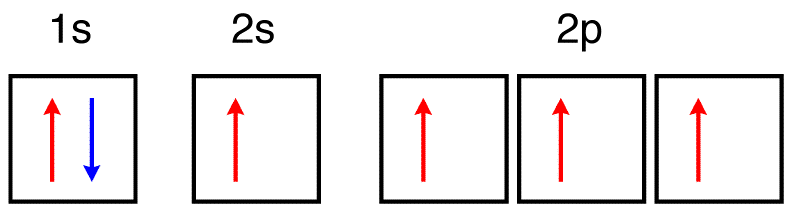
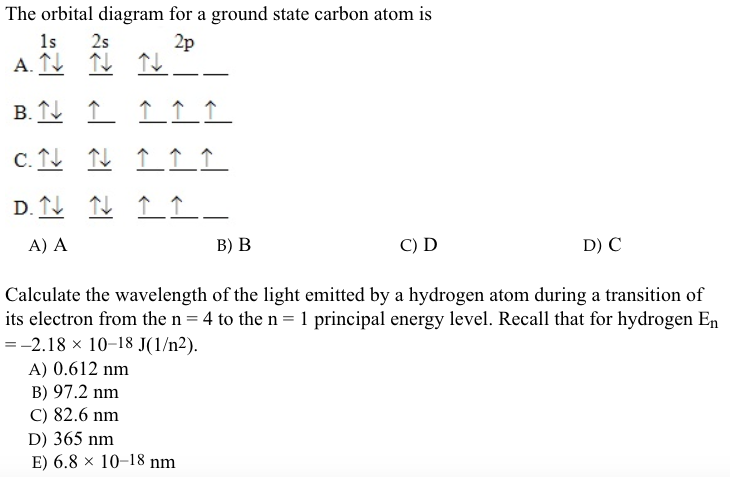
42 the orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is
5. 1 The orbital diagram for a ground state nitrogen (7) atom is: A. 2 The orbital diagram for a ground state oxygen (8) atom is: D. 3 The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon (6) atom is: D. 4 Which ground state atom has an electron configuration described by the following orbital diagram? Phosphorus. From the ground state electron configuration, one can see that carbon has four valence electrons, two in the 2s subshell and two in the 2p subshell. The 1s electrons are considered to be core electrons and are not available for bonding. There are two unpaired electrons in the 2p subshell, so if carbon were to hybridize from this ground state ...
The ground state is 1s2 2s2 2p2. So as you may know in the p subshell there are 3. The orbital diagram for a ground state oxygen atom is. Orbital diagram for ground state oxygen atom. The orbital diagram for a ground state oxygen atom is a a b b c c d d e e which element has the following ground state electron configuration.

The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is
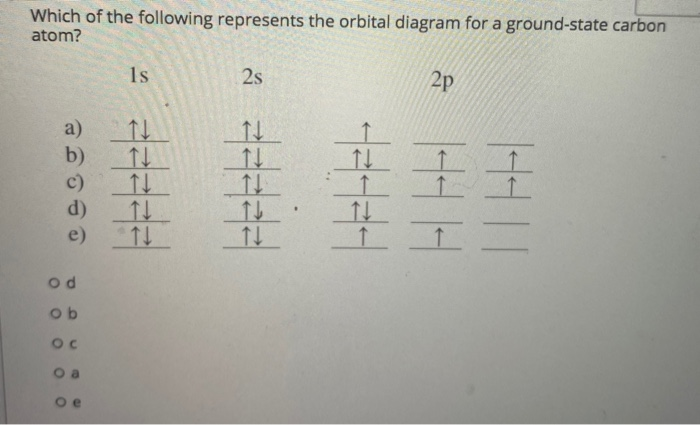
A carbon atom can absorb radiation of various wavelengths with resulting changes in its electron configuration. Rank the orbital diagrams for the electron configuration of carbon that results from the ground state absorbing the three longest wavelengths of radiation it can absorb. The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is. 1s 2s 2p ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ How many unpaired electrons does a ground-state atom of sulfur have? 2. Which element has the following ground-state electron configuration? 1s²2s²2p⁶3s² ... orbital node crevice pit. Node. The ground-state electron configuration of a calcium atom is [Ne]3s2 [Ar]4s13d1 [Ne]3s23p6 [Ar]4s2 [Ar]3d2 ... The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is 1s 2s 2p A ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿⇂ . B ↿⇂ ↿ . ↿ . ↿ . ↿ C ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿ . ↿ . ↿
