37 action potential diagram labeled
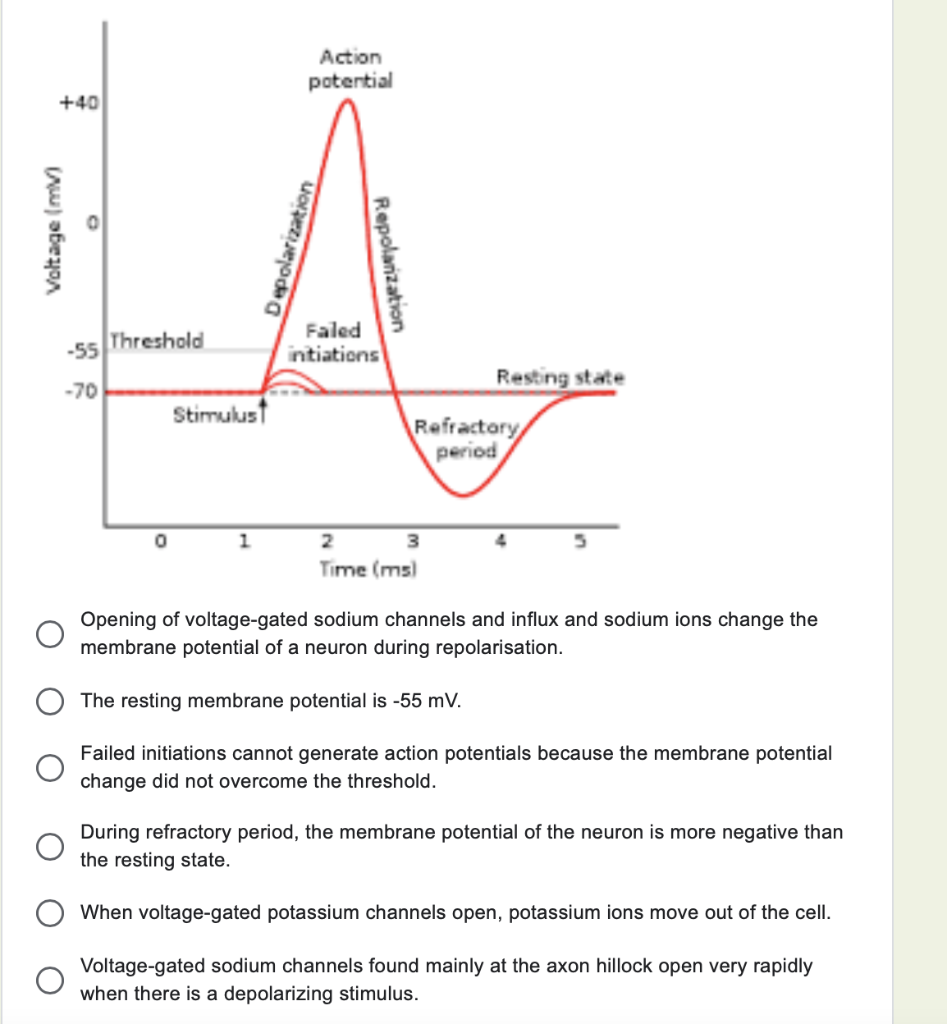
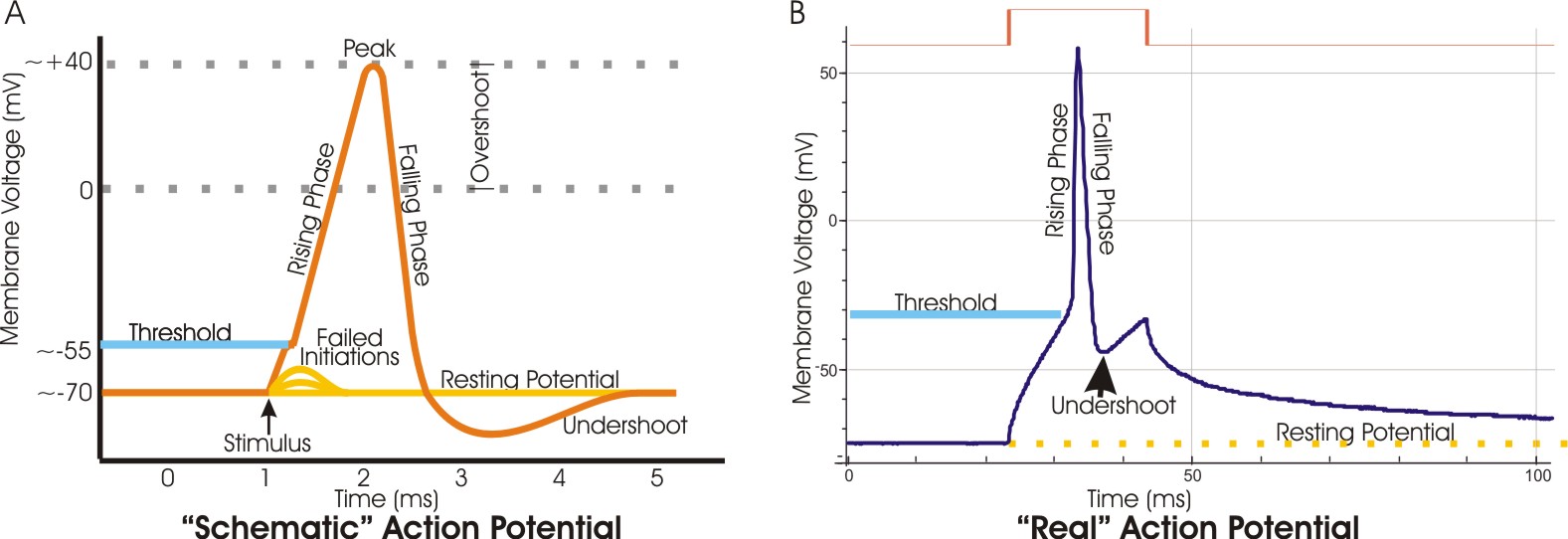
An action potential is a rapid rise and subsequent fall in voltage or membrane potential across a cellular membrane with a characteristic pattern. Sufficient current is required to initiate a voltage response in a cell membrane; if the current is insufficient to depolarize the membrane to the threshold level, an action potential will not fire.
Chapter 50 Neurology: Anatomy & Physiology NEURON ACTION POTENTIAL osms.it/neuron-action-potential Electric signals sent down axons Generated by rapid rising, falling of membrane potential Resting membrane potential (approx. -65mV) determined by intra, extracellular ion concentrations Ion channels open → depolarization of neuron (net influx ...
Action potentials (those electrical impulses that send signals around your body) are nothing more than a temporary shift (from negative to positive) in the neuron's membrane potential caused by ions suddenly flowing in and out of the neuron.

