41 box and pointer diagram
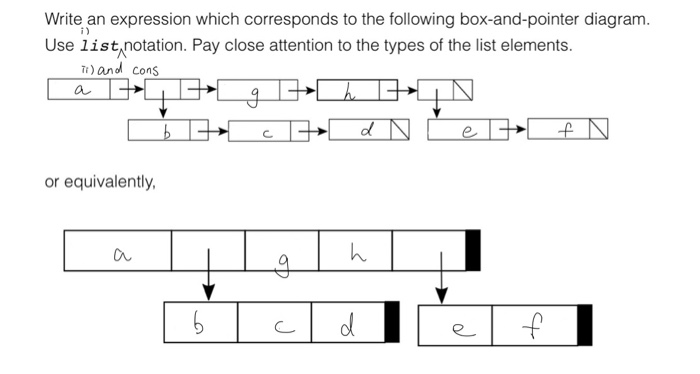
The first is a box and pointer diagrammer. To use the box and pointer diagrammer, just type (view data). (define l (list 1 2 3)) (view l) Figure 1: View of the list (1 2 3) A top-level window will be created containing a diagram of the symbol `l' pointing to the diagram of the list. The window containing the diagram has a label and three ... A pointer in a box & pointer diagram is formed by drawing an arrow. This arrow should typically be drawn from the center of a square to clearly show that it starts from that box and pointing e lsewhere. A simple box with pointers not pointing to anything is shown below: Drawing Simple Box & Pointer Diagrams The simplest type of box & pointer ...
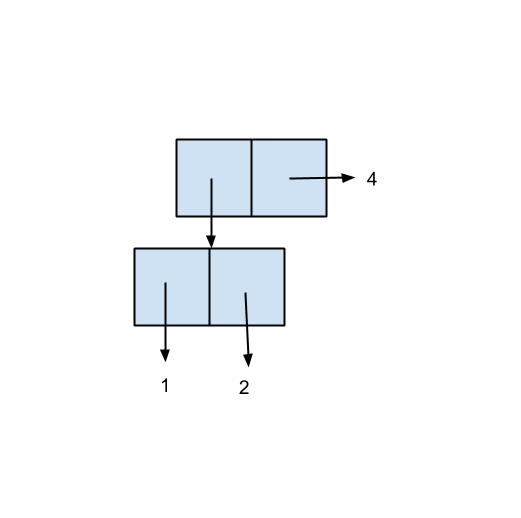
A Box-and-Pointer Diagram displays a snapshot of the variables and their values at a given point of execution of a program. For example, after the code below.5 pages

Box and pointer diagram
Problem 3 (Drawing environment diagrams). Draw the environment diagram that results from the following interactions, and fill in the blank with the value printed: >(define a 8) >(define b 9) > (let ((a 3) (f (lambda (b) (+ a b)))) (f 5)) Problem 4 (List mutation). The following expressions are typed, in sequence, at the Scheme prompt. Circle # ... How to draw a boxes and pointers diagrams. Look at the code. ... If the variable is a non-primitive type, that box is going to contain an arrow.2 pages A Box-and-Pointer Diagram displays a snapshot of the variables and their values at a given point of execution of a program. For example, after the code below.5 pages
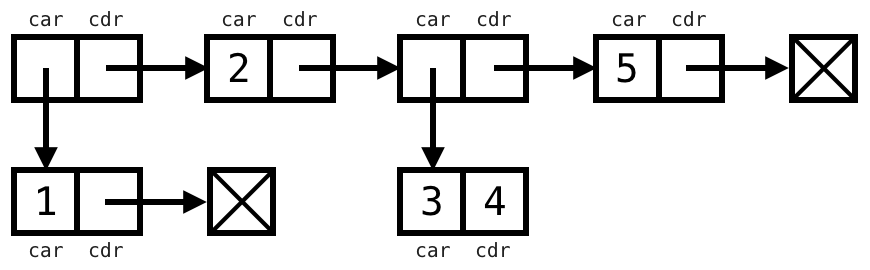
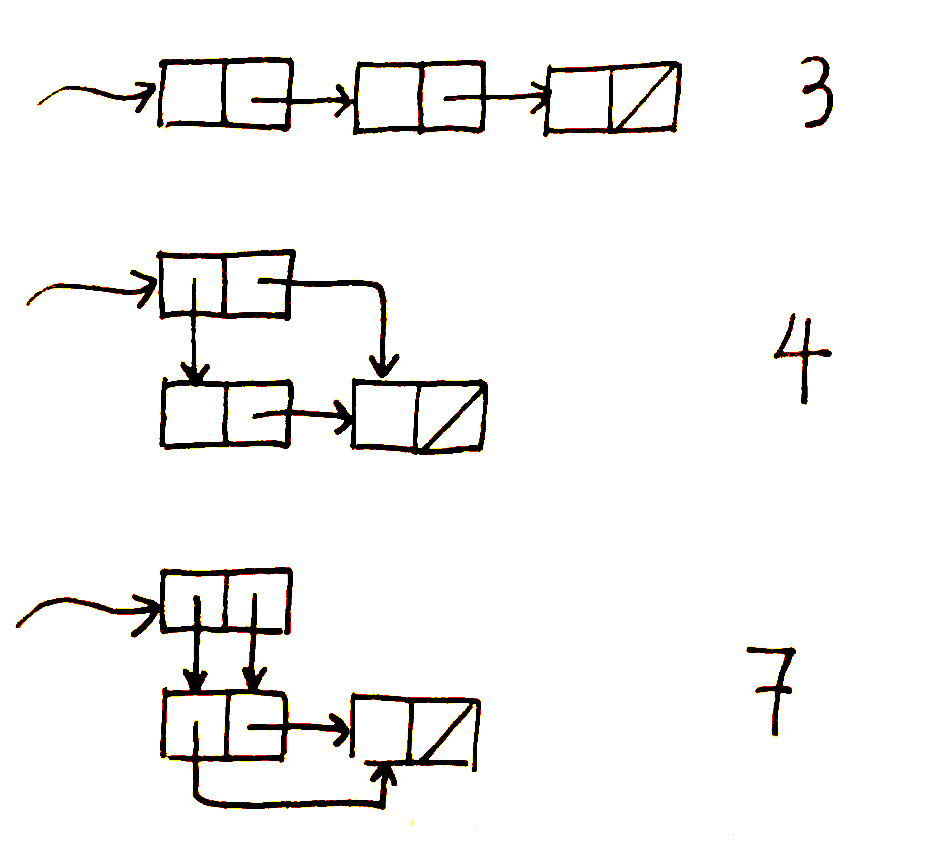
