36 f2+ molecular orbital diagram
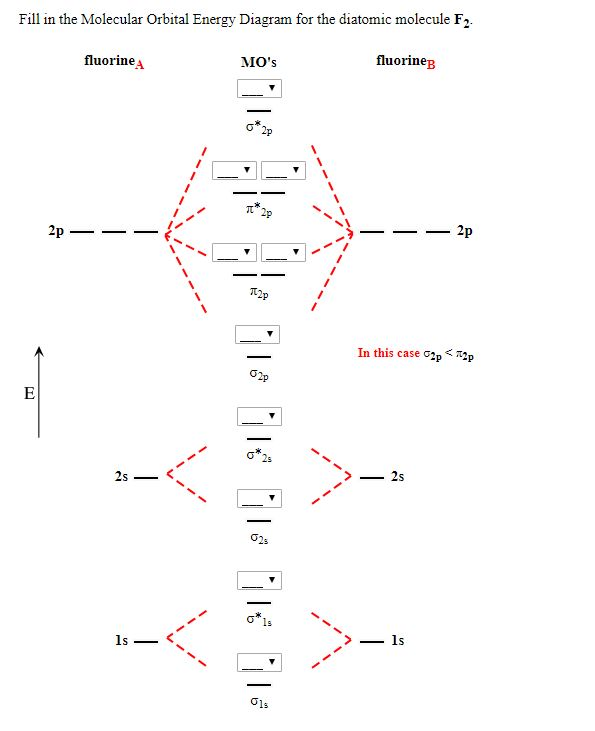
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic ...
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. May 25, By Mrs Shilpi Nagpal 9 . It is paramagnetic in nature. 6)Li2. Molecular orbital energy level of Li2.Molecular orbitals of Li 2, Be 2, to F 2 The molecular orbital theory (MO) has been introduced for the diatomic hydrogen molecules.
Molecular orbital diagram for c2. This video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules. Molecular orbitals are formed combining similar atomic orbitals. Just because some chemical species shows integral value of bond order doesnt mean that it should exist. Molecular orbital diagram for the molecule oxygen o2.
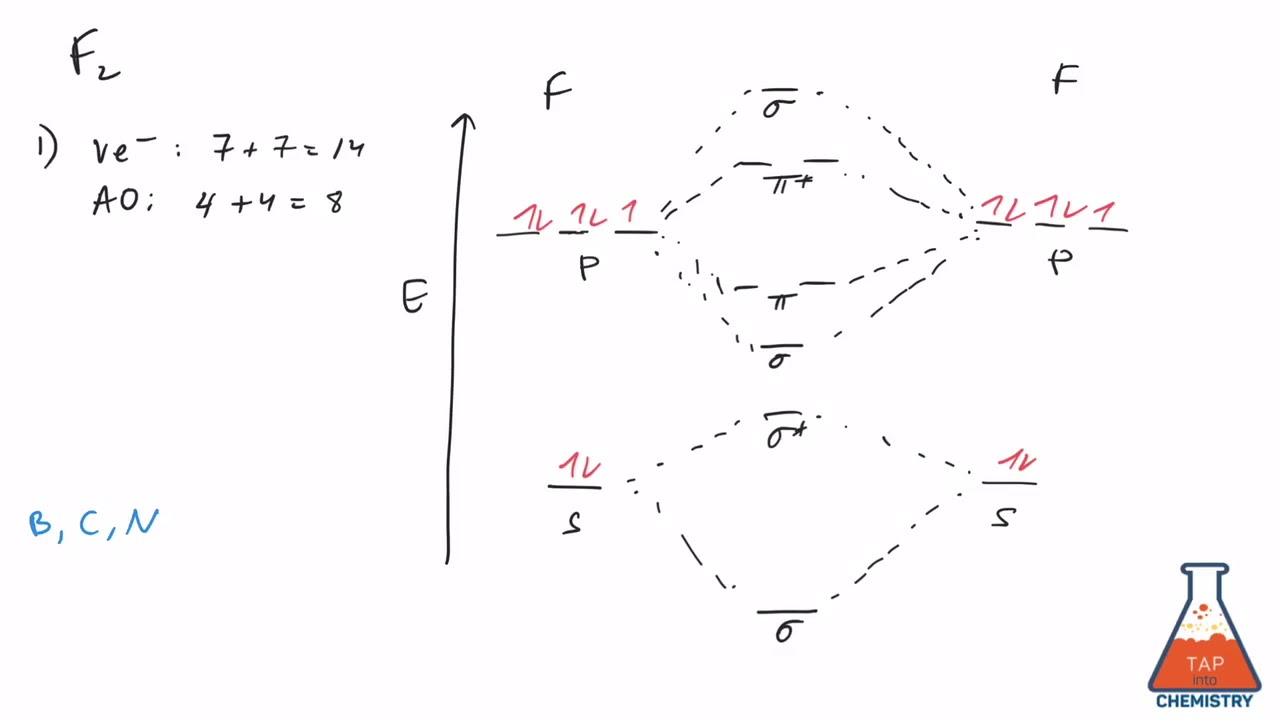
F2+ molecular orbital diagram