The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is. Writing Orbital Diagrams. We will now construct the ground-state electron configuration and orbital diagram for a selection of atoms in the first and second periods of the periodic table. Orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of electrons. We ... We can also display the energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. A portion of the energy level diagram is shown, So we have three ways to represent the electron arrangement in an atom. The orbital diagram, the electron configuration and the energy diagram. ... The orbital energy diagram for carbon is shown below. Nitrogen has seven electrons ... orbital diagram for sodium confirms that the 3s sublevel is lower in energy than the 3p sublevel. The s sublevel is located lower on the page than the p sublevel. 10. The lowest potential energy arrangement of electrons in an atom is called the ground state. Ground state electron configurations can be predicted by a strict set of rules known as the The electron configuration and orbital diagram of helium are: The n = 1 shell is completely filled in a helium atom. The next atom is the alkali metal lithium with an atomic number of 3. The first two electrons in lithium fill the 1 s orbital and have the same sets of four quantum numbers as the two electrons in helium.
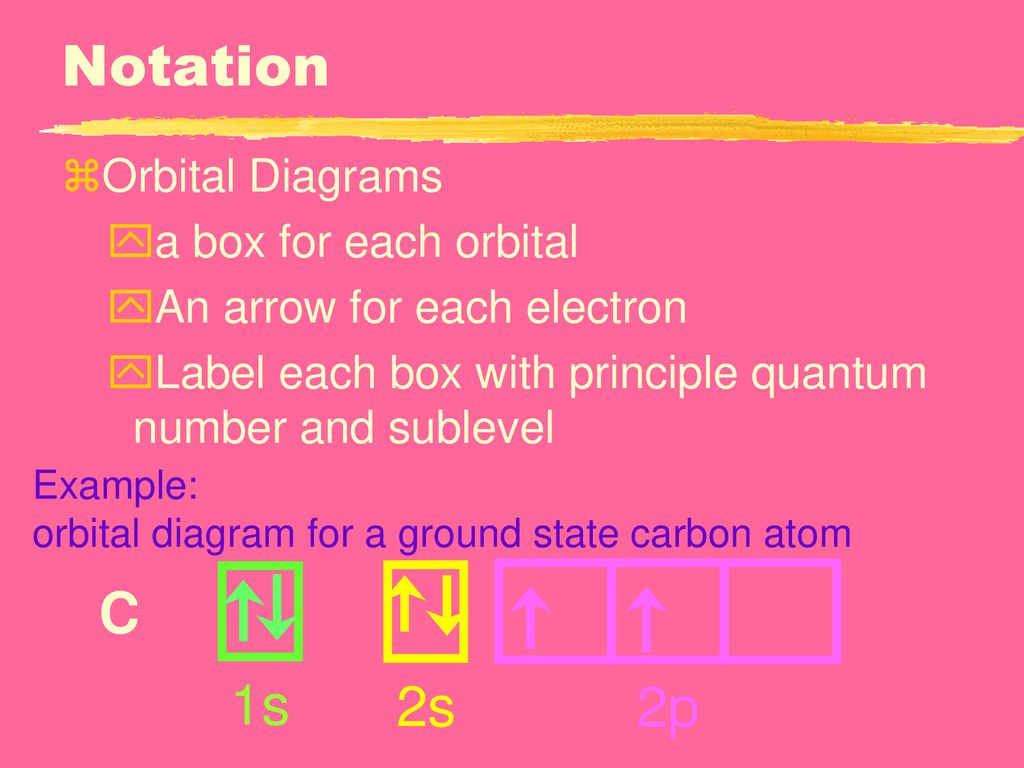
Orbital Diagram: Knowledge of atomic numbers and proper electronic configuration is needed to state an orbital diagram for a given element or atom. Spins are used to show electrons in such diagrams. Orbital Filling Diagrams. An orbital filling diagram is the more visual way to represent the arrangement of all the electrons in a particular atom. In an orbital filling diagram, the individual orbitals are shown as circles (or squares) and orbitals within a sublevel are drawn next to each other horizontally. Apr 06, 2020 · What is the orbital diagram for carbon atom in a ground state? By Hund’s rule, the electron configuration of carbon, which is 1s2 2s2 2p2, is understood to correspond to the orbital diagram shown in c. Experimentally, it is found that the ground state of a neutral carbon atom does indeed contain two unpaired electrons. The ground state electron configuration of p is ne3s23p3. Orbital diagram for ground state oxygen atom. The orbital diagram for a ground state oxygen atom is. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for o go in the 2s orbital. The 3s subshell contains one orbital ml0 which holds two spin paired electrons.
