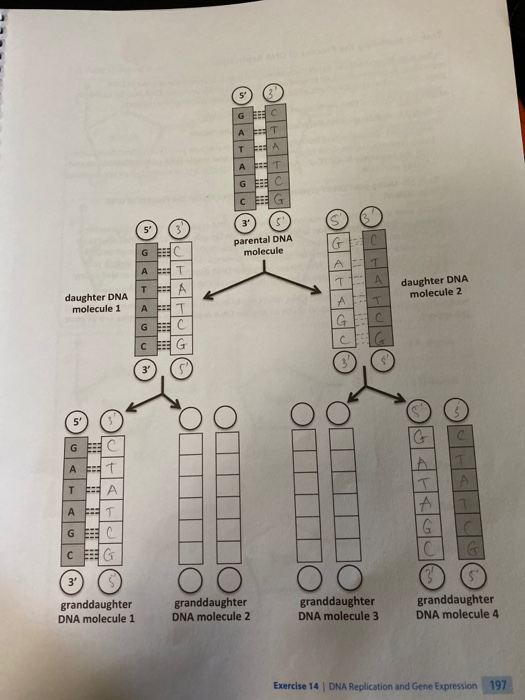
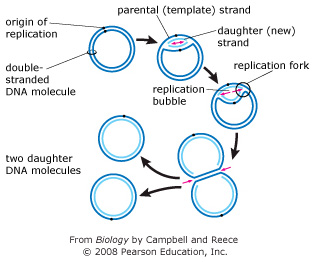
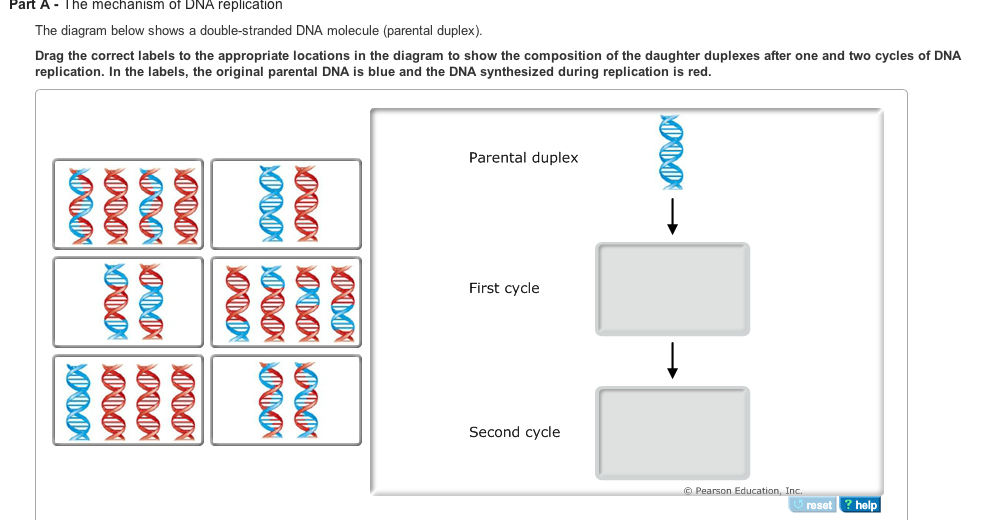
41 the diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental duplex).
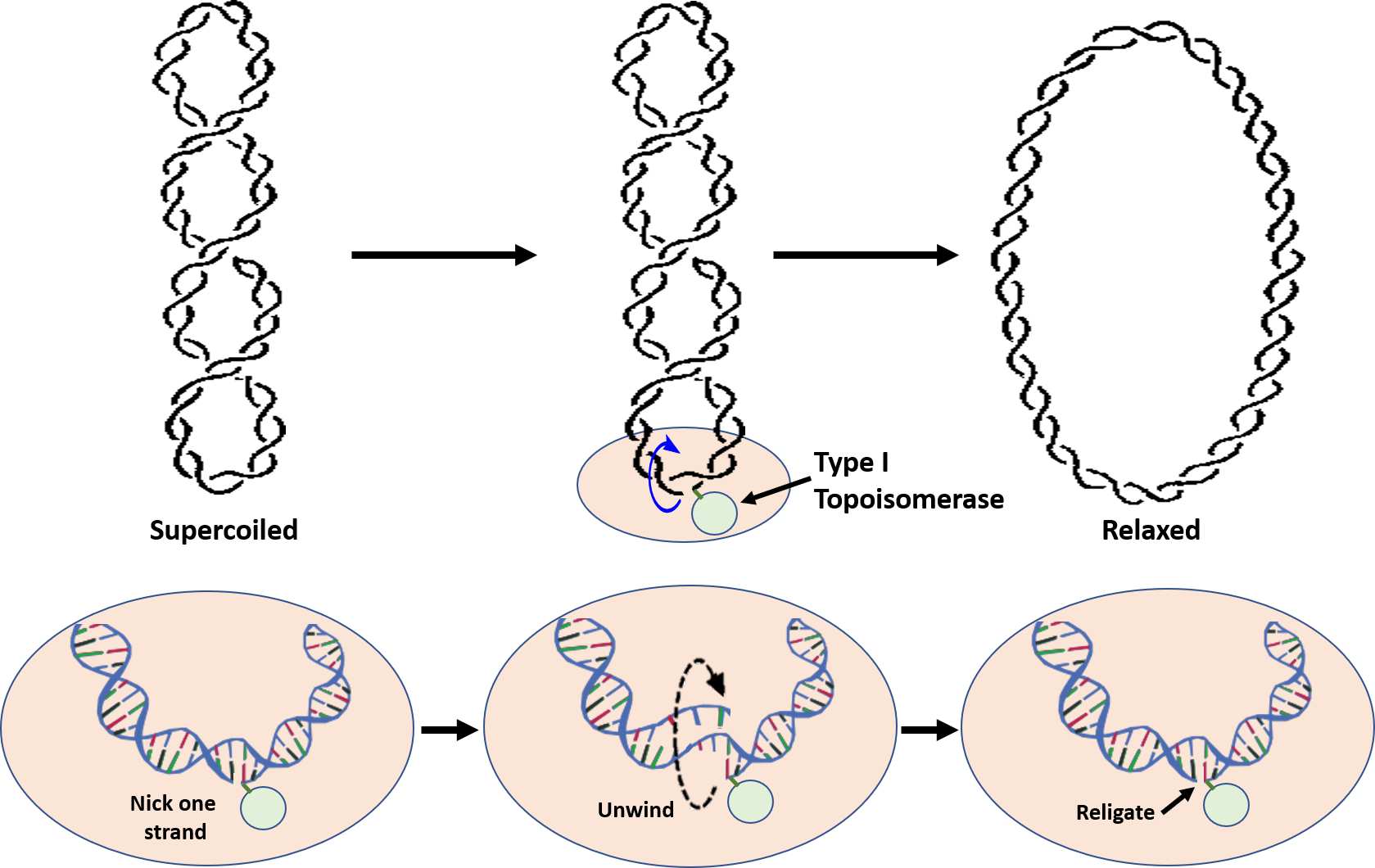
In (a), the general problem of separating the two parental strands is illustrated for a double-stranded DNA ring. In this two-line representation of the duplex DNA ring, each of the circular DNA strands is represented by a closed line. Because of the double helix geometry of DNA, the two strands are topologically linked; the degree The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental duplex. The diagram below shows a replication fork with the two parental dna strands labeled at their 3 and 5 ends. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the diagram to describe the name or function of each structure. The nucleotide pairs in double stranded dna follow ...
Part A The mechanism of DNA replication The diagram below shows a doublestranded DNA molecule (parental DNA)%(11). Mar 19, · The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the diagram to describe the name or function of each structure.
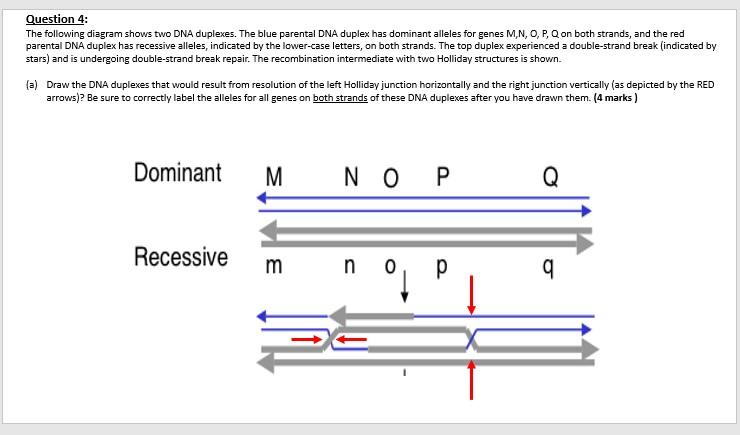
The diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental duplex).
The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental duplex. Use pink labels for the pink targets and blue labels for the blue targets. The origin of replication is indicated by the black dots on the parental strands. The dna molecule actually consists of two such chains that spiral around an imaginary axis to form a double helix spiral. The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental duplex). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter duplexes after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red. The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the diagram to describe the name or function of each structure. Use pink labels for the pink targets and blue labels for the blue targets. Show transcribed image text.
The diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental duplex).. The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental duplex). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter duplexes after one and two cycles of DNA replication. The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter DNA molecules after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red. The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental duplex. The origin of replication is indicated by the black dots on the parental strands. Nucleic acids are made up of chains of many repeating units called nucleotides see bottom left of figure 1 below. The diagram below shows a replication bubble with synthesis of the leading and ... The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental dna. Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter dna molecules after one and two cycles of dna replication. The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental duplex.
In the dispersive model, all resulting DNA strands have regions of double-stranded parental DNA and regions of double-stranded daughter DNA. Figure by Parker, N., et.al. (2019) Openstax Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl devised an experiment in 1958 to test which of these models correctly represents DNA replication (Figure 9.2). The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental duplex. Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter duplexes after one and two cycles of dna replication. In the labels the original parental dna is blue and the dna synthesized during replication is red. The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental dna. As we know cell division is essential for an organism to grow but when a cell divides it must replicate the dna dna replication take place during s phase in its genome so that the two daughter cells have the same genetic information as their parent. The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental duplex. A with t and g with c. Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter duplexes after one and two cycles of dna replication. Part b rna primers on the leading and lagging strands.