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: Solve Study Textbooks. Join / Login >> Class 11 >> Chemistry >> Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure >> Molecular Orbital Theory >> 37. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F
Molecular orbital diagram for f2. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of. C would this ion exist. To further demonstrate the consistency of the lewis structures with mo. For the ion f2. A draw the molecular orbital diagram.
#sigma# molecular orbitals are singly-degenerate, and #pi# molecular orbitals are doubly-degenerate. #sigma# molecular orbitals, in principle, get more stabilized upon overlap than #pi# molecular orbitals do. For example, an #ns//ns# overlap for a homonuclear diatomic molecule gives rise to a partial MO diagram like this:
F2+ molecular orbital diagram.
Arrange the following in order of decreasing stability. a blank molecular orbital diagram (part a 1 figure) has been provided to you. rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. to rank items as equivalent, overlap them. f2, f2+, f2-
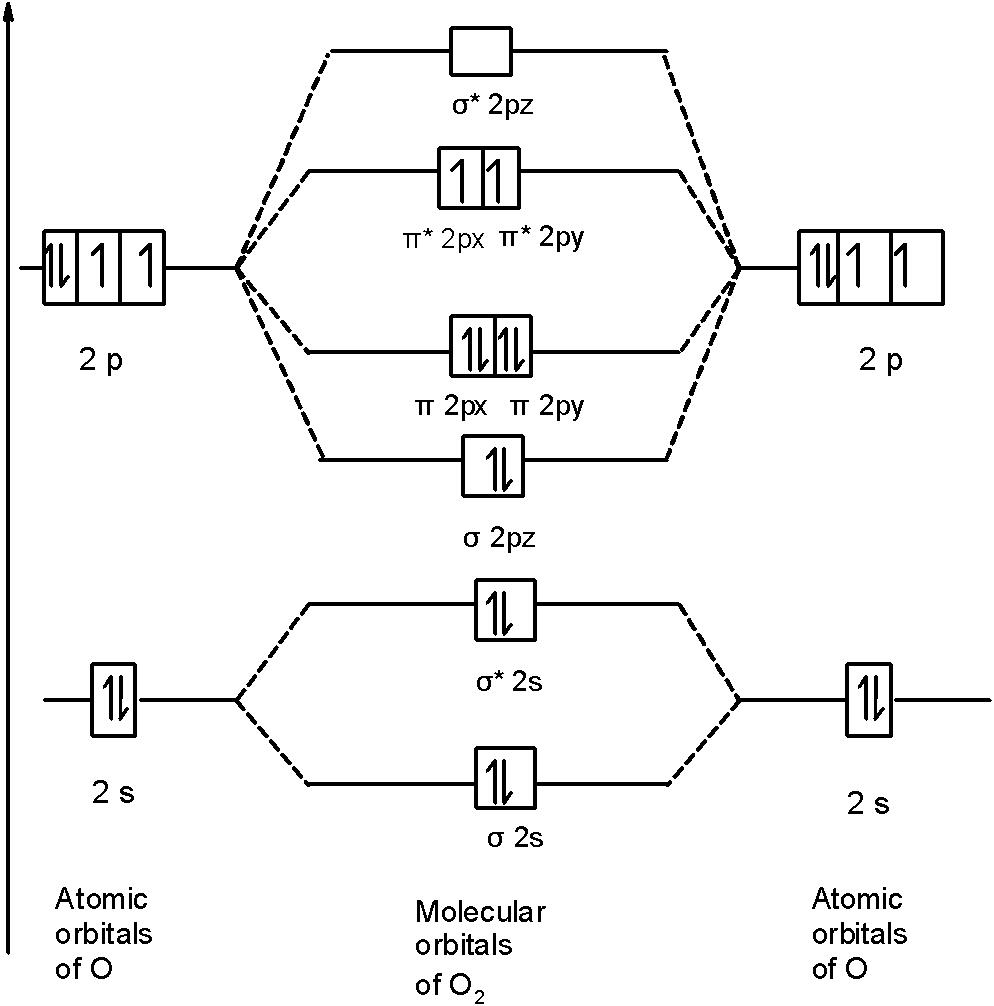
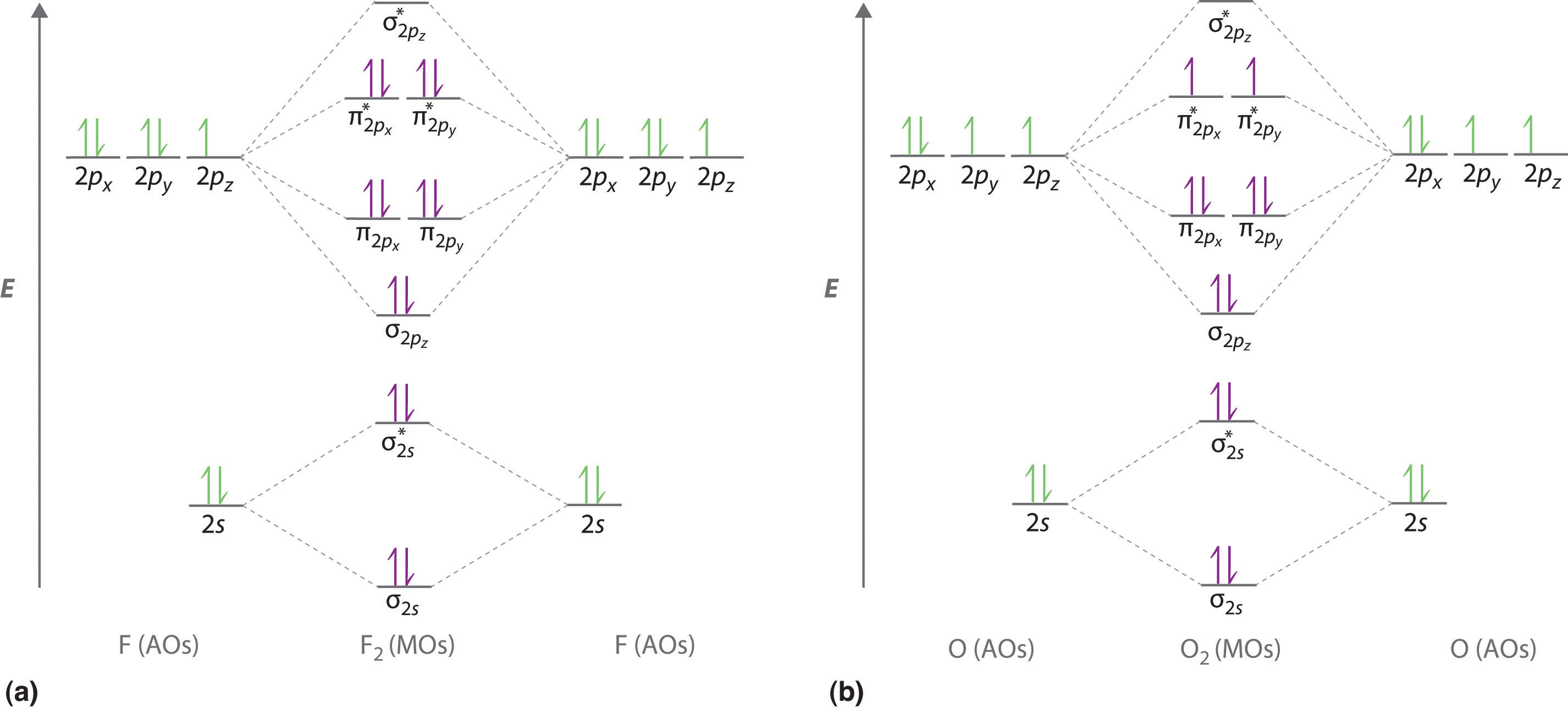
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules chem in chemistry molecular orbital mo theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule image file c5cs a f2 tif READ Hand Tendons Diagram
Molecular Orbital Diagram N2 - Mo Bonding In F2 And O2 Chemistry Libretexts how to build molecular orbitals chemistry libretexts building molecular orbital diagrams for homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecules draw the mo diagram for n2 question 2 draw the mo for o 2 Molecular Orbital Diagram N2 - Molecules Free Full Text
