42 internal squid anatomy diagram
Original Document: Squid Dissection Squid can be purchased from biological supply companies, such as carolina.com or you can buy them at the grocery store packaged as frozen calamari.. External Anatomy (Labeled) : Finding the Jaw . The beak should look like a bird's beak, with two sharp curved points. Start studying Internal Anatomy of a Cephalopod (squid). Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Teacher's guide for dissecting the squid which includes both the internal and external anatomy. Original Document: Squid Dissection squid labeled. In this article we will discuss about the structure of Squid (Loligo) with the help of a diagram. Loligo 1. It is a marine mollusc commonly called squid. 2. Body is.

Internal squid anatomy diagram
C) Class Cephalopoda, fresh-frozen squid Part A: External Anatomy. Examine a fresh-frozen squid, which was thawed out earlier today. Unlike other mollusks, the shell of squids is not external but rather is internal (and much reduced in size). A tough, muscularized mantle completely surrounds the animal (Figure 4). We are pleased to provide you with the picture named Internal Anatomy Of A Squid.We hope this picture Internal Anatomy Of A Squid can help you study and research. for more anatomy content please follow us and visit our website: www.anatomynote.com. Anatomynote.com found Internal Anatomy Of A Squid from plenty of anatomical pictures on the internet. External Anatomy The main part of the body containing all the organs is called the mantle. The mantle is covered in pigment cells called chromatophores. The squid can change color rapidly and use this to camouflage themselves, attract mates, and to communicate with each other. The squid has two fins, on the mantle near the pointed end
Internal squid anatomy diagram. Start studying internal squid anatomy. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. This lesson will focus on the external and internal anatomy of a squid. You are to 'digitally disect' a squid in order to learn about their anatomy and physiology. At the end of the digital dissection label the picture of a squid on the printed pages to demonstrate your knowledge. Squid Dissection 3 Squid Drawing: Kids can label the blank squid diagram below with the listed vocabulary words. 