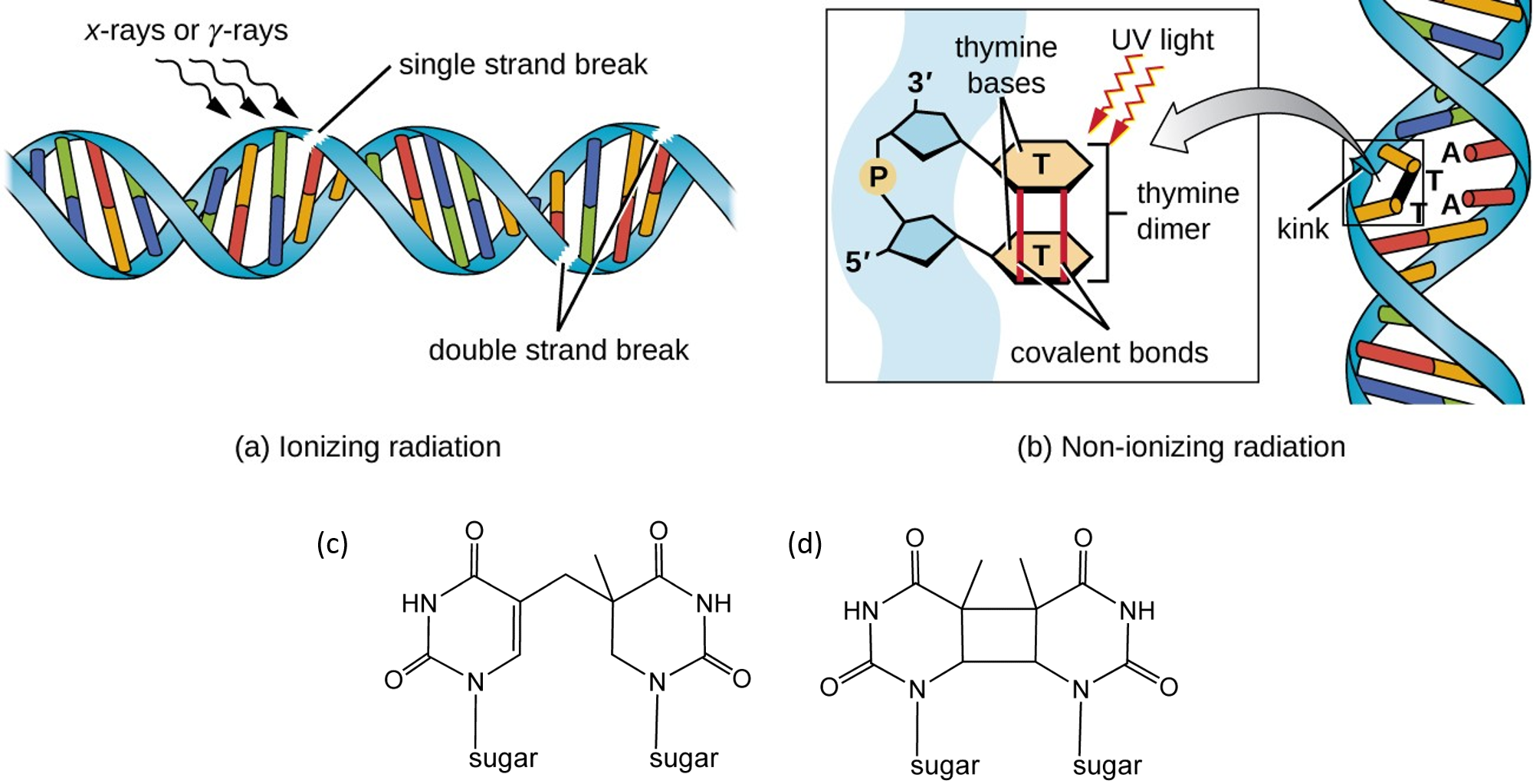
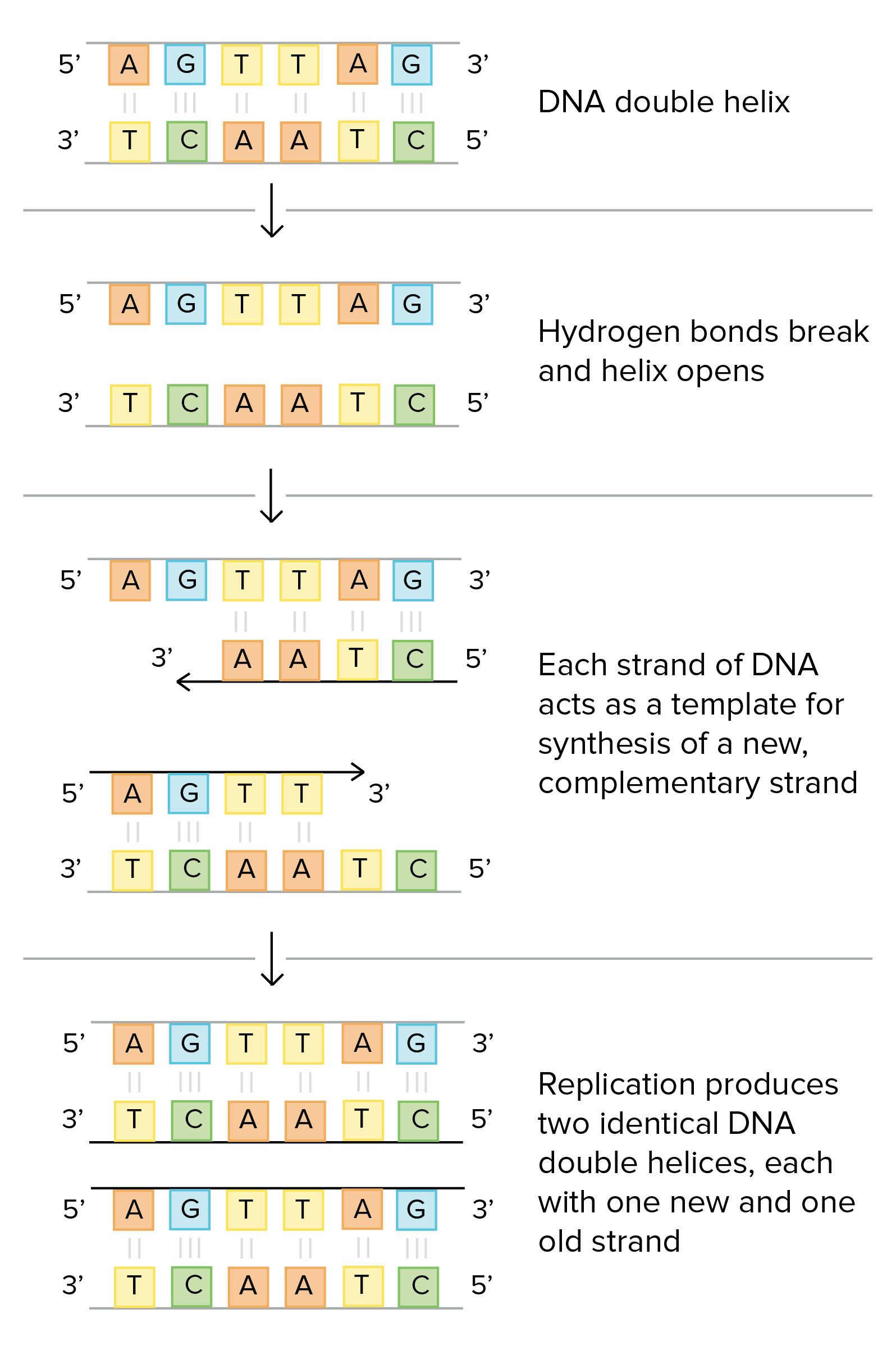
Based upon their model for the structure of DNA, Watson and Crick proposed that DNA replicates in a "Semi-Conservative" manner (Figure 2).In this model, the two strands of the DNA double helix unwind and separate, and each "parent" strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new "daughter" strand. In 1953, Watson and Crick suggested that the two strands of DNA would separate and act as templates for the synthesis of new complementary strands. After the completion of replication, each DNA molecule would have one parental and one newly synthesised strand. This shows that the replication of DNA is a semiconservative process. The ... A nucleotide molecule is consists of three parts, the deoxyribose sugar, the phosphate group, and the nitrogenous base. The diagram below shows the typical structure of a deoxyribonucleotide