39 molecular orbital diagram for hf
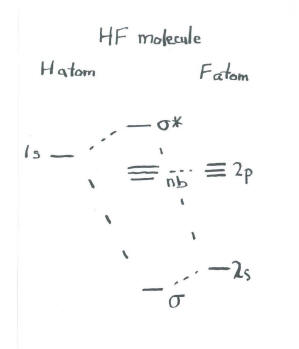
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for HF. Hydrogen Fluoride Hydrogen fluoride is an ionic compound that is formed by hydrogen and the most electronegative atom fluorine. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for HF. Use only the valence electrons for your diagram. The 2s orbital of F atom has an energy more than 26 eV lower than that of the H 1s, so there is very little interaction between them. The F 2p orbital (-18.65 eV) and the H 1s (-13.61 eV), on the other hand, have similar energies, allowing them to.
HF HOMO Orbital. The HOMO orbital is the highest energy molecular orbital occupied by electrons. In HF, the HOMO orbitals are the double degenerate pi 2px and 2py and pi orbitals. To get a 3-D model you can manipulate, click here. Download time may be significant the first time the applet is loaded.

Molecular orbital diagram for hf
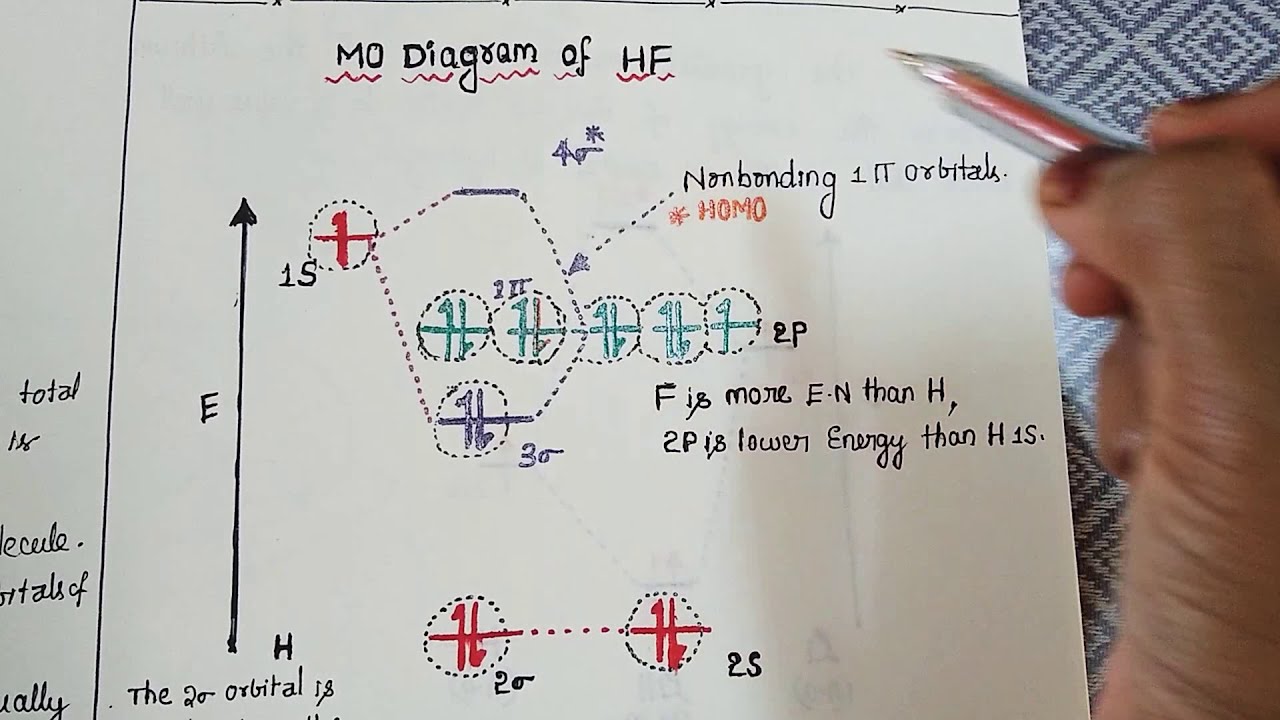
The energy of the nonbonding HBr molecular orbitals is essentially the same as the 4p atomic orbitals in Br. Constructing the HF molecular orbital energy level diagram - YouTube. Energy Aa Energy Bt 0000 Ooo Energy Energy. 4 13 Draw the MO diagram for HBr Assume the atomic orbitals for each element from CHM 101 at Health and Science School. Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma-bonding and a sigma-antibonding molecular orbital, as shown below. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF. (CC BY-SA-NC 2.0 UK: England & Wales License; Nick Greeves). The molecular orbital diagram for the HF molecule is given below. This shows the formation of the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals (sigma...