1. Label the squid diagram with the following words: - Fin - Eye - Tentacle - Club - Arm - Mouth - Siphon - Mantle - Head Squid Analogy Poems: Write poems or riddles that compare parts of a squid to parts of another animal. Squid Internal Anatomy Diagram Lab Sheet Squid Dissection regarding Squid Internal Anatomy Diagram. Diagram Squid Internal Anatomy Diagram pertaining to Squid Internal Anatomy Diagram. Cephalopods inside Squid Internal Anatomy Diagram. Lab Sheet Squid Dissection throughout Squid Internal Anatomy Diagram. Squid Anatomy Carlson Stock Art within...
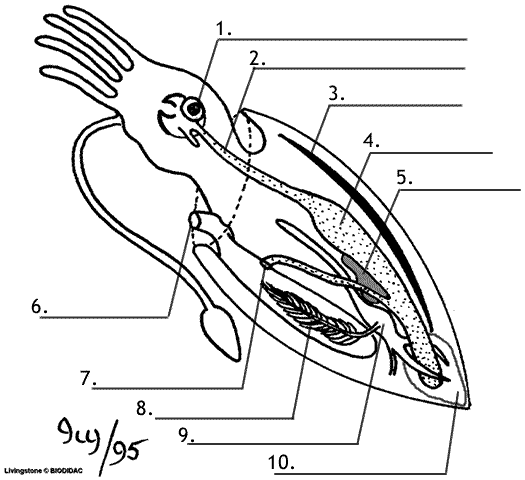
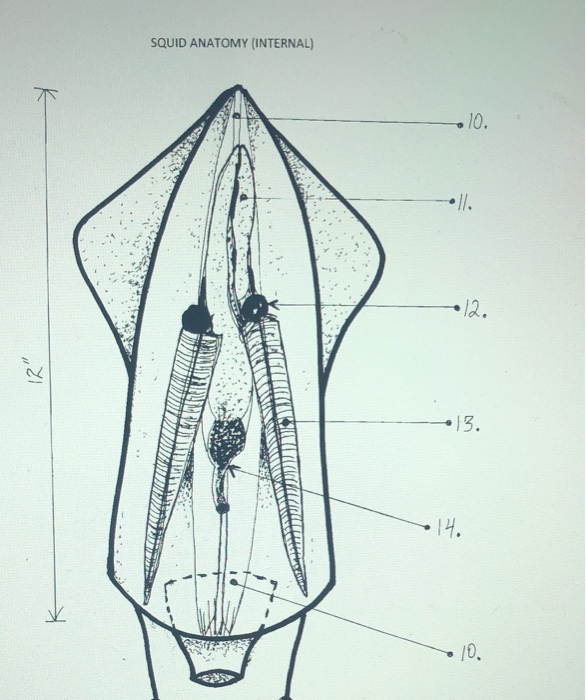
Squid are invertebrates in the phylum Molluska, a group that includes snails, . Draw and label the external parts of the squid: arms, tentacles (have suckers. of the body organs such as heart, stomach and gills. Squid have a large bulb in on the internal anatomy squid diagram and label it. 10) Look and try to find the. To study the internal and external anatomy of the cephalopod squid. Materials Dissecting pan, dissecting kit, lab apron, plastic gloves, safety glasses, preserved squid Procedure 1. Put on your lab apron, safety glasses, and plastic gloves. 2. Place a squid in a dissecting tray and identify the dorsal, ventral, anterior and posterior parts of ... Squid Dissection: Internal Anatomy On the diagram below label the: Ink sac, gills, gill hearts, systemic heart, kidney, esophagus, digestive gland, intestine, anus, funnel retrac-tor muscles, and gonad (label as ovary or teste). State the function of each. Ink sac: Produces ink for protection. Funnel Retractor Muscle: Steers during jet propul-sion. Part 2: Internal Anatomy of the Squid. Scissors are the best tool to open the squid's body cavity. You can easily raise the mantle just where the water jet is located and cut to the anterior end of the squid (toward the fins). The photo below shows the mantle of the squid cut, but has not been pinned.
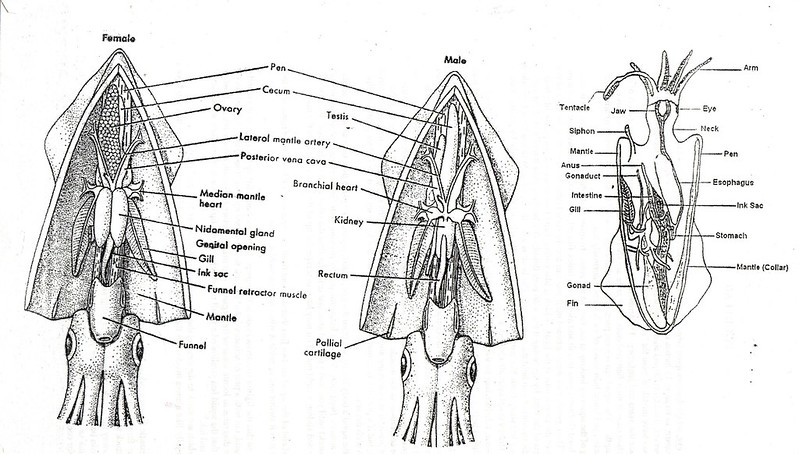
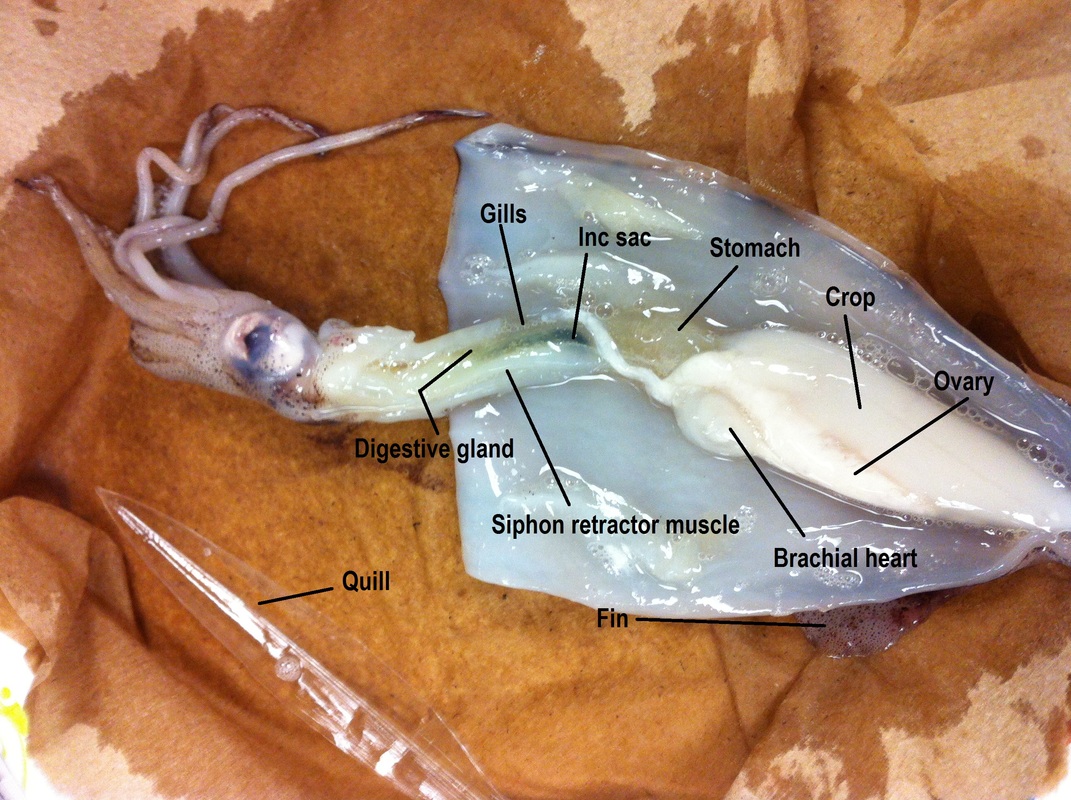
The squid diagram above shows the internal organs of a squid. From the three hearts, two hearts feed each of the gills, and one larger heart that pumps blood to the rest of the body. The main body mass of a squid is enclosed in the mantle, which has a swimming fin along each side. Squid Dissection Objectives: As a result of this lesson, students will be able to: Locate and identify major external and