molecule. DNA segment with one double- to single-stranded transition like type II molecules; there was also, however, a single-stranded branch emerging from the duplex portion of the molecule, like type I molecules. Type I, type II and type l/II molecules accounted for 85-90% of the molecules that contained both single- and double-stranded DNA (excluding ob-
Part A The mechanism of DNA replication The diagram below shows a doublestranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter DNA molecules after one and two cycles of DNA replication.
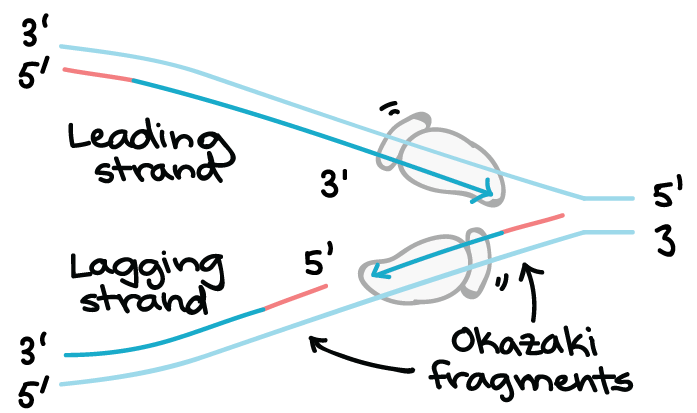
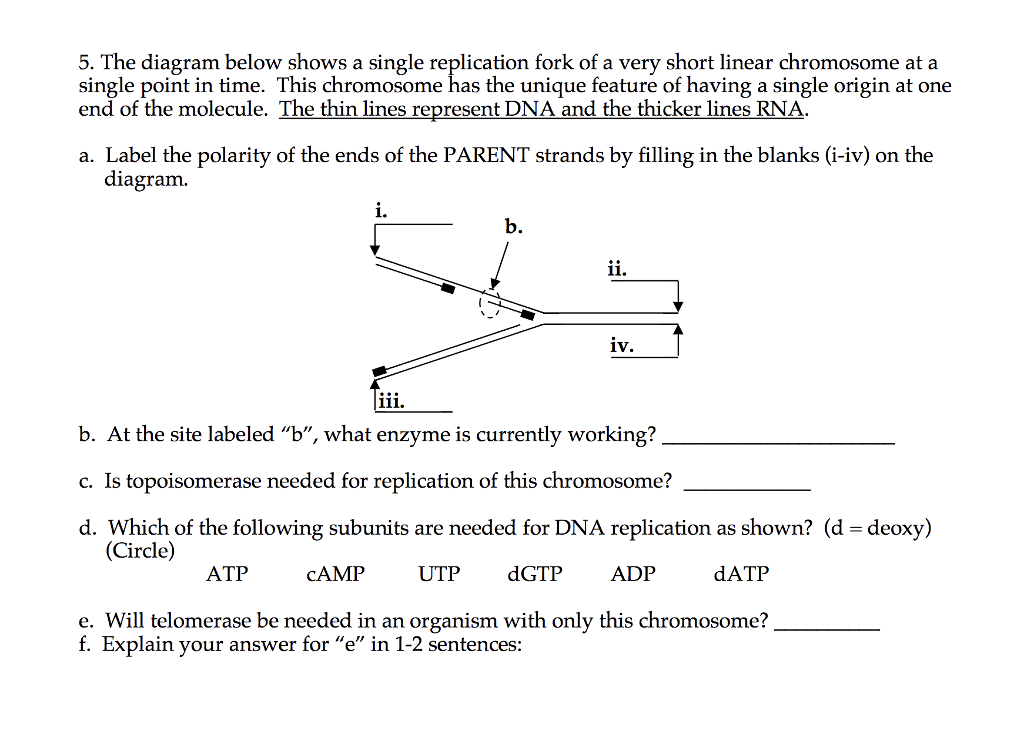
6. The diagram below shows a DNA molecule in the process of replication. Arrows show the direction of new DNA synthesis. a. Some of the enzymes and features are labeled, but some labels are incomplete or have been omitted. Fill in the boxes with the appropriate labels. b.
