40 orbital diagram for f ion
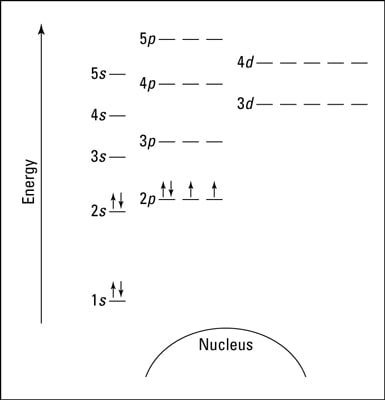
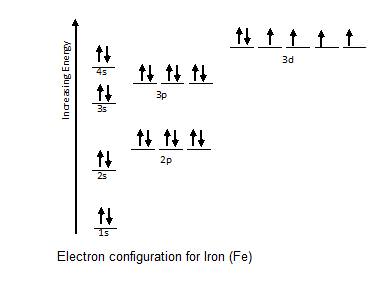
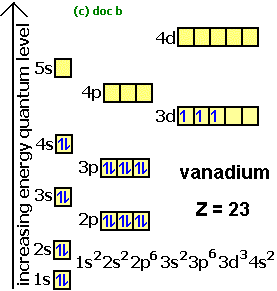
In addition to listing the principle quantum number n and the subshell ell the orbital diagram shows all the different orientations and the... Do some orbital configurations or diagrams for some metal cat ions. So first example is going to be for chromium three plus. So as we follow the periodic table and fill the electrons properly, first row of the periodic table.
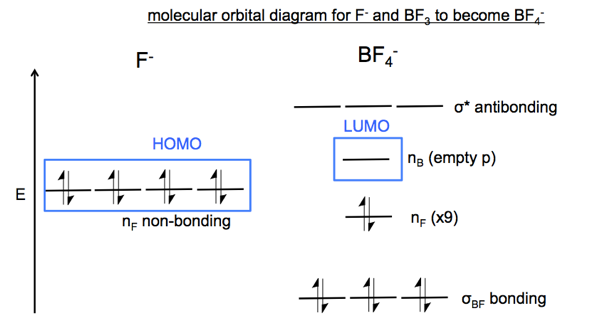
In this video we will write the electron configuration for F-, the Fluoride ion. We'll also look at why Fluorine forms a 1- ion and how the electron...
Orbital diagram for f ion
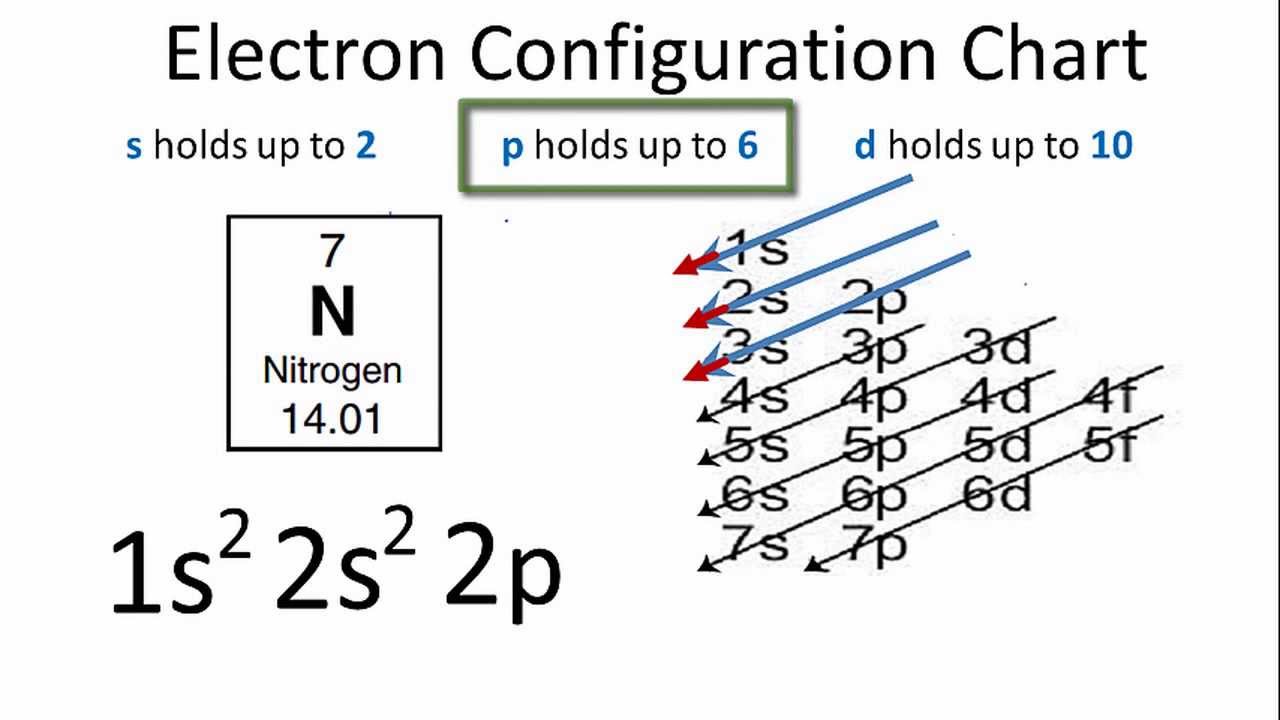
1 s 2 p 3 d and 4 f for the orbital and the superscript number tells you how many electrons are in that orbital. Construct the orbital diag... Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. Upgrade to remove adverts. Only RUB 193.34/month. Orbital Diagram for each Ion.
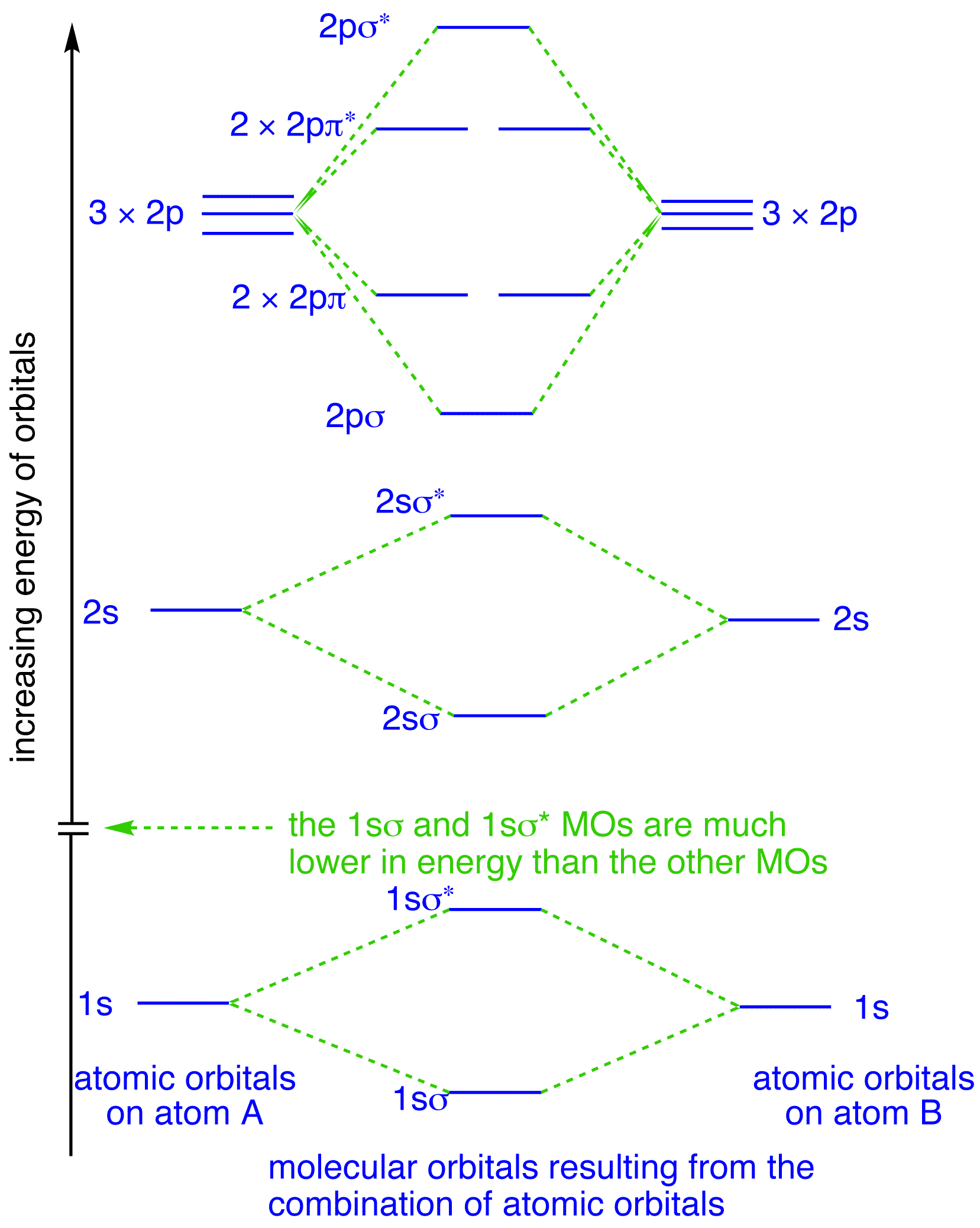