Action potential diagram labeled
It is the core of the neuron, similar to a cell that contains the nucleus and all other cellular organelles. The cell body is also the largest part of a neuron enclosed by a cell membrane that protects the cell from its immediate surroundings and allows its interaction with the outside environment. They attach to all the dendrites and thus integrate all the signals.
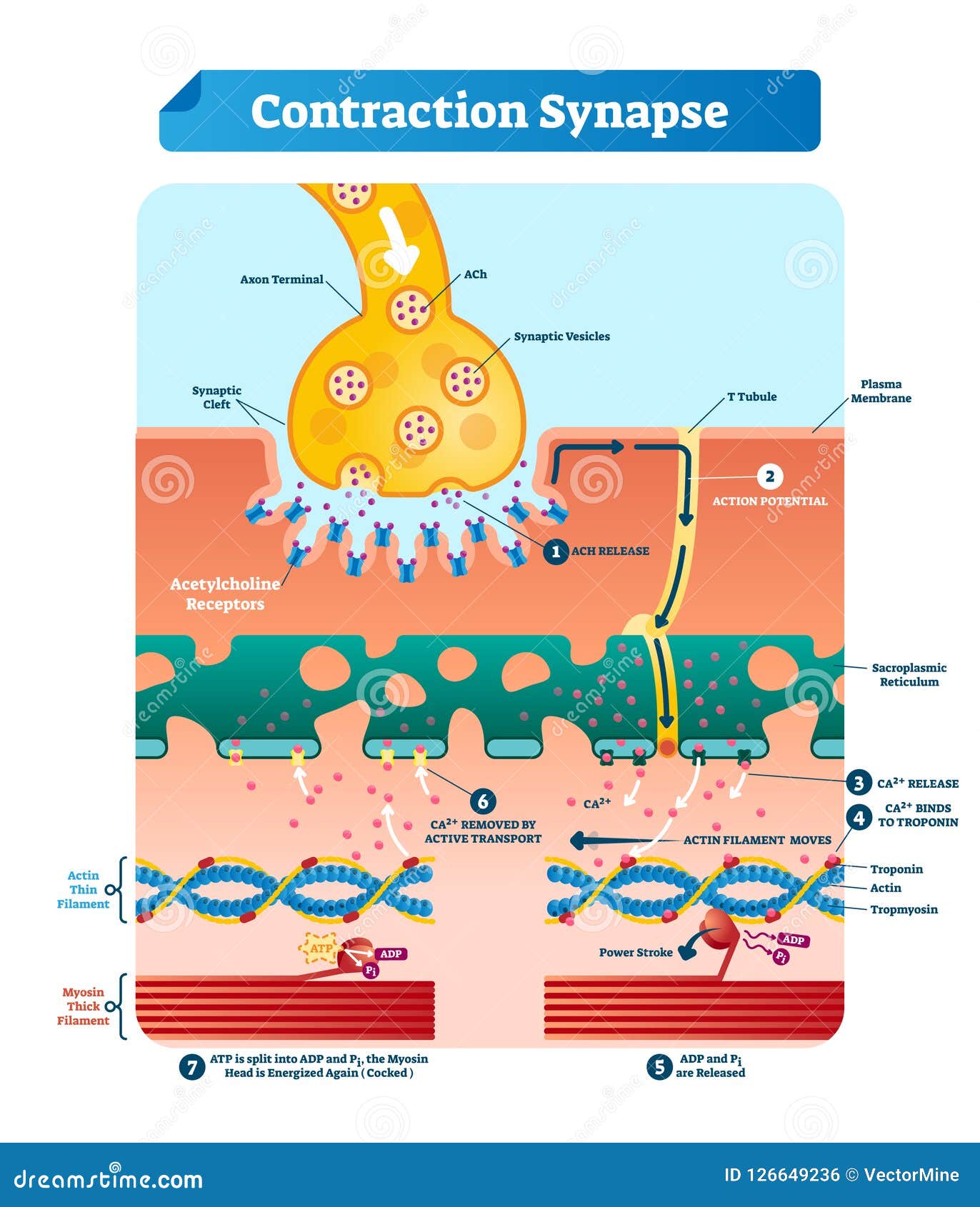
During an action potential event, the cell membrane potential at a specific point on the axon rapidly rises then drops, causing the membrane potential to drop elsewhere along the axon. An action potential event in Neuron A causes the release of neurotransmitters in the synapse that can either excite or inhibit an action potential event in neuron B.
An action potential is defined as a sudden, fast, transitory, and propagating change of the resting membrane potential. Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of generating an action potential; that property is called the excitability. This article will discuss the definition, steps and phases of the action potential. Contents Definition Steps
Action potential diagram labeled.
Sodium-potassium pump (diagram) The concentration gradient will later contribute to generating an action potential, because of one of the laws of physics.By concentration gradient definition, every element modifies its concentration gradient to seek equilibrium.For example, ions will diffuse from a place of higher concentration to a place of lower concentration until the concentration of the ...
Compound Action Potential . The top trace in the diagram opposite shows the A-alpha only peak over a longer time course. The stimulus necessary to initiate an action potential in small axons is larger than for larger diameter axons. As the stimulus is increased, smaller axons begin to generate their action potential, and these potentials are ...