The elucidation of the structure of the double helix by James Watson and Francis ... DNA molecule being a hybrid of a parental strand and a daughter strand.

Structure Of A Duplex Dna Containing A Thymine Glycol Residue In Solution Journal Of Biological Chemistry
The diagram below shows part of a DNA molecule. a) From the diagram, draw a single nucleotide in your jotter. b) Name parts X and Y. c) Name the two DNA bases not shown in the diagram. d) What sequence would the complementary strand be? e) Redraw the diagram in your jotter and label the 5' and 3' ends of the strand. f) DNA is normally ...

Initiation Of Dna Replication At Palindromic Telomeres Is Mediated By A Duplex To Hairpin Transition Induced By The Minute Virus Of Mice Nonstructural Protein Ns1 Journal Of Biological Chemistry
The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental dna. The origin of replication is indicated by the black dots on the parental strands. In the labels the original parental dna is blue and the dna synthesized during replication is red. The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental duplex.

A Dna Molecule Is Made Of Four Types Of Nucleotides Adenine Guanine Thymine And Cytosine A Describe How These Nucleotides Are Connected Together To Make A Dna Strand B How Are
by B Alberts · 2002 · Cited by 16 — However, the DNA double helix is very stable under normal conditions; the base pairs are locked in place so strongly that temperatures approaching that of ...
DNA structure and function. DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.
In double-stranded DNA, the two strands wrap around each other to form a double helix . The two strands are held together by base pairing and are antiparallel. Thus, if one strand is oriented in the 5′ to 3′ direction, the other strand will be 3′ to 5′. This double-helical structure of DNA was first proposed in 1953 by J. D. Watson and ...

Structure Specific Dna Replication Fork Recognition Directs Helicase And Replication Restart Activities Of The Pria Helicase Pnas
The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental duplex. In this tutorial you will learn how dna is replicated and understand the roles of the proteins involved in the process. C thymine adenine b guanine adenine d cytosine thymine. The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins.
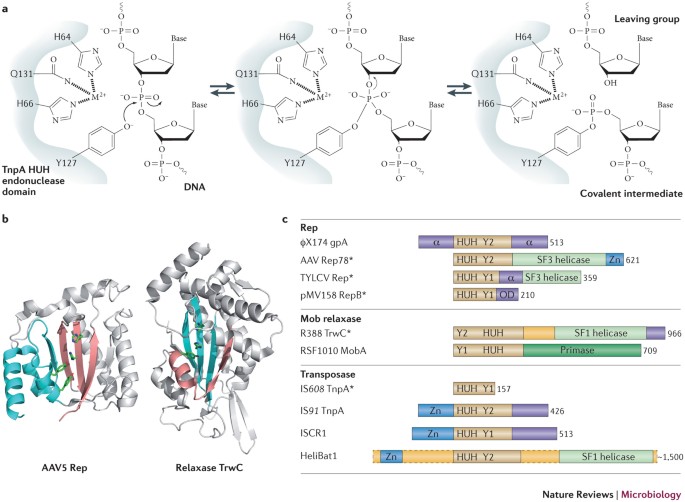
Breaking And Joining Single Stranded Dna The Huh Endonuclease Superfamily Nature Reviews Microbiology
Each of the two daughter dna molecules contains one strand from the original dna molecule and one newly synthesized strand. Part a the mechanism of dna replication the diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental duplex. Dna structure can you correctly label various parts of a dna molecule.
Below is a replication fork (one side of an origin): a double-stranded DNA ... The diagram below shows a DNA molecule in the process of replication.7 pagesMissing: duplex). | Must include: duplex).
Figure 2 below shows the structural formula of DNA in greater detail. The nitrogen bases are ring compounds with their carbon and nitrogen atoms arranged in single or double rings. Only certain bases can pair together to form base pairs. In DNA, Adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T), and guanine (G) always pairs with cytosine (C).
Both strands of parental DNA serve as templates for newly synthesized daughter strands that inherits a new double helix DNA containing one old and one new daughter strands arising from the parental duplex. This mechanism would require one daughter strand to polymerize in the 5′-to-3′ direction and the other in the 3′-to-5′ direction ...
Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. This is known as semiconservative replication. When two DNA copies are ...