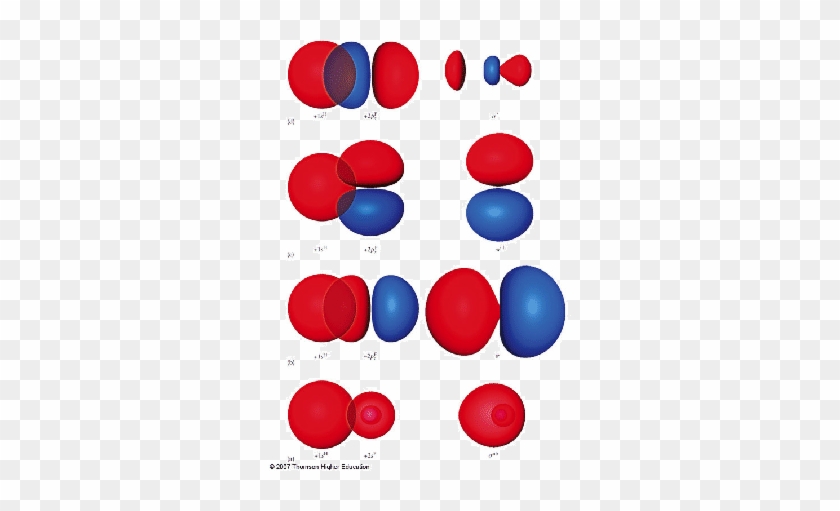
Molecular orbital diagram for hf. Density diagrams of the molecular orbitals for the LiH, CH, and HF molecules are .Molecular orbital. source: diagramweb.net Relationship between Electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour: 1) Bond order: It is defined as the number of covalent bonds between the two combining atoms of a molecule. The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The 1s atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding o molecular orbital and an antibonding o molecular orbital. A diagram showing the partial charges on the atoms in a water molecule. An important feature of water is its polar nature. The structure has a bent molecular geometry for the two hydrogens from the oxygen vertex. The oxygen atom also has two lone pairs of electrons. One effect usually ascribed to the lone pairs is that the H–O–H gas-phase bend angle is 104.48°, which is smaller … Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
It is said that the 1s orbital of hydrogen overlaps and fuses with the 2p orbital of fluorine in a molecule of HF. According to Molecular Orbital Theory, the 2s orbital of F is non-bonding, and the 2pz orbital of F combines with 1s of H. HF Polarity. Polarity is yet another important topic of chemistry that we are going to discuss in this article. Molecular orbital diagram for the hf molecule interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma bonding and a sigma antibonding molecular orbital as shown below. The molecular orbitals formed in the case of hf molecule will not be symmetrical. MO diagram for HF molecule Orbital-orbital Interactions and Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations; ... Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen Fluoride. CONTROLS . Click on the HF molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules.