internal features and organs of a squid. Understand and use basic dissection techniques and terms. Critically examine the functions of several squid features and organs. Teaching Notes: This lab is a very thorough … Continue reading "Squid Dissection" Squid Anatomy Diagram . Squid - Internal Features (Male) siphon (cut) Ink sac gill heart r vena cava gonad (testis) penis -kidney caecum siphon retractor muscle . Squid - Internal Features (Female) ink sac siphon land ovary sto ac caecu posterior cava nida pen accessory nidamental gland siphon retractor muscle . Author: Chalmers, Jacob Squid Dissection: Squidward we go! Captivating the hearts of many starring in such worldwide venues as "Spongebob Squarepants" and all the oceans you've ever known, squid are truly amazing. There are over 300 species of these wonderful creatures, and being …
bulb in on the internal anatomy squid diagram and label it . 10) Look and try to find the beak. The beak is hard and is a dark brownish color. Draw the beak in on the internal anatomy squid diagram and label it . If there is time we will zoom in on it under the camera. 11) Now, lay your squid ventral side up (lighter side). Locate the collar .
Lay the squid dorsal side down on a piece of wax paper laid over some newspapers. Lay the squid with its head to the left and its siphon opening upward (Fig. 3.71.1). Reach under the animal and remove the pen from the dorsal side by grasping it firmly with your fingers and pulling it free from the mantle.
Squid Dissection: Internal Anatomy On the diagram below label the: Ink sac, gills, gill hearts, systemic heart, kidney, esophagus, digestive gland, intestine, anus, funnel retrac-tor muscles, and gonad (label as ovary or teste). Fins: At the tail (posterior) end of the squid students will notice the two fins on the mantle.
The suction cups help the squid to hoid onto food 9) Hoid your squld like a flower, let the arms lay back so you can see the mouth. bulb in on the internal anatomy squid diagram and label it. internal anatomy squid diagram and label it.
The overall anatomy of the squid is different from other types of creatures found in the water. However, as you can see it does work out quite well for them. Their survival in the water depends on their unique anatomy. They have continued to evolve too over the course of time in order to continue being a part of our world.