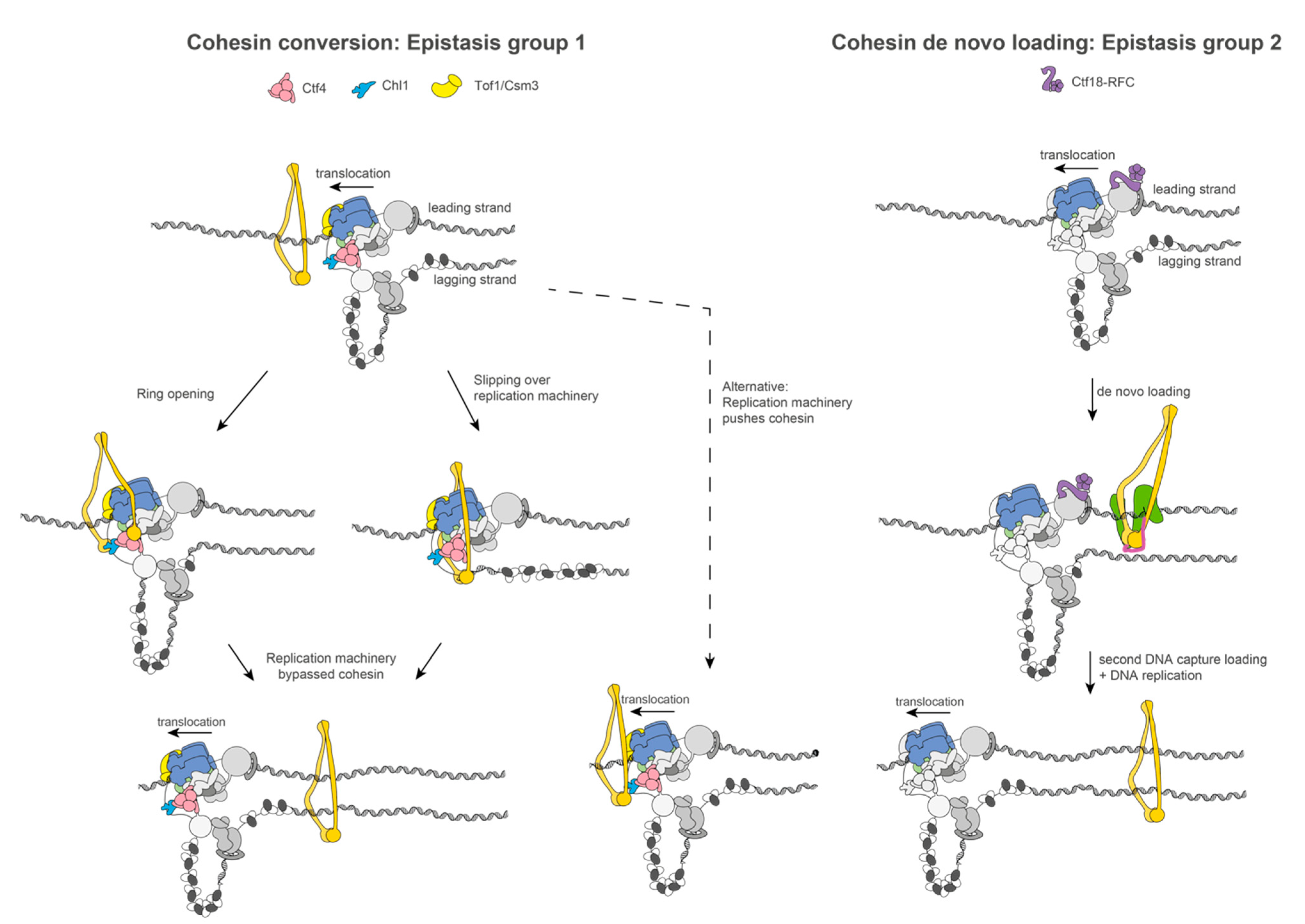
Biology Free Full Text Towards A Structural Mechanism For Sister Chromatid Cohesion Establishment At The Eukaryotic Replication Fork Html
Jul 24, 2017 — The parental dna is shown in dark blue the newly synthesized dna is light blue and the rna primers associated with each strand are red. The ...
The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins. The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins. The newly synthesized dna strands are not shown but the polymerase on each parental strand is shown labeled 1 and 2. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the diagram to.