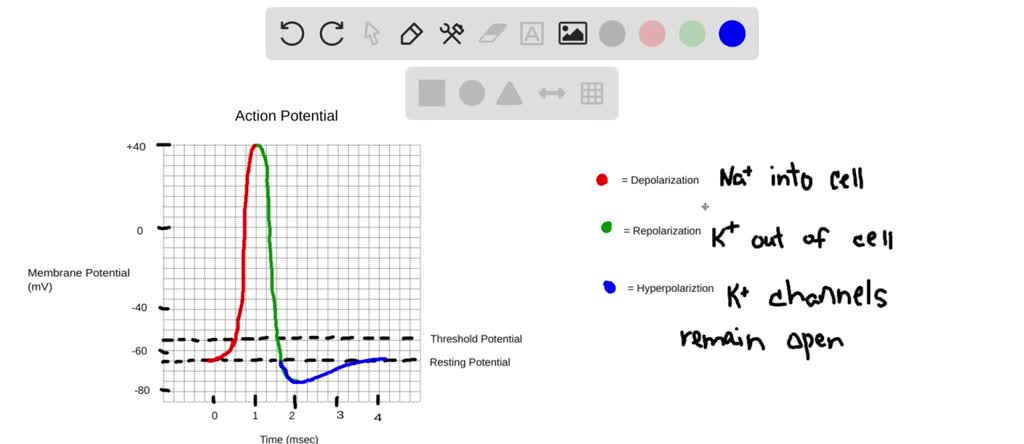
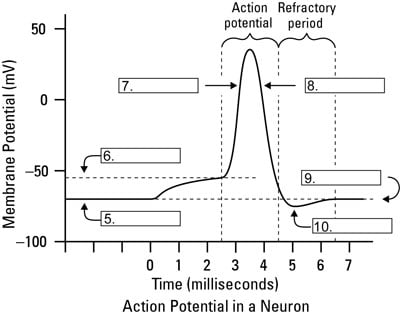
Na+ channels are the FIRST to open and Na+ enters the cell. It causes the inside of the cell to depolarize, or become more positive. K+ Channels open When the K+ channels open, K+ leaves the cell Na+ channels close No more Na+ enters the cell. Repolarization K+ entering the cell, thus the inside of the cell becomes more negative.
An action potential begins at the axon hillock as a result of depolarisation. During depolarisation voltage-gated sodium ion channels open due to an electrical stimulus. As the sodium ions rush back into the cell, their positive charge changes potential inside the cell from negative to more positive.
The action potential generated by the SA node travels through the atria and enters the AV node. Conduction velocity is slowed through the AV node to allow time for the atria to contract before the ventricles are depolarized. This pause in conduction at the AV node appears as the PR segment on EKG. QRS Complex
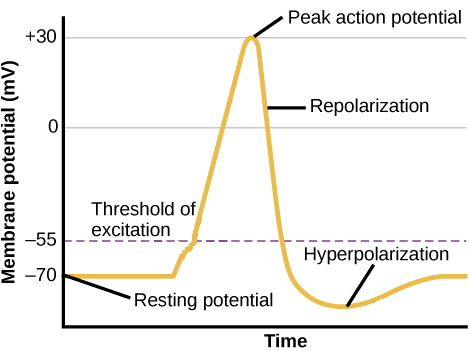
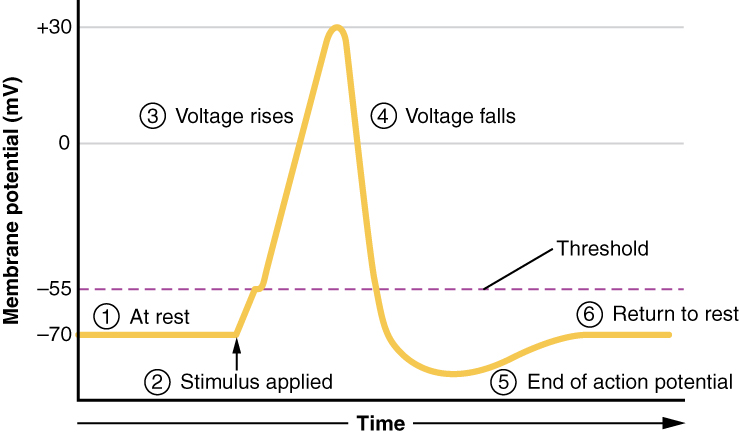
The action potential is a brief but significant change in electrical potential across the membrane. The membrane potential will begin at a negative resting membrane potential, will rapidly become positive, and then rapidly return to rest during an action potential.
Label the membrane, the voltage-gated sodium channel, the potassium leak channel, the voltage-gated potassium ... Set up an axonal membrane as shown in the diagram below and to the left. Remember to set up ... membrane, an action potential cannot be generated there. The inward current that
So, here's how the steps of an action potential unfold as you're reading: 1. Depolarization Sensory neurons, like the ones that sense light in your eyes, are activated by a stimulus, like light....
Describe what is happening during the phase of the cardiac action potential labeled 2 in the diagram. Phase 2 is the plateau phase which occurs due to opening of slow voltage-gated calcium channels, which allow continued inflow of Ca+2 from ICF into the cytosol.