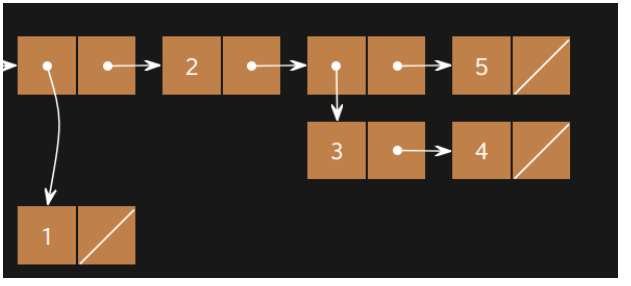
Box and pointer diagram. How to draw the box and pointer diagram for (define list8 (list (cons 3 4) (list 5 6))). From UMass Lowell's COMP.3010 Organization of Programming Languages ... Discussion: Box-and-pointer diagrams help you trace by hand and understand code, especially code that features pointers (and/or arrays, which can be thought ...4 pages A pointer in a box & pointer diagram is formed by drawing an arrow. This arrow should typically be drawn from the center of a square to clearly show that it starts from that box and pointing elsewhere. A simple box with pointers not pointing to anything is shown below: Drawing Simple Box & Pointer Diagrams The simplest type of box & pointer ... Specifically, draw a box-and-pointer diagram with a box for every stack frame, local variable, object, and field in memory at that moment. Include the stack frames for all methods in progress, and illustrate which entities are inside those stack frames. Entities on the stack should be on the left-hand side of the page, and entities on the heap ...
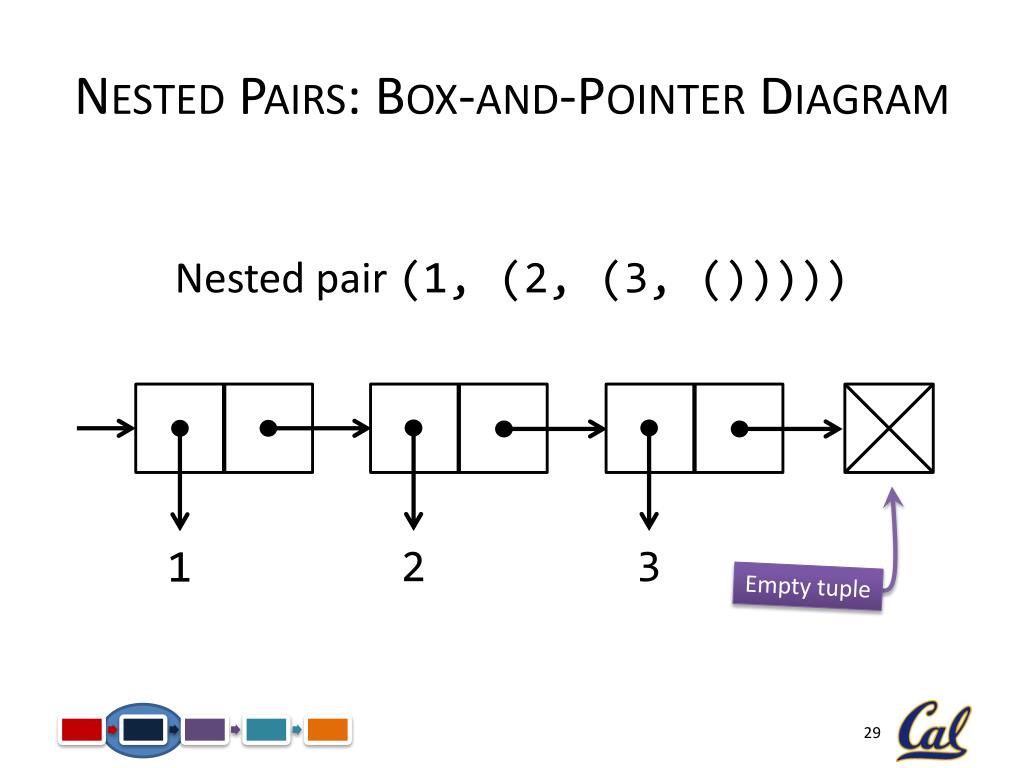
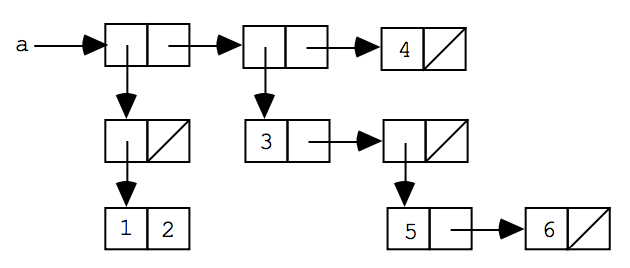
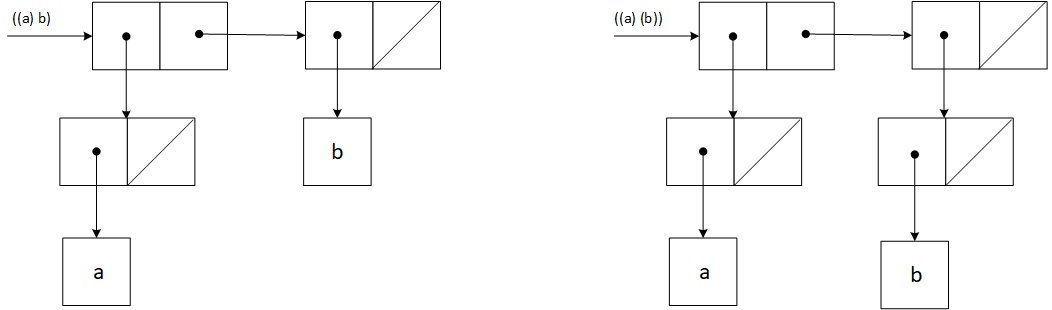
One good approach to learning how box & pointer diagrams work is to be able to talk to a program which knows how to draw them. In Lisp's long ago golden age we had wonderful conversational interfaces on our Lisp machines which let graphics and text be intermingled, along with nice graph-drawing programs from which tools could easily be built to ... Exercises. Draw a box-and-pointer diagram showing the program state after the following Python code has been executed: corge = Foo (1, 2) grault = Foo (3, 4) garply = Bar ( corge, grault) Draw