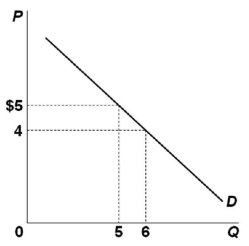
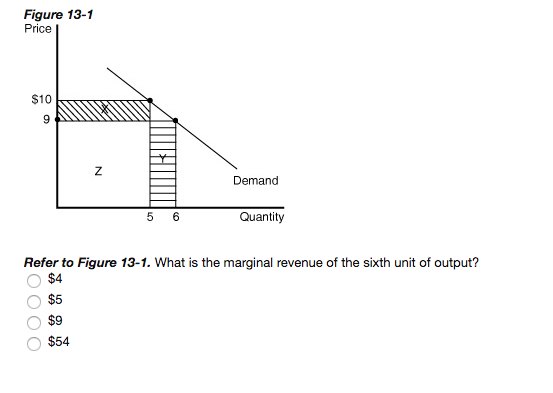
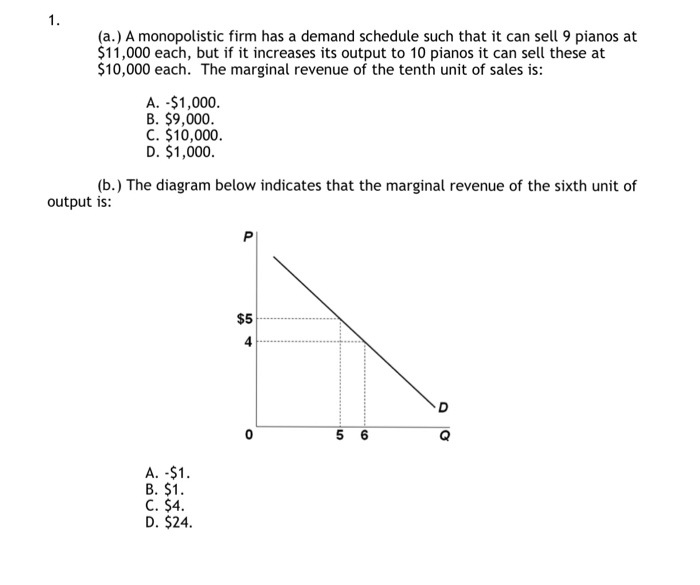
40 the diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is
The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is: -$1. Which of the diagrams correctly portrays a nondiscriminating pure monopolist's demand (D) and marginal revenue (MR) curves? The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is A. -$1. Correct B. $1. C. $4. D. $24. Why is it A? Question: The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is A. -$1. Correct B. $1. C. $4. D. $24.
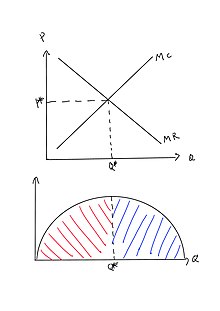
intersection of the firm's marginal cost and the market demand curve). As usual, the monopoly determines its optimal output on the basis of MR = MC. Here, however, it cannot charge a price in excess of p*. So, for any output less than Q(p*) (where Q(p) is the demand function) its marginal revenue is p*. On the graph below that gives: qm q* MR ...
The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is
Marginal revenue is the additional revenue generated from selling one more unit of output. The formula is the change in total revenue divided by the change in quantity or output. Total revenue is the price times quantity and since the price is constant for each good sold, the marginal revenue in a purely competitive market is simply the price ... The marginal cost of producing the sixth unit of output is. 8. ... marginal revenue. total revenue divided by output. → all of these. ... The firm represented by the diagram would maximize its profit where: the vertical distance between curves (3) and (4) is the greatest. B) marginal revenue divided by marginal product. C) total revenue multiplied by total product (output). D) marginal revenue multiplied by marginal product. Answer: D 2. In the table above, if the wage rate is $8.00 per hour, the profit-maximizing number of workers is A) 1. B) 2. C) 4. D) 5. Answer: C 3. A firm in a competitive labor market will ...
The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is. If marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue, the firm: a. is most likely to be at a profit-maximizing level of output. b. should increase the level of production to maximize its profit. The above diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is: -$1. Which of the above diagrams correctly portray a nondiscriminating pure monopolist's demand ( D ) and marginal revenue (MR) curves? The graph below indicates that at output Qpm, marginal cost equals marginal revenue in the upward sloping portion of the marginal cost curve. At this output, the price is Ppm. For a monopolist, the marginal revenue curve and the demand (price) curve are different. Therefore, marginal revenue and price at the profit-maximizing output are different. (E) A wood-carver has a marginal cost of $5.00 for a unit of output, but sells that unit at $6.00. Questions 6-7 are based on the table below, which gives cost information for a perfectly competitive firm. Average Average Fixed Variable Marginal Quantity costs costs costs 0 1 $100.00 $55.00 $55.00 2 50.00 45 .oo 35.00
The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is $1 $4-$1 $24-$1. ... The marginal revenue obtained from selling the third unit of output is A) $5 B) $1 C) $6 D)$3. $1. ... there is a gap in the marginal revenue curve within which changes in marginal cost will not affect output or price. The above diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is:-$1. Which of the following is incorrect? Imperfectly competitive producers:do not compete with one another. The monopolist will select its profit-maximizing level of output somewhere within the: 1-3 unit range of output. The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is −$1. Which of the following is incorrect?Imperfectly competitive producers do not compete with one another. The MR = MC rule applies both to pure monopoly and pure competition. An unregulated pure monopolist will maximize profits by producing that output at which MR = MC. If a monopolist's marginal revenue is $3 ... 44) The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is: A) $1. B) $4. C) $24. D) -$1. Answer: D. 45) A monopolist finds that it can sell its fiftieth unit of output for $50. We can surmise that the marginal: 46) Below is the demand schedule facing Nina, a monopolist selling baskets.