Molecular orbital diagram for n2 o2 c2 f2 also h2o. Electronic configuration of c2 molecule is σ 1s2 σ1s2 σ2s2 σ2pz 2 2px 1 2py orbital s what is the origin of differences between mo schemes o₂ and n₂ chemistry stack exchange c2 2 lewis structure how to draw the for c2 2 youtube figure orbital correlation diagram for homonuclear ...
A) F2; B) F2^2+ C) Ne2^2+ D) O2^2+ E) F2^2-2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic.
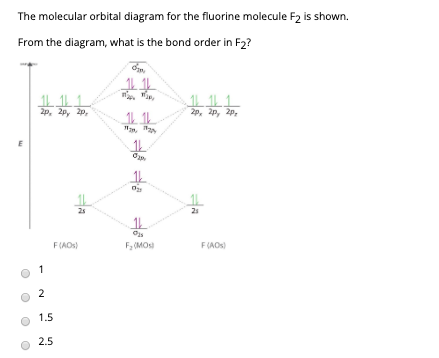
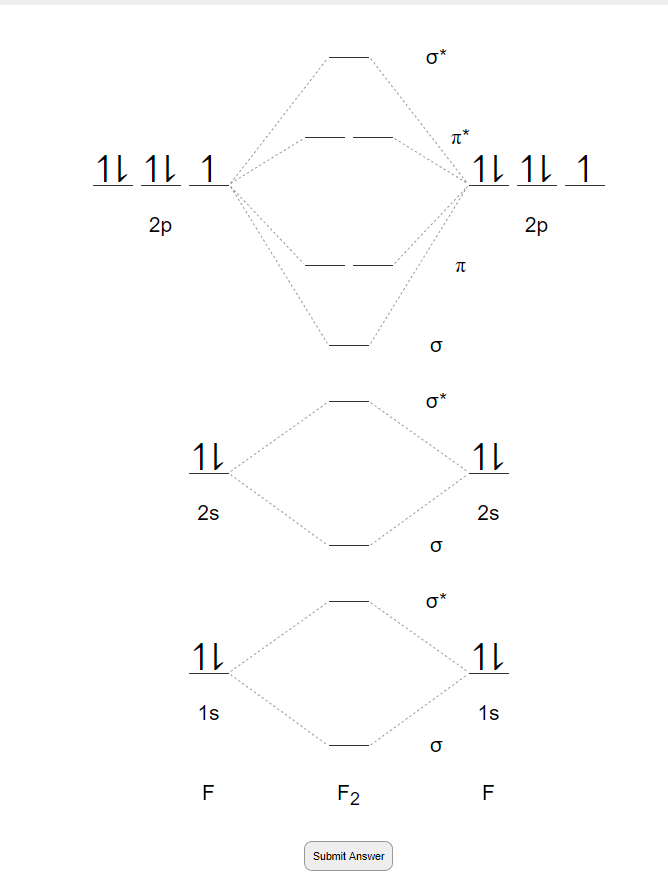
Below is the molecular orbital diagram for the fluorine molecule (F2) and images of several molecular orbitals that exist in this molecule. Fill the blanks below. Fatom F Fatom А ** tttt pfltit >pft t11 to f1 f1 att с D E F .t1 s stt 24 TL 1. a. The bond order for the F2 molecule is (enter a numeral). b. The F2 molecule is [paramagnetic
When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so ...