You are required to draw 4 labeled diagrams. a) Draw a well-labeled diagram on a nerve action potential under normal conditions. b) Draw a well-labeled diagram on the changes you would expect to see in Na+ and K+ conductance across a nerve membrane when membrane potential is above threshold in the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX, puffer fish toxin).
READ MORE BELOW!In this video, we discuss the events of the cardiac muscle action potential by viewing the action potential graph/diagram.INSTAGRAM | @thecat...
An action potential is the result of a very rapid rise and fall in voltage across a cellular membrane, with every action potential (impulse) similar in size. The response of a nerve or muscle cell to an action potential can vary according to how frequently and for what duration the action potentials are fired. An action potential requires an ...
The action potential must propagate from the trigger zone toward the axon terminals. Propagation, as described above, applies to unmyelinated axons. When myelination is present, the action potential propagates differently, and is optimized for the speed of signal conduction.
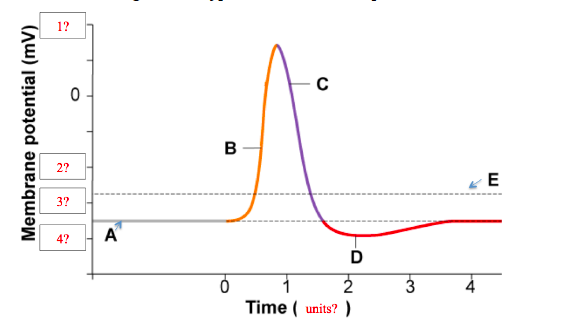
Draw a graph of an action potential and label the axes label the parts of the graph and explain whic
The action potential thus moves along the axon as a wave of depolarization traveling away from the cell body. • Label where the action potential is in these two diagrams: Page 17. Conduction Velocity Depends on Diameter and Myelination of the Axon • Conduction velocity is the speed with which an action potential is propagated.
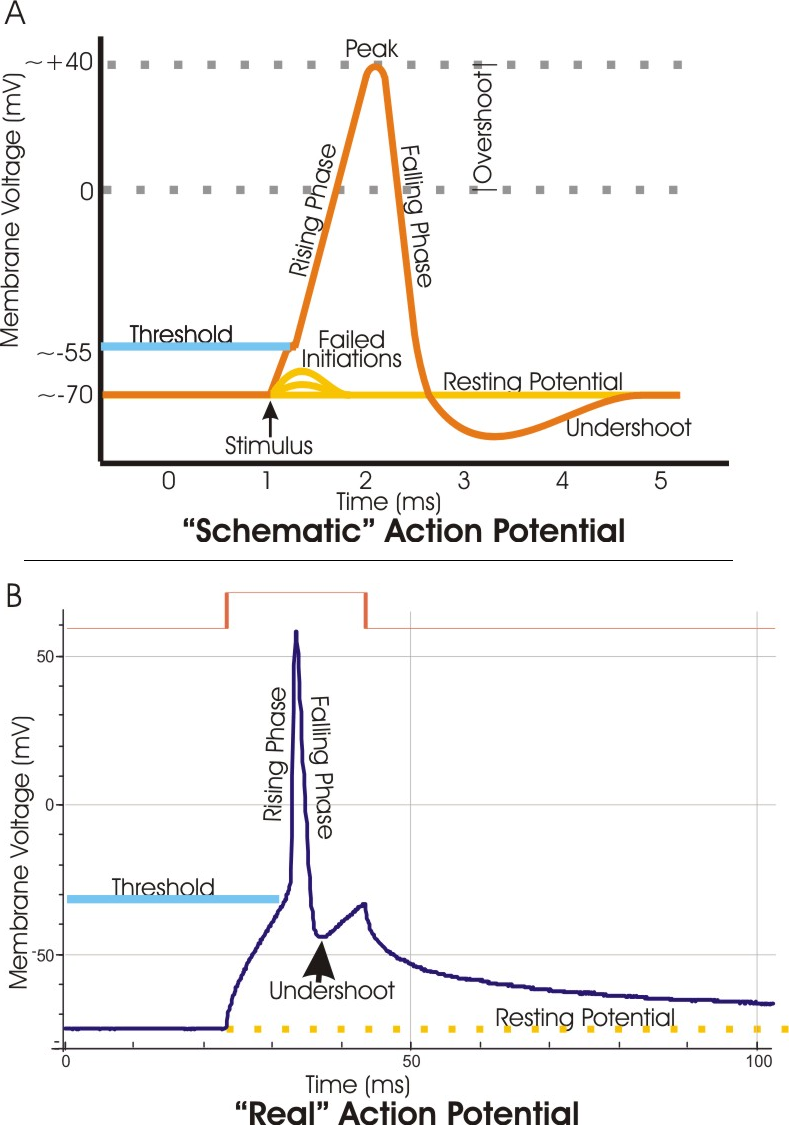
Aug 13, 2020 — Action potential is a brief reversal of membrane potential in which ... These diagrams of real and schematic action potential indicate peak, ...
In the diagram below, the action potential A is initiated at the same time in neurons labeled (1) and (2). Action potentials B and C are formed at the same time although at different distances along the neurons. Which one of the following statements explains the illustration below? (C) both A and B statements may explain the illustration above
The action potential moves through a single neuron cell in the form of an electrochemical cascade which allows a net inward motion of positively charged ions inside the axon. The ends of the axon contain vesicles packed with neurotransmitters, ready to be freed. Synapse is the gap between the end of an axon of a cell and the dendrites of another.
In physiology, an action potential (AP) occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls: this depolarization then ...Membrane potential · Threshold potential · Cardiac action · Saltatory conduction
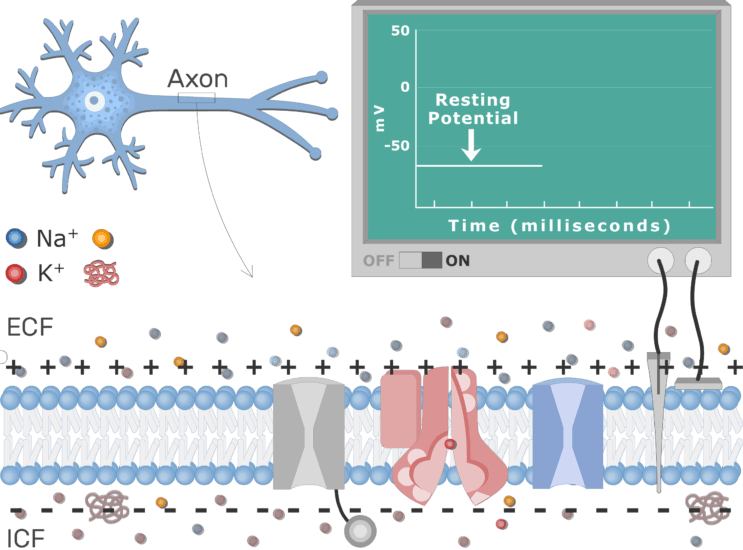
When that voltage becomes less negative, the channel begins to allow ions to cross the membrane (Figure 4). This is a two part diagram. Both diagrams show a ...Apr 11, 2013 · Uploaded by Interactive Biology
The Action Potential Resting membrane potential describes the steady state of the cell, which is a dynamic process that is balanced by ion leakage and ion pumping. Without any outside influence, it will not change. To get an electrical signal started, the membrane potential has to change. This starts with a channel opening for Na + in the membrane.
Instructions: Choose an answer and hit 'next'. You will receive your score and answers at the end. question 1 of 3 Which of the following section of the graph is represents depolarization? 1 2 3 4...
Once an action potential is initiated at one point in the nerve cell, how does it propagate to the synaptic terminal region in an all-or-nothing fashion? Figure 3.1 shows a schematic diagram of an axon and the charge distributions that would be expected to occur along the membrane of that axon.
This post will walk you through the conduction pathway step-by-step using a labeled diagram of the heart. Once you understand the conduction system of the heart, you will be able to apply it to conduction system diseases, disorders, and abnormalities (discussed in other EZmed posts).
External Website. Watch this video to learn about the release of a neurotransmitter. The action potential reaches the end of the axon, called the axon terminal, and a chemical signal is released to tell the target cell to do something—either to initiate a new action potential, or to suppress that activity.
• Label the parts of this diagram: Page 5. Depolarization vs. Repolarization • If depolarization reaches threshold, the contractile cells, in turn, generate action potentials, first ... • Overview of action potential generation in contractile cells: 1. Depolarization.


















:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11522/Action_potential_curve.png)



0 Response to "37 action potential diagram labeled"
Post a Comment