The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is 1s 2s A) A B) B C) D D) C Calculate the wavelength of the light emitted by a hydrogen atom during a transition of its electron from the n-4 to the n-1 principal energy level. Recall that for hydrogen En -一2.18 × 10-18 J (1/n2) A) 0.612 nm B) 97.2 nm C) 82.6 nm D) 365 nm E) 6.8 × 10-18 nm. When we write the configuration we'll put all 14 electrons in orbitals around the nucleus of the Silicon atom. In writing the electron configuration for Silicon the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Silicon go in the 2s orbital. The nex six electrons will go in the 2p ... A ground-state atom of vanadium has ___ unpaired electrons and is _____. A) 0, diamagnetic B) 2, diamagnetic C) 3, paramagnetic ... The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is . 33. The bonds of oxygen molecules are broken by sunlight. The minimum energy required MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Carbon is the sixth element with a total of 6 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for carbon the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for C goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining two electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Therefore the C electron configuration will be ...
Ground State Electron Configuration For Nitrogen. When we talk about the electronic configuration, then the ground state Nitrogen Electron Configuration is written as 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3.Below you can get the full image representation which will help you to understand the topic more easily.
The orbital diagram for a ground-state oxygen atom is 1s (up down) 2s (up down) 2p (up down, up, up) Which of the following is the electron configuration of an excited state of an oxygen
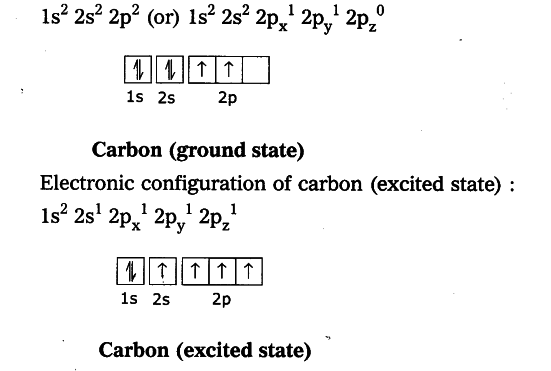
Explain The Four Unpaired Electrons In Carbon Atom Through Excited State Cbse Class 10 Science Learn Cbse Forum
When we write the configuration we'll put all 15 electrons in orbitals around the nucleus of the Phosphorus atom. In writing the electron configuration for Phosphorus the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Phosphorous go in the 2s orbital.
The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is A) A B) B C) C D) D ... The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is A) A B) B C) C D) D. D. section 7.9 A possible set of quantum numbers for the last electron added to complete an atom of gallium (Ga) in its ground state is A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E.
The orbital diagram for a ground state oxygen atom is a a b b c c d d e e which element has the following ground state electron configuration. Electrons in an orbital with l 3 are in a a. So since you have 4 electrons in the p orbital 2 of them will get there own orbital and 2 will have to share an orbital but they will spin in opposite directions.
Answer (1 of 9): That depends …. If you had a single carbon atom, then you could say that it has two unpaired electrons in the 2p sublevel, where each is in a separate orbital and each has the same spin. This is dictated by Hund's rule. But what are the chances of having a single carbon atom? W...
