed ...
mitochondria. organelle in which aerobic cellular respiration takes place. glucose. chemical that is broken down in glycolysis to make pyruvate and a net 2 ATP. NADH. electron carrier produced in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. OTHER SETS BY THIS CREATOR.
The electron transport chain is the last stage of the respiration pathway and is the stage that produces the most ATP molecules. The electron transport chain is a collection of proteins found on ...
The electron transport chain is the last stage of the respiration pathway. It is the stage that produces the most ATP molecules. In total, 38 ATP molecules are produced from one molecule of ...
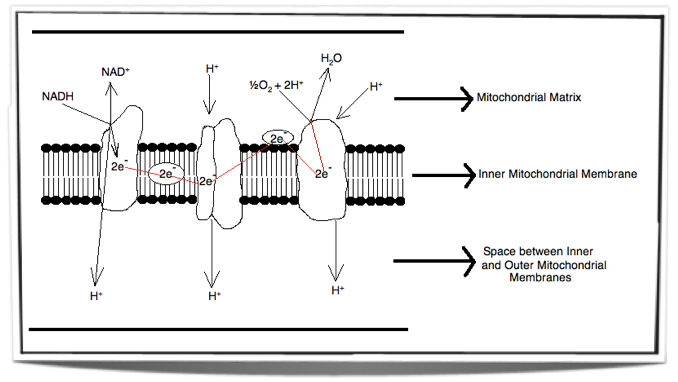
Electron Transport Chain The electron transport chain uses the high-energy electrons produced by the Krebs cycle to move hydrogen ions from one side of the inner membrane to the other. Label the diagram with the following terms: electron, hydrogen ion, and inner membrane. Intermembrane space 2 H20 FADH2 2 NADH FAD 2 NAD* 4 H+ 02 Matrix
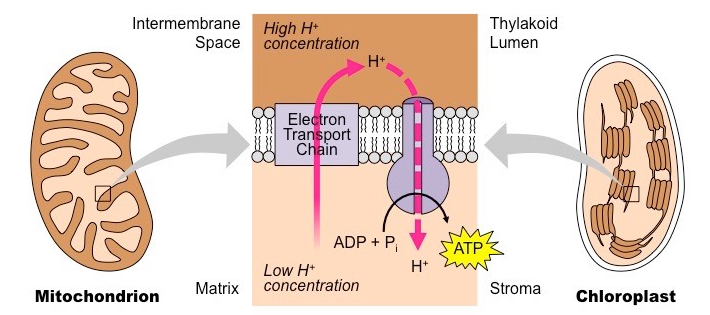
The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation. It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. In the former, the electrons come from breaking down organic molecules, and energy is released.
The cellular respiration process includes four basic stages or steps: Glycolysis, which occurs in all organisms, prokaryotic and eukaryotic; the bridge reaction, which stets the stage for aerobic respiration; and the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain, oxygen-dependent pathways that occur in sequence in the …
Phases of Cellular Respiration Citric acid cycle Occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion and produces NADH and FADH 2 In series of reaction releases 4 carbons as CO 2 Turns twice (once for each pyruvate) Produces two immediate ATP molecules per glucose molecule Electron transport chain Extracts energy from NADH & FADH 2
The electron transport chain (ETC; respiratory chain) is a series of protein complexes that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H + ions) across a membrane.The electron transport chain is built up of peptides, enzymes, and other ...
Thus, the total ATP yield in the cellular respiration process is 36 or 38 ATP molecules. Hope this article on simple cellular respiration diagram has helped you understand the process well. The process of cellular respiration is a very complex reaction that involves many enzymes, coenzyme, and molecules. 10.9.2015 · Mitochondrial respiration involves the carbon balance in the whole plant ...
3. Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation Electron Transport Chain (Source: Wikimedia) The final pathway in the cellular respiration is comprised of the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation which both occur in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
More About Cellular Respiration So now we know that cellular respiration is a three stage process that converts glucose and oxygen to ATP and releases carbon dioxide and water. What are the 3 phases that do this? 1) Glycolysis 2) Krebs Cycle 3) The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) This is a very simple overview of these 3 stages: Glycolysis (Stage 1)











/electron-transport-chain-58e3be435f9b58ef7ed96112.jpg)






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ATP_ADP-358b5b4c26b443629b0f3ab9044bfbb1.jpg)





0 Response to "42 cellular respiration electron transport chain diagram"
Post a Comment