Given the molecular hybridization orbital model that we are using this implies that four sp 3 orbitals are formed from the nitrogen atom’s 2s and 2p orbitals leading to four electron density centers around the nitrogen. The figure shows three representations of ammonia. The first indicates the N–H bonds but fails to show the lone pair orbital. The second uses the wedge … The bonding molecular orbital is fully filled with two electrons .The rest of the electrons remain in their atomic orbitals. The molecular orbitals formed in the case of HF molecule will not be symmetrical. The symmetry occurs because the energies of H(1s) and F(2pz) atomic orbitals are not the same.Molecular orbital diagram for HF molecule is ... #molecularorbitalenergyleveldiagramofbo,no,hcl#molecularorbitalenergyleveldiagram#drsarbjitralaII Molecular orbital energy level Diagram of BO, NO, HCl, HF I... HF Molecular Orbital Diagram. Hydrogen fluoride is another example of a heteronuclear molecule. It is slightly different in that the π orbital is non-bonding, as well as the 2s σ. From the hydrogen, its valence 1s electron interacts with the 2p electrons of fluorine. This molecule is diamagnetic and has a bond order of one.
LCAO MO Energy Diagram for H2 Energy H-H ∆E1 ∆E2 • ∆E2> ∆E1, so the antibonding orbital is always more anti-bonding than the bonding orbital is bonding H2molecule: two 1s atomic orbitals combine to make one bonding and one antibonding molecular orbital. Ha Hb
Figure 1: LCAO MO Diagram for HF (Author: LeeAnn Sager. Used with permission.) The purpose of this activity is to use Hartree-Fock self-consistent-field approach to calculate the molecular orbitals of HF in the minimal atomic basis (STO-3G) and to compare the molecular orbitals to the qualitative LCAO approach.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
General Notes on Molecular Orbital Diagrams. The Y-axis of a MO diagram represents the total energy (not potential nor Gibbs Energy) of the orbitals. Individual atomic orbitals (AO) are arranged on the far left and far right of the diagram. Overlapping atomic orbitals produce molecular orbitals located in the middle of the diagram.
Heteroatomic molecular orbitals Heteroatomic molecular orbitals Mix atomic orbitals For discussion, treated simplistically as one orbital from each center Often close to correct because a single orbital predominates Must mix orbitals of Similar energy Same symmetry Molecular orbital energies Rough estimation by diagram
In this screencast, Andrew Burrows walks you through how to construct the MO energy level diagram of HF. http://ukcatalogue.oup.com/product/9780199691852.do#...
Answer (1 of 3): The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combi...
However, in the anti-bonding $4 \sigma^*$ orbital, this polarity is reversed. Caveat: The preceding paragraph may support your intuition and may be right in a few simple cases, but I wouldn't rely on it too heavily. Given below is a diagram showing $2 \sigma$ , $3 \sigma$ and $1 \pi$ MOs in HF
The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The Is atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding sigma molecular orbital and an antibonding sigma* molecular orbital.
Download scientific diagram | Molecular orbital diagrams for HBr and HF. from publication: Total energy partitioning within a one-electron formalism: A Hamilton population study of surface-CO ...
Molecular Mycobateriology. South African Medical Research Council Collaborating Centres: Clinical and Community HIV-Tuberculosis Research. Tuberculosis Biomarker-Targeted Intervention : Other research entities . Share on. Contact us today: +27 21 650 3407: idm@uct.ac.za . Quick Links. Membership; Contacts ; COVID-19 and H&S Resources; COVID …
Hartree-Fock self-consistent-field (HF SCF) usually converges fairly well with a good initial guess Stretched bonds, diradicals, transition metals, high-spin states, etc., can cause problems for convergence In high-symmetry cases, the program can guess the wrong orbital occupations, and then have trouble recovering from this
molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the NO molecule. We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is 2.5. Figure 9.42: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure 9.43: A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule.
The molecular orbital diagram for the HF molecule is given below. This shows the formation of the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals (sigma...
Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma-bonding and a sigma-antibonding molecular orbital, as shown below. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF. (CC BY-SA-NC 2.0 UK: England & Wales License; Nick Greeves).
The energy of the nonbonding HBr molecular orbitals is essentially the same as the 4p atomic orbitals in Br. Constructing the HF molecular orbital energy level diagram - YouTube. Energy Aa Energy Bt 0000 Ooo Energy Energy. 4 13 Draw the MO diagram for HBr Assume the atomic orbitals for each element from CHM 101 at Health and Science School.























0 Response to "39 molecular orbital diagram for hf"
Post a Comment