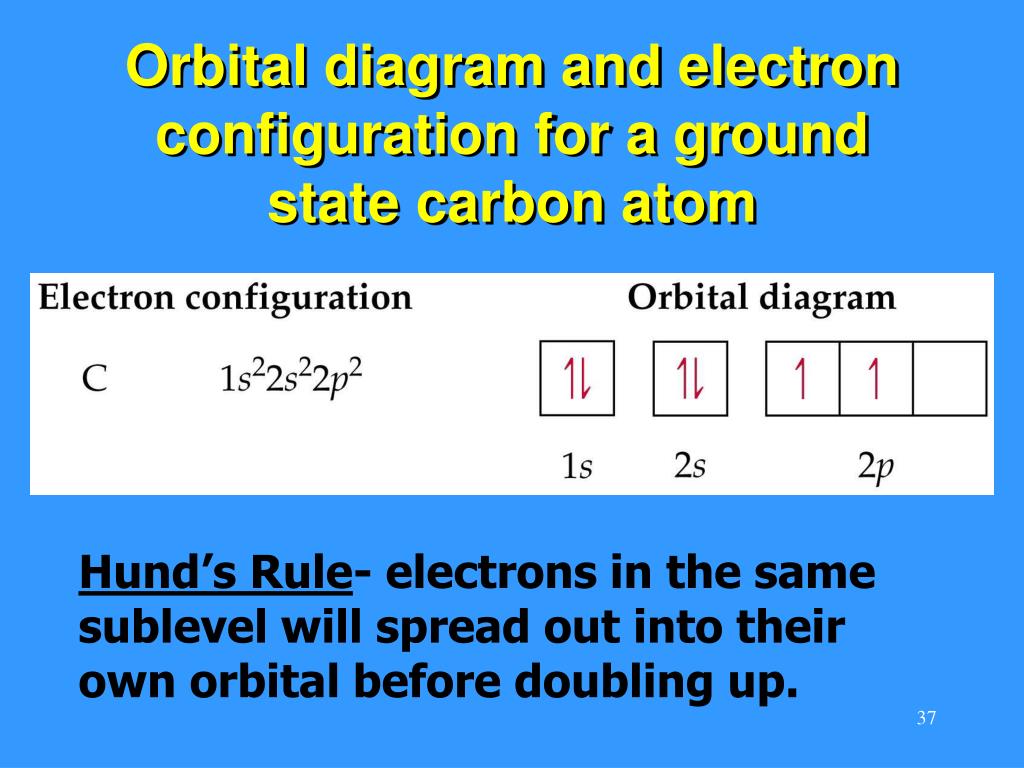
Ppt Unit 6 Chapters 11 12 Pages 295 366 Atomic Electron Configurations And Periodicity Powerpoint Presentation Id 5955487
eg. Consider a carbon atom whose electron configuration is the following. The total energy of the electrons in this carbon atom can be lowered by transfering an electron from a 2P orbital to the 2S orbital. Therefore, this carbon atom is an excited-state carbon atom. see also ground-state atom. OCHEMPAL IS NOW IN THE FORM OF A BOOK*
A nitrogen atom has 3 orbitals; the 1s orbital, the 2s orbital, and the 2p orbital. In this case, the 2s and 2p orbitals are the valence orbitals, as they have the electrons with the most energy.

Which Of The Orbital Diagrams Represent S An Excited State Nitrogen Atom Choose One Or More 1 2p Homeworklib
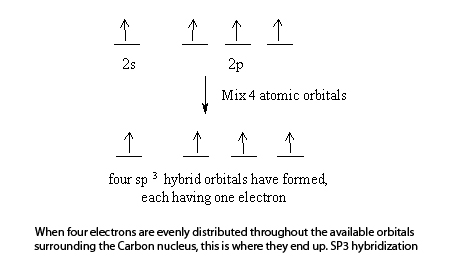
Orbital hybridization is essentially a process of mixing orbitals together and spitting out new ones that are all identical in "symmetry" and "composition" to the orbital (s) from the other, incoming atom (s). Solution: Consider the electron configuration of a carbon schematron.org the orbital diagram of carbon before sp3 hybridization.