Orbital diagram for f ion. Orbital diagram for f ion. How many electrons does a f ion. The first number is the principal quantum number n and the letter represents the value of l Draw the partial valence level orbital diagram. Construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion. Video by lacie long for professor knuckleys... An orbital diagram, or orbital filling diagram, is a type of notation which illustrates an atom's electron distribution and electron spin within orbitals. We know how to write electron configurations for neutral atoms and ions. But, an electron configuration does not give us the full picture. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the H2 molecule. (b) The shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave functions for MO1 and MO2. • In order to participate in MOs, atomic orbitals must overlap in space.
In which orbital does an electron in a phosphorus atom experience the greatest effective nuclear charge? a. 1s b. 2s c. 2p d. 3s e. 3p I originally thought 3p, since those are the outer electrons, but that was marked wrong. what is the orbital diagram for Au+, how do you fit the f orbitals in? No thanks 1 month free. An ion of an isotope has a 2 charge an atomic mass of 569397 amu 2 electrons at the n4 energy level and 13 electron... You are watching: Write full orbital diagram for f. Electron Configuration. For example, we know that Oxygen always forms 2- ions once it makes an ion. This would include 2 electron to its regular configuration making the new configuration: O2- 1s22s22p6. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for f go in the 2s orbital. The arrow diagram for the outermost orbitals would be...
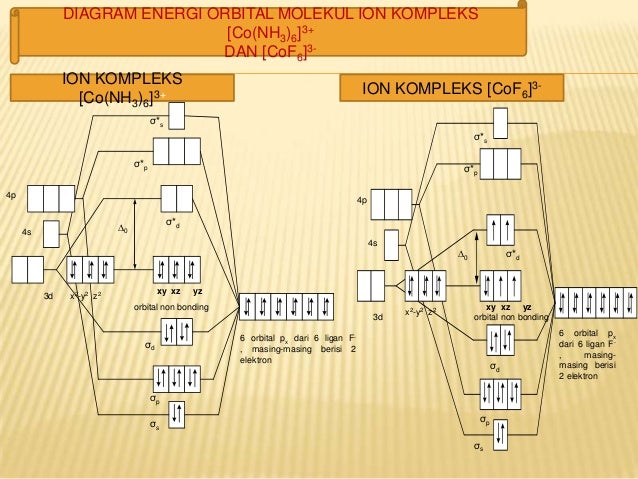
: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2 + ion, (b) the He 2 + ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. is the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for He 2 + . This ion has a total of three valence electrons. Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O2. Ion Predictions with MO Diagrams Give the molecular orbital configuration for the valence electrons in C22−. Will this ion be stable? Create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. What is the orbital diagram for sc3. Lcao For Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecu... Nitric oxide molecular orbital diagram what is an free wiring strontium be2 using the electron configuration chart youtube.