Squid Dissection: From Pen to Ink Through squid dissection, students will examine some of the unique features which have allowed squid to adapt and thrive in Southern California waters and throughout the world. This beginning dissection lesson will allow students to identify internal and external anatomy of the squid and
Dissection of Internal Anatomy Mantle Cavity: Reorient the squid on your plate so squid's ventral side (funnel side) is facing up. Students will cut using scissors down the middle of the squid's mantle starting from the funnel. Students must be careful they cut the mantle
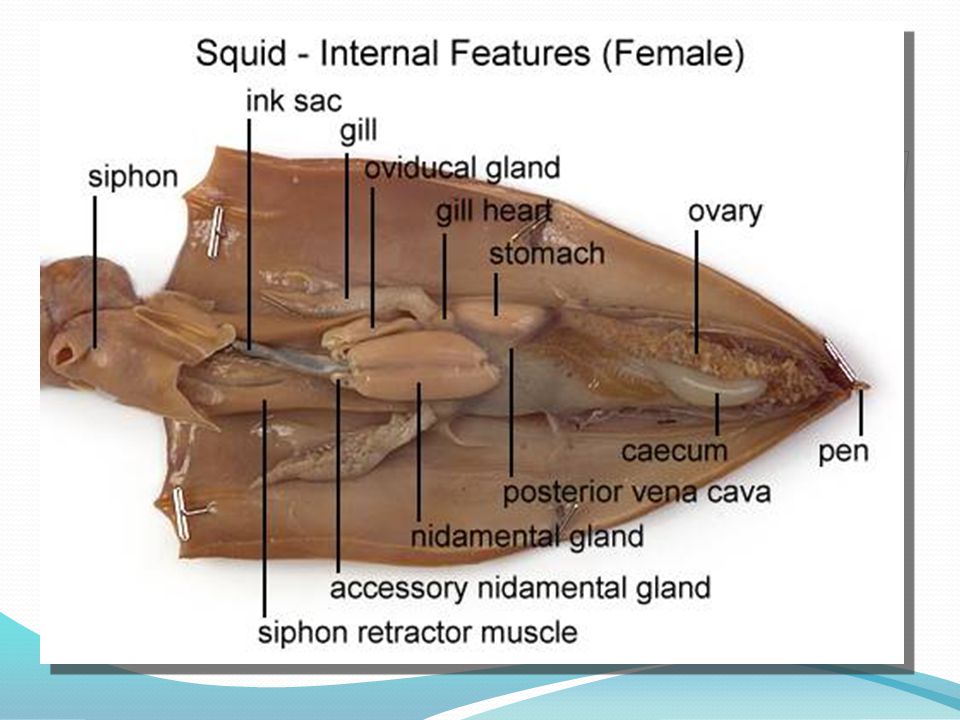
Squid internal organs diagram. In this image, you will find Squid internal organs diagram in it. Health care advices from Overseas Doctor . We are pleased to provide you with the picture named Squid internal organs diagram. We hope this picture Squid internal organs diagram can help you study and research. for more anatomy content please follow ...
9. Open the "flaps" of the mantle and lay them out on the tray. The internal organs will now be exposed. Remember to label the various parts you see on the diagram provided at the back of this packet. 10. Use the Squid Anatomy Diagram to help you identify and label the internal structures as you proceed through the dissection. 11.
External and internal anatomy of a squid (Loligo sp.). Phylum Mollusca, Class Cephalopoda. Both male and female anatomy are examined. Female digestive, cardi...
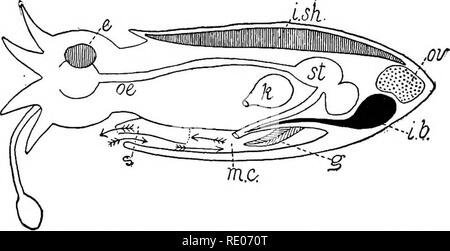
Fig. 3.71.2. Diagram of internal squid anatomy. Image by Byron Inouye. Fig. 3.71.2. Diagram of internal squid anatomy
External Anatomy The main part of the body containing all the organs is called the mantle. The mantle is covered in pigment cells called chromatophores. The squid can change color rapidly and use this to camouflage themselves, attract mates, and to communicate with each other. The squid has two fins, on the mantle near the pointed end
We are pleased to provide you with the picture named Internal Anatomy Of A Squid.We hope this picture Internal Anatomy Of A Squid can help you study and research. for more anatomy content please follow us and visit our website: www.anatomynote.com. Anatomynote.com found Internal Anatomy Of A Squid from plenty of anatomical pictures on the internet.
C) Class Cephalopoda, fresh-frozen squid Part A: External Anatomy. Examine a fresh-frozen squid, which was thawed out earlier today. Unlike other mollusks, the shell of squids is not external but rather is internal (and much reduced in size). A tough, muscularized mantle completely surrounds the animal (Figure 4).


























0 Response to "42 internal squid anatomy diagram"
Post a Comment