a box-and-pointer diagram showing the program state after the following Python code has been executed: waldo = Foo (5, 6) fred = waldo fred. baz = 7. We can draw box and pointer diagrams for lists by simply rewriting every list as a nested cons. For example, the box and pointer diagram for (list 1 2 3) is the same as the one for (cons 1 (cons 2 (cons 3 '()))): Thus, we learn a very important key idea: every list is a pair. The reverse is not true though - not all pairs are lists. In a box-and-pointer diagram, ordinary variables have a box associated with them, depicting the place in memory where the variable's value is stored.2 pages
Pointers are an abstraction of machine addresses A box-and-arrow diagram p represents at the hardware level p n n for some memory address n. But in C, we are not supposed to care about actual hardware addresses. The view in C of memory is a graph: nodes = chunks of memory (often a struct) edges = pointers That is why box-and-arrow diagrams are ... A Box-and-Pointer Diagram displays a snapshot of the variables and their values at a given point of execution of a program. For example, after the code below.5 pages How to draw a boxes and pointers diagrams. Look at the code. ... If the variable is a non-primitive type, that box is going to contain an arrow.2 pages Problem 3 (Drawing environment diagrams). Draw the environment diagram that results from the following interactions, and fill in the blank with the value printed: >(define a 8) >(define b 9) > (let ((a 3) (f (lambda (b) (+ a b)))) (f 5)) Problem 4 (List mutation). The following expressions are typed, in sequence, at the Scheme prompt. Circle # ...






















0 Response to "41 box and pointer diagram"
Post a Comment