The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the diagram to describe the name or function of each structure. Use pink labels for the pink targets and blue labels for the blue targets. Show transcribed image text.

A Dna Molecule Is Made Of Four Types Of Nucleotides Adenine Guanine Thymine And Cytosine A Describe How These Nucleotides Are Connected Together To Make A Dna Strand B How Are
The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental duplex). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter duplexes after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red.
The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental duplex. Use pink labels for the pink targets and blue labels for the blue targets. The origin of replication is indicated by the black dots on the parental strands. The dna molecule actually consists of two such chains that spiral around an imaginary axis to form a double helix spiral.
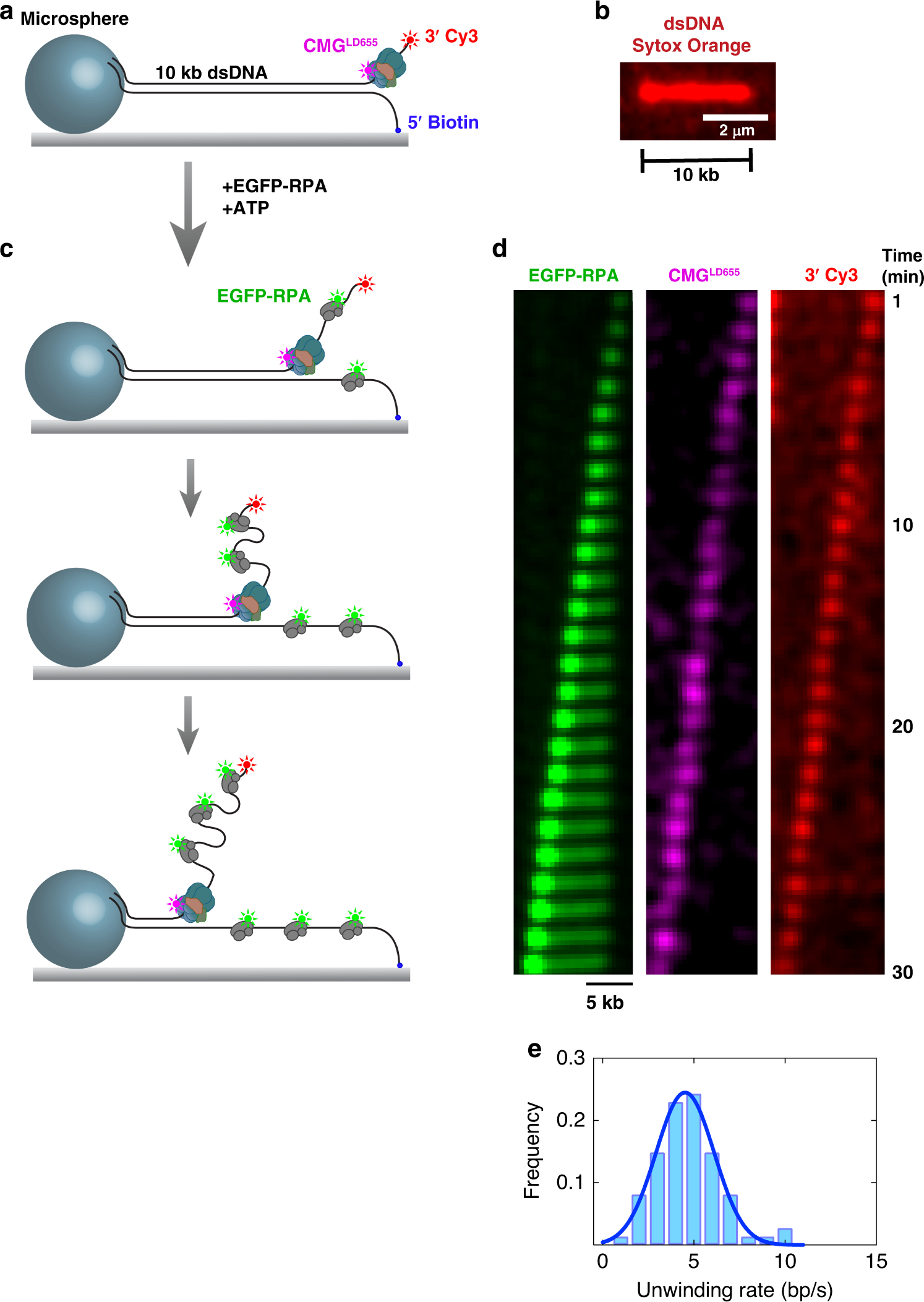
Duplex Dna Engagement And Rpa Oppositely Regulate The Dna Unwinding Rate Of Cmg Helicase Nature Communications
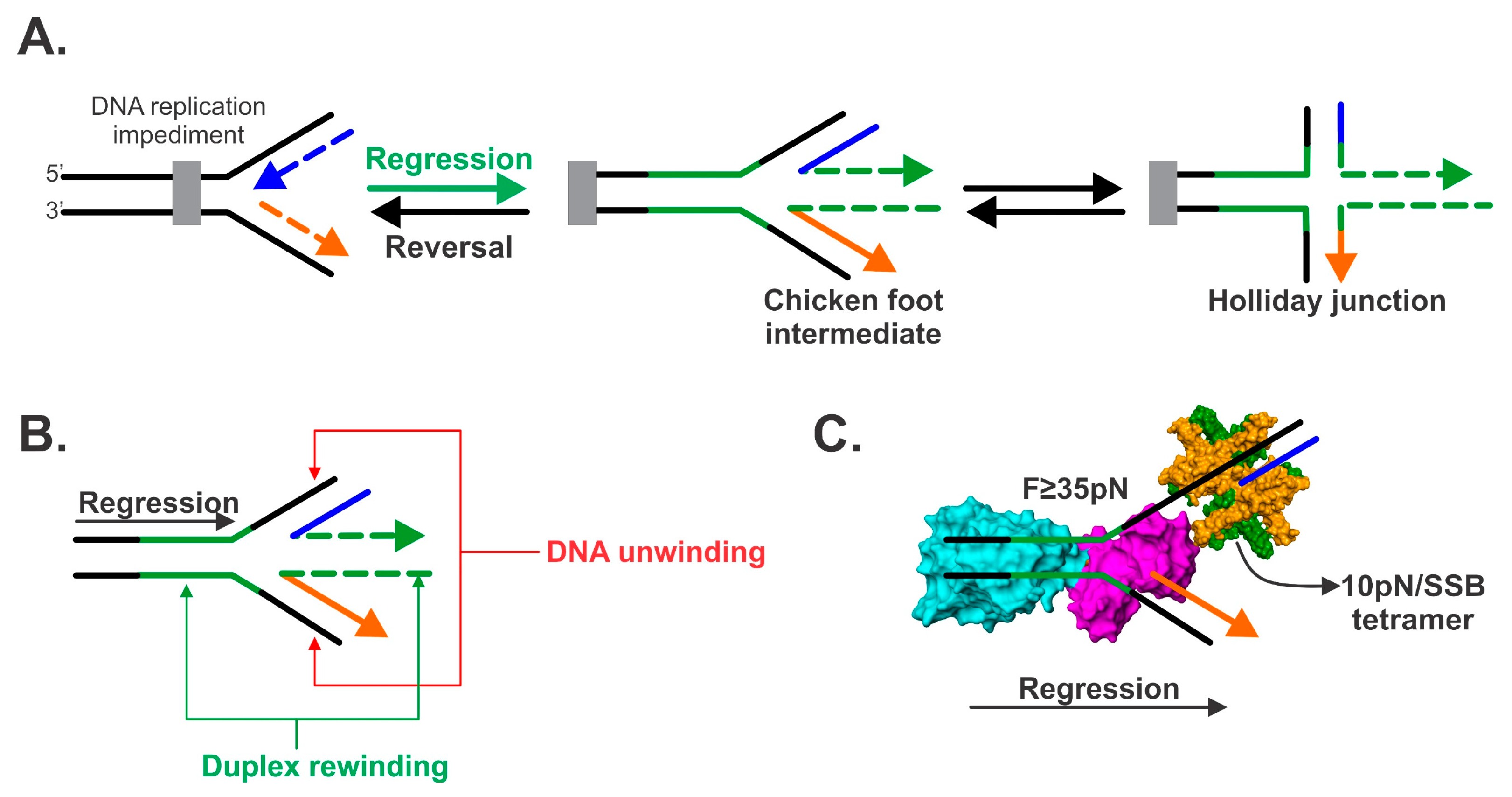
Genes Free Full Text Dna Helicase Ssb Interactions Critical To The Regression And Restart Of Stalled Dna Replication Forks In Escherichia Coli Html
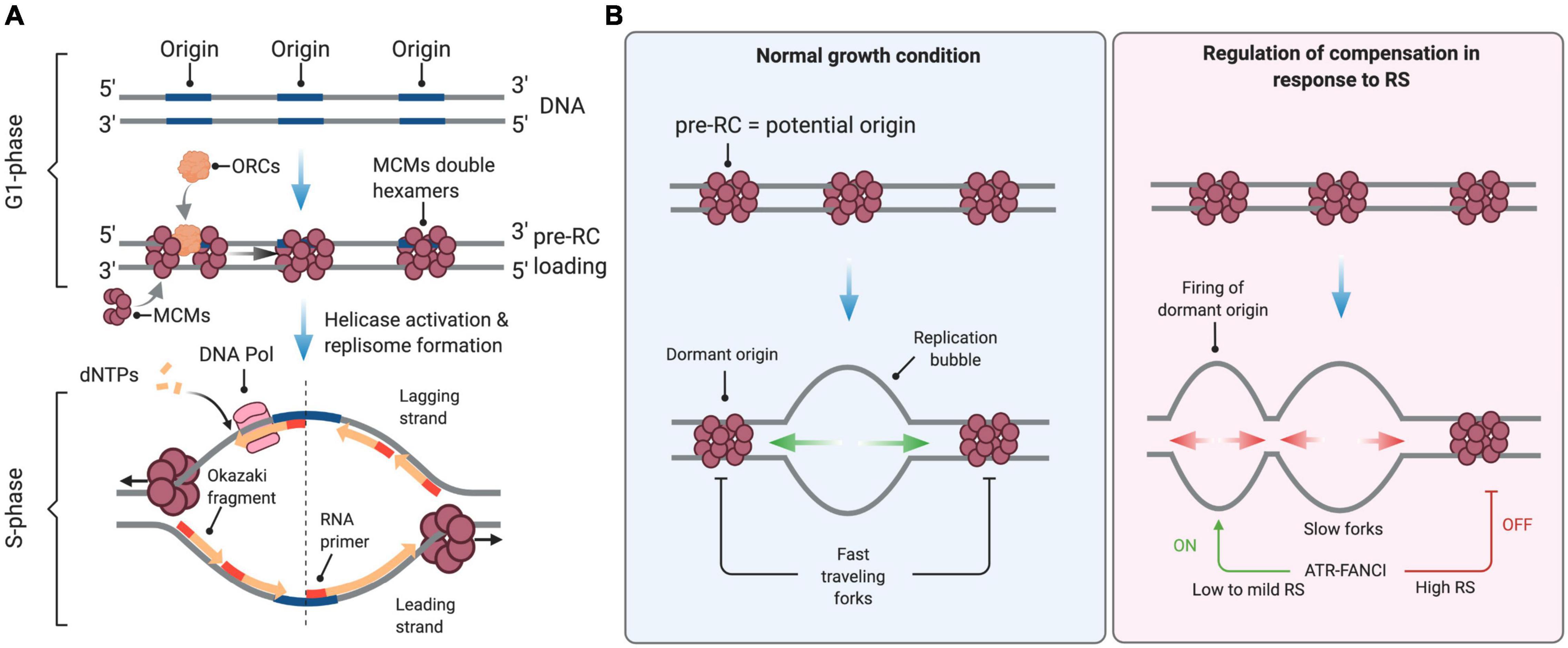
Frontiers The Replication Stress Response On A Narrow Path Between Genomic Instability And Inflammation Cell And Developmental Biology


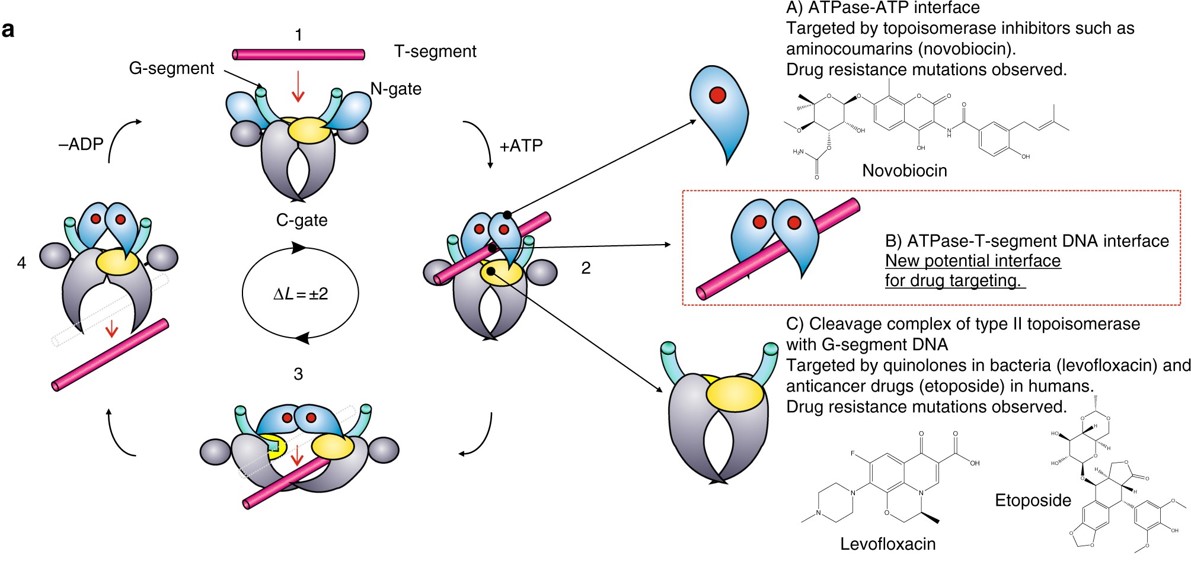










0 Response to "41 the diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental duplex)."
Post a Comment