Building Orbital Diagrams. Hund's rule specifies that when orbitals of equal energy are available, the lowest energy electron configuration has the maximum Electron Affinity (EA) is the energy change that occurs when 1 mol of electrons is added to 1 mol of gaseous atoms or ions. Atoms with a low EA...
I would like to understand how to create a molecular orbital diagram for the hydroxide ion from scratch. This includes understanding the shape of But this makes no sense. I haven't used up all the available electrons of the oxygen atom, and the diagram seems to suggest that there is a bond order...
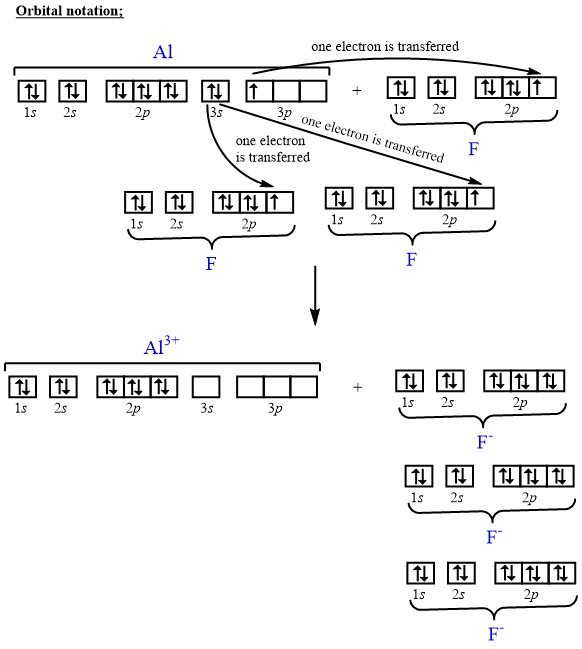
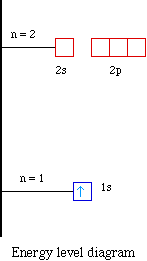
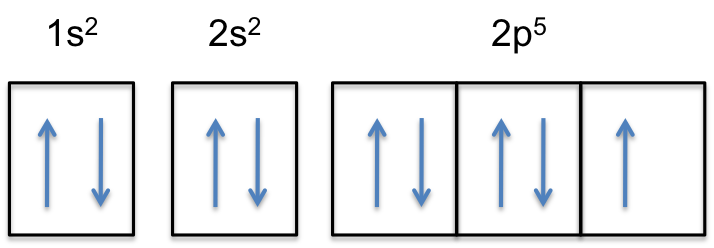
Transcribed image text: Construct the orbital diagram of the F^- ion. A neutral fluorine atom has 9 electrons. How many electrons does a F^- ion have?
An orbital is a region of space that an electron can exist in. A neutral fluorine atom has 9 electrons.
The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one at a time until you have used The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is.
For orbital diagrams, this means two arrows go in each box (representing two electrons in each orbital) and the arrows must point in opposite directions Electron Configurations of Ions. Ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons. A cation (positively charged ion) forms when one or more...
A neutral fluorine atom has 9 electrons. An orbital is a region of space that an electron can exist in. 6 4 Elect...