Dec 14, 2016 · The ground state is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^2. In the explanation below, I show a common means of diagramming this. Using arrows to show the spin orientation of each electron, the orbital diagram is often shown this way: The single electrons in the two p-orbitals is in accordance with Hund's Rule.
Boron is the fifth element with a total of 5 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for Boron the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for B goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining electron will go in the 2p orbital. Therefore the B electron configuration will be 1s 2 ...
orbital node crevice pit. Node. The ground-state electron configuration of a calcium atom is [Ne]3s2 [Ar]4s13d1 [Ne]3s23p6 [Ar]4s2 [Ar]3d2 ... The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is 1s 2s 2p A ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿⇂ . B ↿⇂ ↿ . ↿ . ↿ . ↿ C ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿ . ↿ . ↿
The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is. 1s 2s 2p ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ How many unpaired electrons does a ground-state atom of sulfur have? 2. Which element has the following ground-state electron configuration? 1s²2s²2p⁶3s² ...
A carbon atom can absorb radiation of various wavelengths with resulting changes in its electron configuration. Rank the orbital diagrams for the electron configuration of carbon that results from the ground state absorbing the three longest wavelengths of radiation it can absorb.

Solved For The Molecule C2h2 14m A Draw The Orbital Diagram Of The Carbon Atom With Its Valence Electrons At Ground State 2 B Draw The Orbital Diagram Of The Carbon Atom With
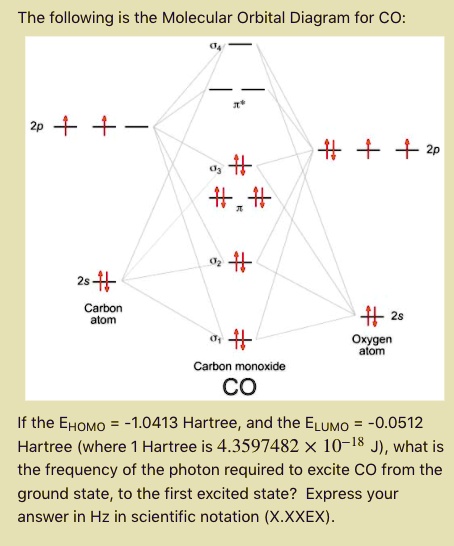
Solved The Following Is The Molecular Orbital Diagram For Co 2 2s Carbon Atom 2s Oxygen Diom Carbon Monoxide Co If The Ehomo
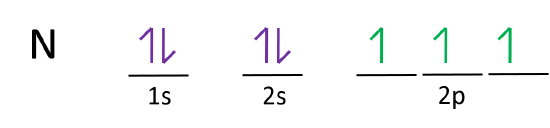
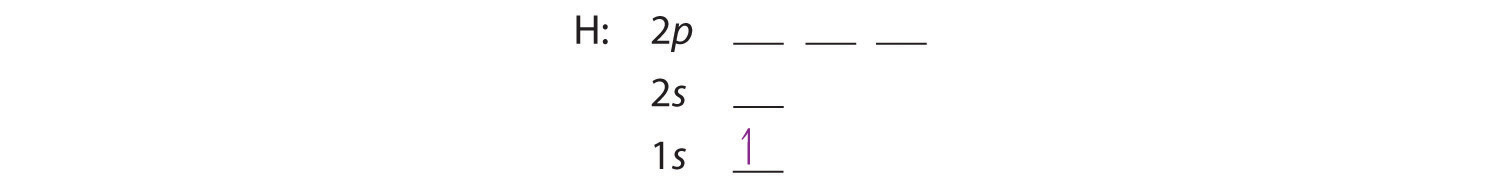















/chapter2/pages17and18/page17and18_files/mobute.png)





0 Response to "42 the orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is"
Post a Comment