b. Total revenue and marginal revenue are the same in perfect competition. c. Economic profit per unit is found by subtracting . MC. from price. d. Economic profit is always positive in the long run. e. The marginal cost curve serves as the firm's supply curve above the break-even point. 18. Draw a short-run diagram showing a U-shaped average A nondiscriminating pure monopolist finds that it ca sell its 50th unit of output for $50. We can surmise that the marginal: A. cost of the 50th unit is also $50 B. revenue of the 50th unit is also $50 C. revenue of the 50th unit is less than $50 D. revenue of the 50th unit is greater than $50 The above diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is: A. -$1. B. $1. ... If a nondiscriminating pure monopolist decides to sell one more unit of output, the marginal revenue associated with that unit will be: ... The monopolist will produce and sell the sixth unit if its marginal cost is: A. $4 or less. B. $3.90 ... Award: 1.00 point The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is − $1. $1. $4. $24. References Multiple Choice Difficulty: 02 Medium Learning Objective: 12-03 Explain how demand is seen by a pure monopoly.
At the sixth unit, our marginal revenue is 175 and the marginal cost is 140. At seven units the marginal cost would exceed the marginal revenue. In looking at the column on the far right, we verify that this is the quantity that maximizes profits. At six units of output, the mid-point elasticity between five and six units is 1.42, which is elastic.
If the marginal revenue of the seventh unit is $5, then the: B. price of the seventh unit is $11. 13. The vertical distance between the horizontal axis and any point on a nondiscriminating monopolist's demand curve measures: D. product price and average revenue. 14. The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is:
Quick Quizzes. 1. When a competitive firm doubles the amount it sells, the price remains the same, so its total revenue doubles. 2. The price faced by a profit-maximizing firm is equal to its marginal cost because if price were above marginal cost, the firm could increase profits by increasing output, while if price were below marginal cost, the firm could increase profits by decreasing output.
Note that the marginal cost of the first unit of output is always the same as total cost. We can also consider average and marginal costs for average costs as well. The first five columns of Table 6.6 (after all of the graphs below) duplicate the table 6.5 (the Clip Joint example), but the last three columns show average total costs, average ...
revenue O v z w output AR X X+1 The firm currently produces output OX. Which area(s) will measure the firm's marginal revenue if it produces an additional unit of output? A w + v B w + z C w - v D w only 12 The diagram shows the cost and revenue curves for the production of a textbook.
per unit of output . Price of download Quantity of downloads demanded TR MR . $10 0 $0 - $8 1 $8 $8 $6 3 $18 $5 $4 6 $24 $2 $2 10 $20 $-1 $0 15 $0 $-4 ... as shown in the diagram. Marginal revenue equals marginal cost at a quantity of 2 diamonds. So De Beers will sell 2 diamonds at a price of $300 each.
Producing q2 units and charging a price of p2 the above diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is. There are three quantities q 1 q 2 and q 3 units of labor. Some point that cannot be determined with the above information. Refer to the above data. In the above diagram where will total product be at a maximum.
6) Refer to Figure 13 -3. The marginal revenue from one additional unit sold is the sum of the gain in revenue from selling the additional unit and the loss in revenue from having to charge a lower price to sell the additional unit. Based on the diagram in the figure, 6) A) X + Z represents the loss (output effect) and Y the gain (price effect).
This problem has been solved! The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is. How do I find the marginal revenue and show it on the graph for a monopoly? Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
View Notes - econ final 15 from ECON 1 at University of Phoenix. 44. The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is: A) $1. B)-$1. C) $4. D) $24. Ans: B Level:
Suppose a pure monopolist is charging a price of $12 and the associated marginal revenue is $9. We thus know that: ... Total revenue is increasing. 5. The above diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is: A. -$1. B. $1. C. $4. D. $24. 6.
B) marginal revenue divided by marginal product. C) total revenue multiplied by total product (output). D) marginal revenue multiplied by marginal product. Answer: D 2. In the table above, if the wage rate is $8.00 per hour, the profit-maximizing number of workers is A) 1. B) 2. C) 4. D) 5. Answer: C 3. A firm in a competitive labor market will ...
The marginal cost of producing the sixth unit of output is. 8. ... marginal revenue. total revenue divided by output. → all of these. ... The firm represented by the diagram would maximize its profit where: the vertical distance between curves (3) and (4) is the greatest.
Marginal revenue is the additional revenue generated from selling one more unit of output. The formula is the change in total revenue divided by the change in quantity or output. Total revenue is the price times quantity and since the price is constant for each good sold, the marginal revenue in a purely competitive market is simply the price ...



















.png)
0 Response to "40 the diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is"
Post a Comment