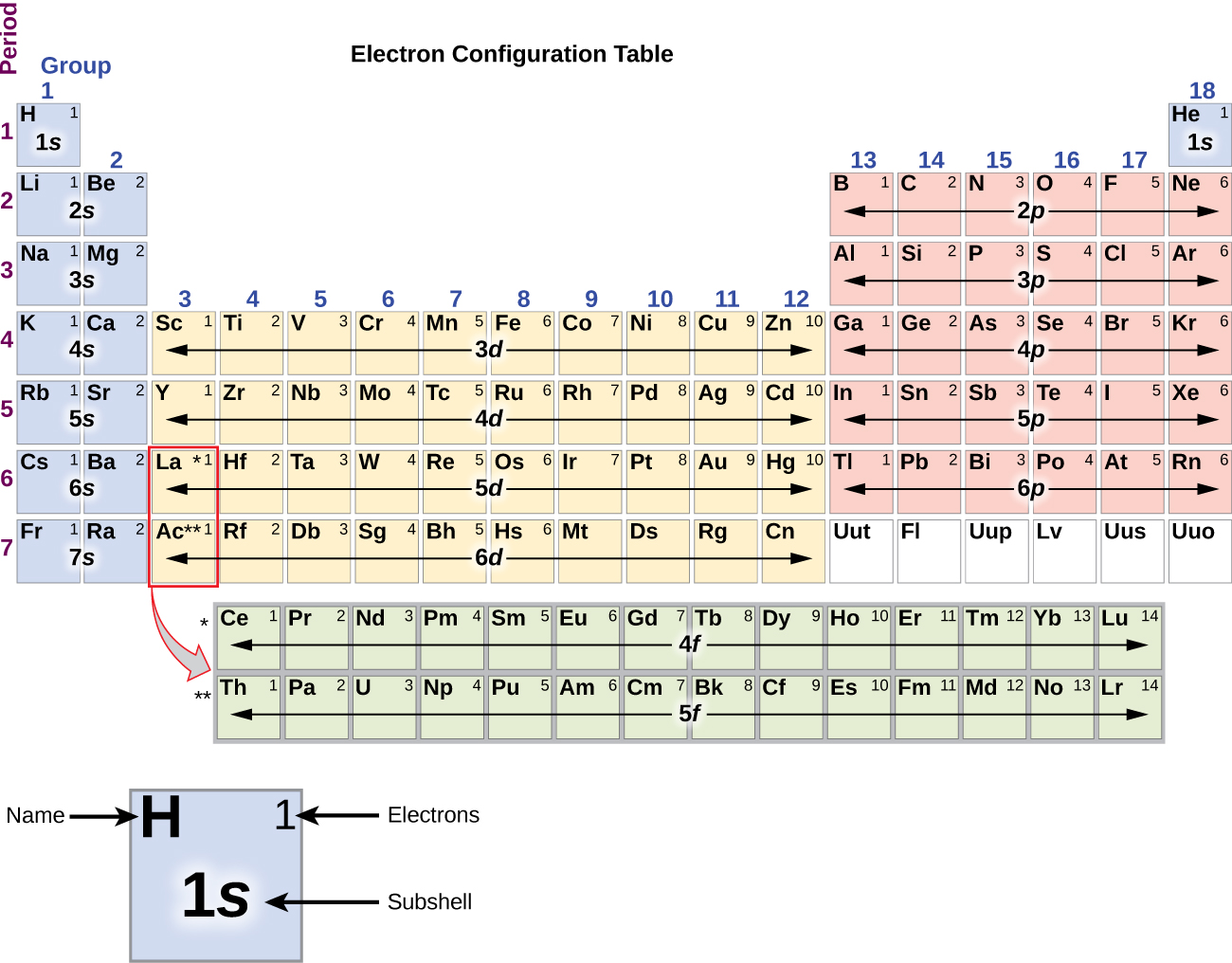
Orbital diagrams give you all of the information you need about the electron configuration and occupied spin states for chemistry or physics, and are easy Dot diagrams are very different to orbital diagrams, but they're still very easy to understand. They consist of the symbol for the element in the...
An orbital diagram is similar to electron configuration, except that instead of indicating the atoms by total numbers, each orbital is shown with up and the lium ion has lost an electron, losng this electron from the outermost orbital totally depopulates this orbital, if the orbital has no electrons in it, it...
Following these rules, we can write the electron orbital notation of Cl^-1 as: 1s_2 2s_2 2p_6 3s_2 3p_6 To draw this as a diagram, draw a circle representing an orbital for every two electrons, and fill them up one by one with lines representing electrons. X X XXX X XXX Note that you cannot add a second...
Methods: Ion-pairing reversed-phase ultra-high-performance LC separation of the Pt(IV) complex anions present in aqueous solutions prior to detection by A robust reversed phase ion-pairing RP-HPLC method has been developed for the unambiguous speciation and quantification of all possible...
Orbital Diagrams & Electron Configurations for Atoms and Ions Orbital diagrams represent the arrangement of electrons in orbitals. • boxes or lines represent each orbital • arrows within boxes represent the electrons • max two per box • opposite direction (represents opposite spin) Section 3.5...
Upgrade to remove adverts. Only RUB 193.34/month. Orbital Diagram for each Ion.
Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
1 s 2 p 3 d and 4 f for the orbital and the superscript number tells you how many electrons are in that orbital. Construct the orbital diag...












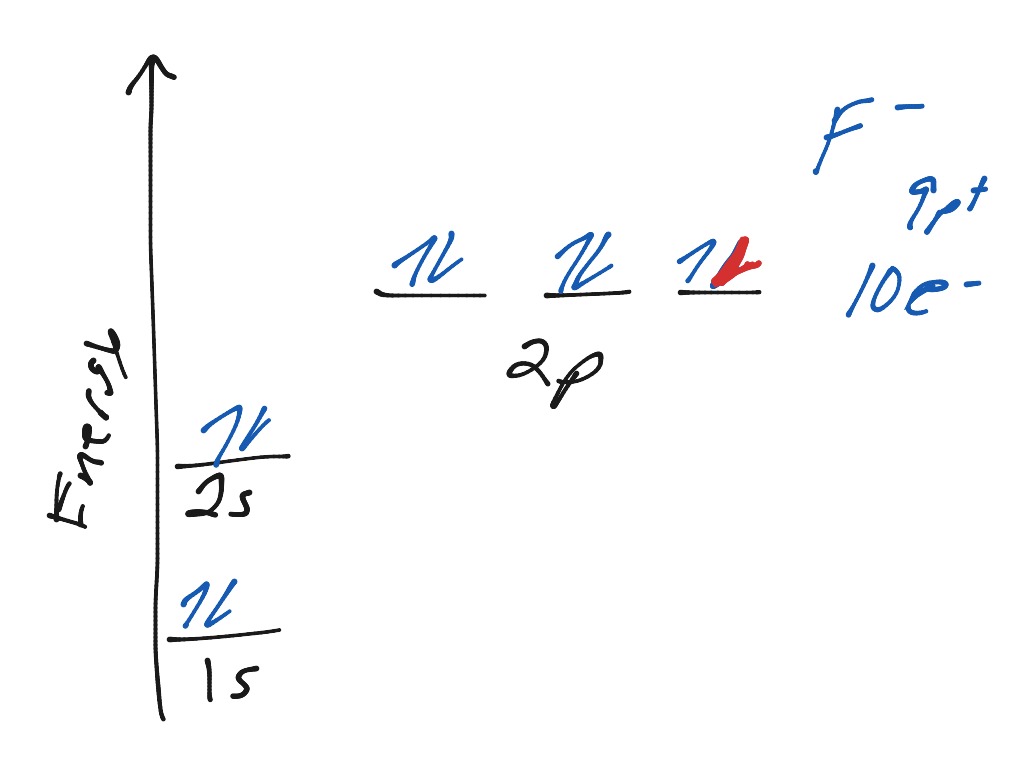


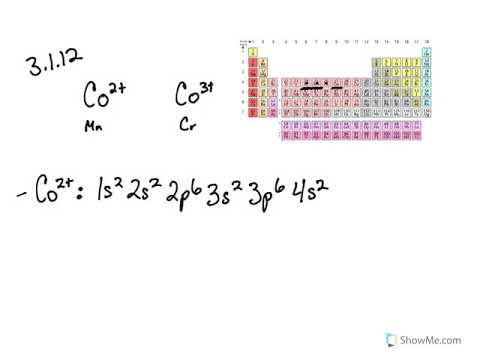

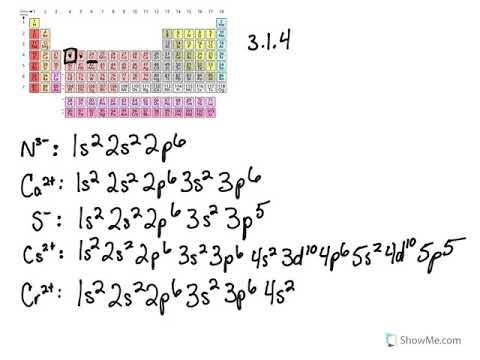
/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)



0 Response to "40 orbital diagram for f ion"
Post a Comment