Printable O2 molecular orbital diagrams are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson.This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.a.F22+b. Ne22+c. F22-d. O22+e. F2
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
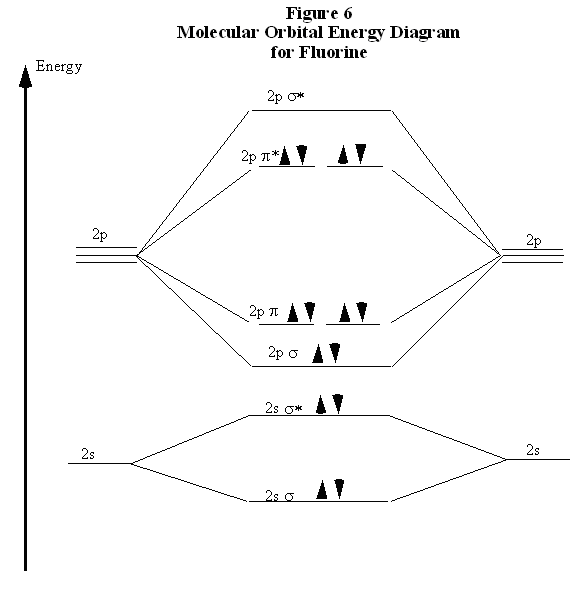
F2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao method in particular. Use molecular orbital theory to predict whether or.
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.
The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is
F2 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram As per molecular orbital (MO) theory, all the constituent atoms in a molecule contribute to the formation of molecular orbitals. These MOs are a linear combination of the atomic orbitals. Thus, the electrons in a molecule are not individually assigned to atomic orbitals but to molecular orbitals.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
Molecular orbitals: Orbitals that span two or more atoms. These are constructed by overlapping atomic orbitals (AOs) which match in symmetry and size. In principle, To construct MO diagram of a any Molecule, first, set up Schrödinger wave equation for that molecule and then, solve it!!!
The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is
15 F2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. We assume that the electrons would fill the molecular orbitals of molecules like electrons fill atomic we will use this diagram to describe o2, f2, ne2, co, and no. The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2p_ (sigma), so that is where the extra electron will be added.
For the ion F2+:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this ion exist?d) Write the electron configuration of the ion.————...
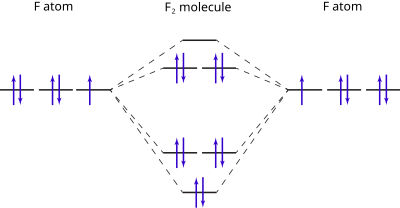
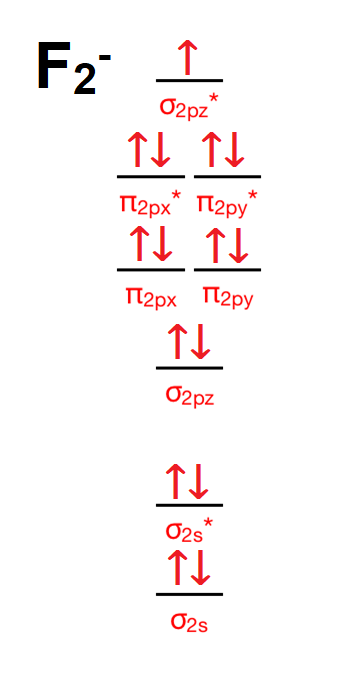
When we make the molecular orbital energy level diagram of f2 molecule then, we will get this configuration: 1σs 2, 1σ*s 2, 2σs 2, 2σ* 2, σ2pz 2, π2p x2, π2p y2, πp x * 2, π2p y * 2. From this electronic configuration, we can see that there are a total of ten bonding molecular orbitals and eight antibonding molecular orbitals.
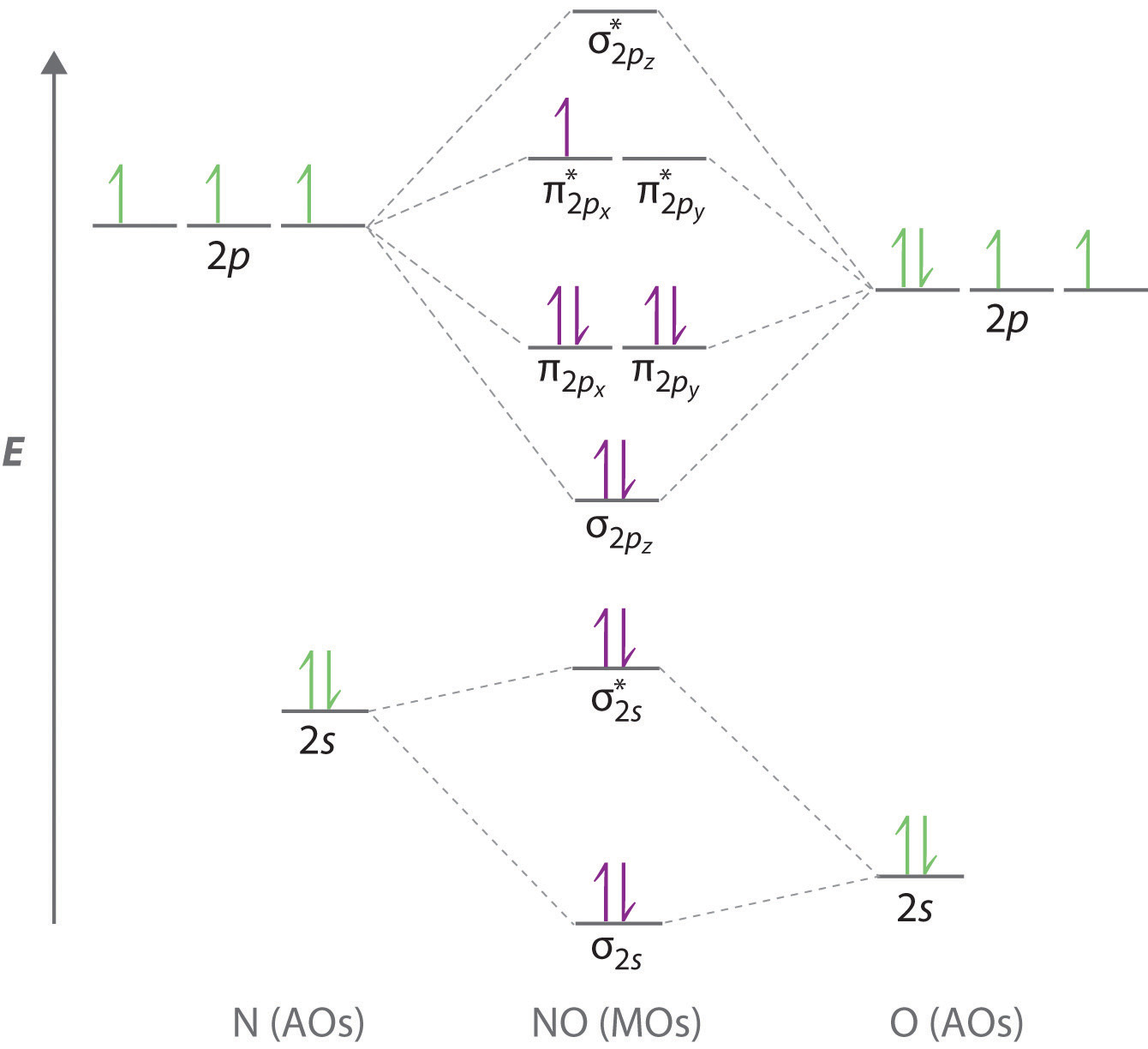
Molecular orbital theory is a method for describing the electronic structure of the molecule. Now, let us draw the molecular orbital diagram of $ {N_2}$ . Now, first let us understand what magnetic behavior and bond order means. As we know the electron has an electron magnetic dipole moment, which is generally generated by the electron's spin ...


















0 Response to "36 f2+ molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment