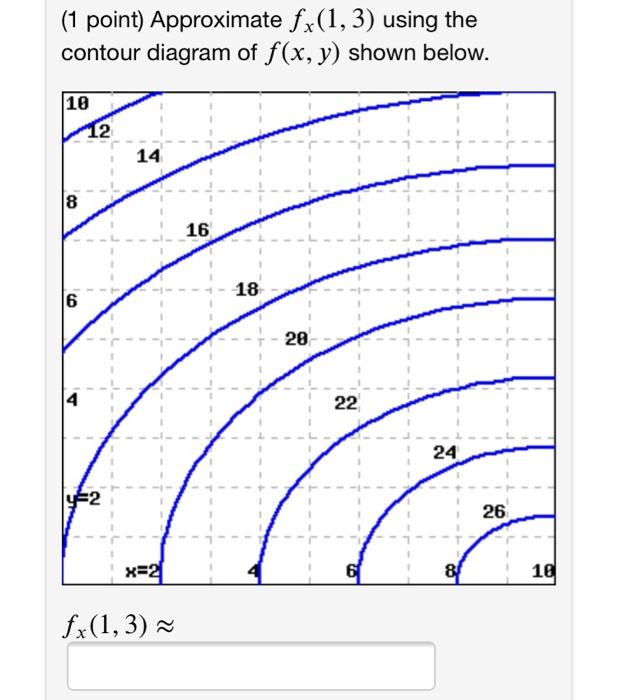
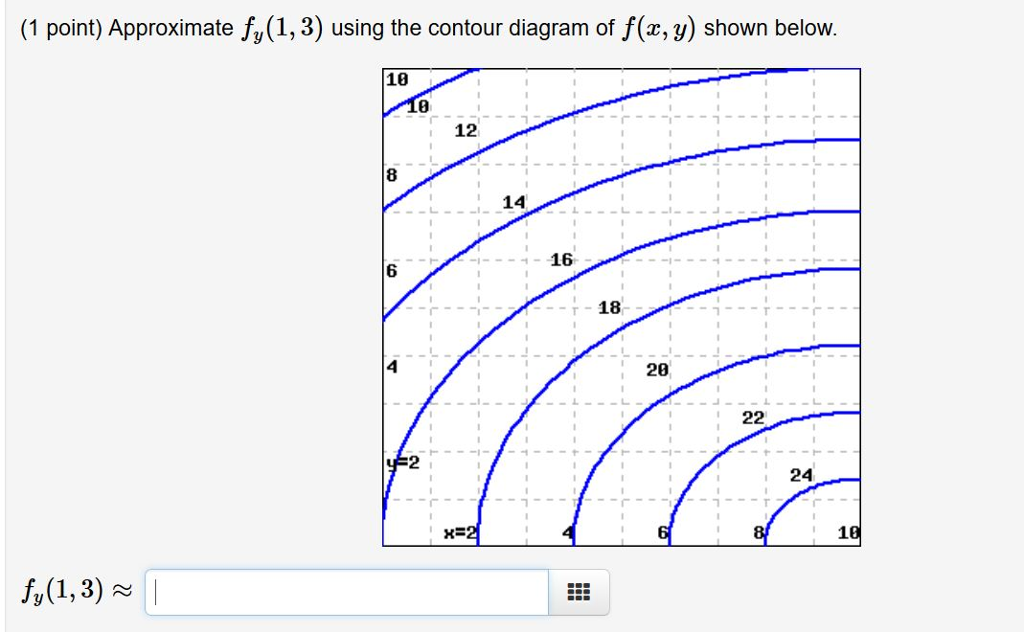
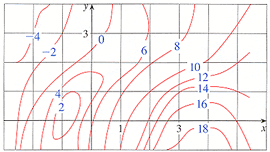
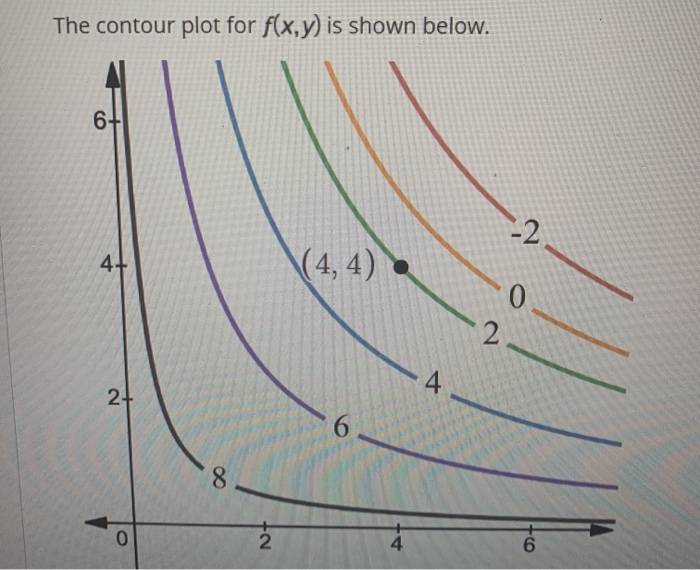
40 approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.
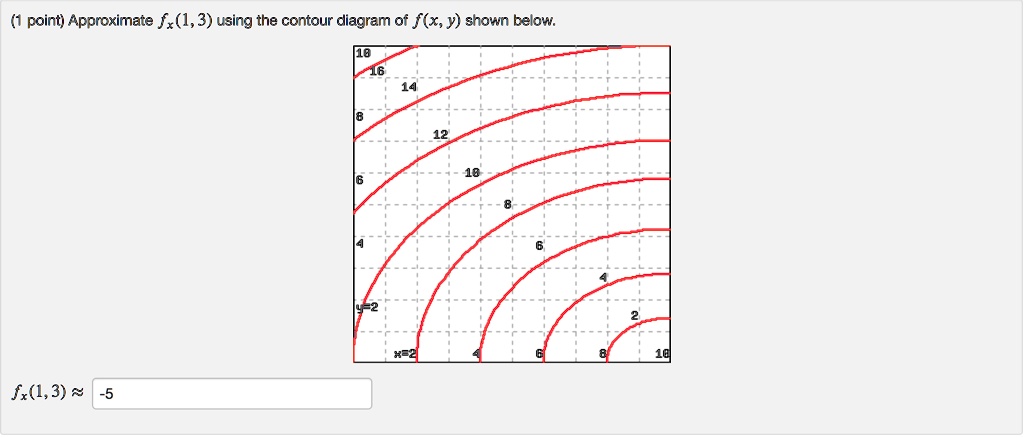
See the answer See the answer done loading. Approximate f x (1,3) using the contour diagram of f (x,y) shown below. Solve for f x (1,3) = ????? Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (21 ratings) Question: Approximate fy(1, 3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. 10 12 8 10 8 x=2 10 fy(1,3) · This problem has been solved! · Expert Answer. Who ...
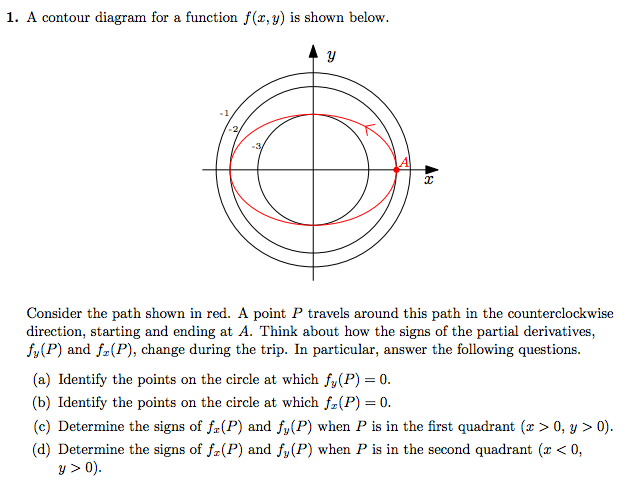
A contour diagram for a function f(x;y) is shown in the gure below. (a) On the graph, sketch a reasonably accurate estimate of the gradient r~f at each of the points A, B, and C.
Approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.
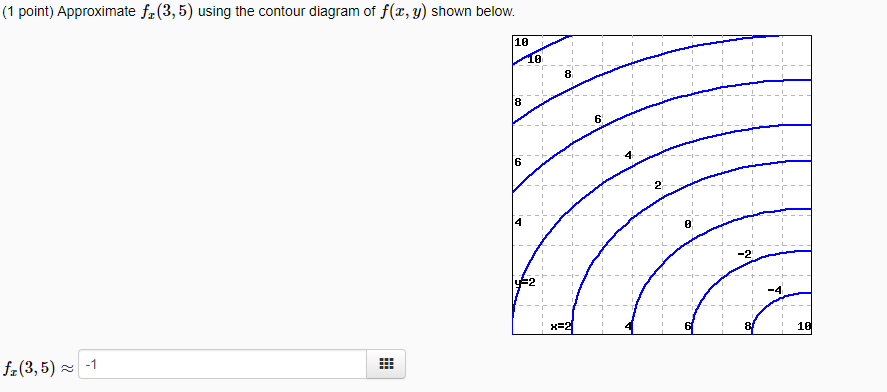
Answer to Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below.... This video explains how to use the slope of a secant line to determine the value of a partial derivative using a contour map.Site: http://mathispower4u.com sponding point (1;0) is one of the corners, and we will consider it separately below. the line y= 0: f(x;0) = x2 2x: Computing the derivative and setting it to 0 we find 2x 2 = 0 =)x= 1. This gives the corner (1;0) as before. the line y= 2: f(x;2) = x2 +2x+4 with critical point x= 1 which is again a corner. Finally, we check the four corners
Approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. from contour map., f (3,5) = 10 now …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Approximate f_y (3, 5) using the contour diagram of g (x, y) shown below. F (x, y) approximate. Question: Approximate fy(1, 3) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. 10 2 8 10 12 14 16 x=2 8 10 fy(1,3) · This problem has been solved! · Expert ... 1. (1 point) Approximate f y(1;3) using the contour diagram of f(x;y) shown below. f y(1;3)ˇ Answer(s) submitted: -0.8 (correct) 2. (1 point) Find the partial derivatives indicated. Assume the variables are restricted to a domain on which the function is defined. z= x5 +x y 6: ¶z ¶x = ¶z ¶y = Answer(s) submitted: 6((xˆ5+x-y)ˆ5)*(5*xˆ4 ... This is the course webpage for Math 53, Lecture 2, Summer 2011 at UC Berkeley, taught by James McIvor. Please carefully read the syllabus for the course. It contains all the important information, including test dates, grading scheme, etc · HW is collected every Tuesday and Friday, and the ...
Mathematics 205 HWK 9a Solutions Section 14.1 p644 Problem 2, §14.1, p644. Use difference quotients with ∆x = 0.1 and ∆y = 0.1 to estimate In Exercises 1-6, use the contour diagram of f in Figure 14.31 to decide if the specified directional derivative is positive, negative, or approximately zero. 1. Question: Approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. f_y(1, 3) almostequalto ______. This problem has been solved! See the answer ... February 21, 2021 - Answer to approximate fx(1,3) using ... the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. This video explains how to use the slope of a secant line to determine the value of a partial derivative using a contour map.site: mathispower4u. (1 pt) approximate f y (1, 3) using the contour diagram ...
Question: Approximate fy(1, 3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. This problem has been solved! See the answer ... 3 3. Determine the sign of f x and f y at the point using the contour diagram of f in the gure below. (a) P (b) Q (c) R (d) S 4. Approximate f x(3;5) using the contour diagram of f(x;y) shown in the gure below. The partial derivative f z, for instance, is simply the derivative of f ( x, y, z) with respect to z, keeping the variables x AND y fixed now. Information about the partial derivatives of a function z = f ( x, y) can be detected also from the contour map of f. Indeed, as one knows from using contour maps to learn whether a path on a mountain is ... f(x+u1h,y)− f(x,y) h = fy. Example 1.3. If the following is a contour diagram for f(x,y) with the z = 0 contour at the origin, going up by 1 for each concentric circle, ... Drawing a vector out from the point (1,1) in the direction of ~u =~i+~j, we can use a difference quotient to approximate the rate of change. Specifically, the vector ~u ...

Lubricants Free Full Text Improvement In The Hard Milling Of Aisi D2 Steel Under The Mqcl Condition Using Emulsion Dispersed Mos2 Nanosheets Html
Now with axes labelled and a plot label : Plot x, x^2, x^3, x^4 , x, 1, 1 , AxesLabel x, y , PlotLabel "Graph of powers of x" -1.0 -0.5 0.5 1.0 x-1.0-0.5 0.5 1.0 y Graph of powers of x Notice that text is put within quotes. Or to really jazz it up (this is an example on the Mathemat-
2 LINEAR APPROXIMATIONS In Example 1, we found that an equation of the tangent plane to the graph of the function f(x, y) = 2 x2 + y2 at the point (1, 1, 3) is: z = 4 x + 2 y - 3
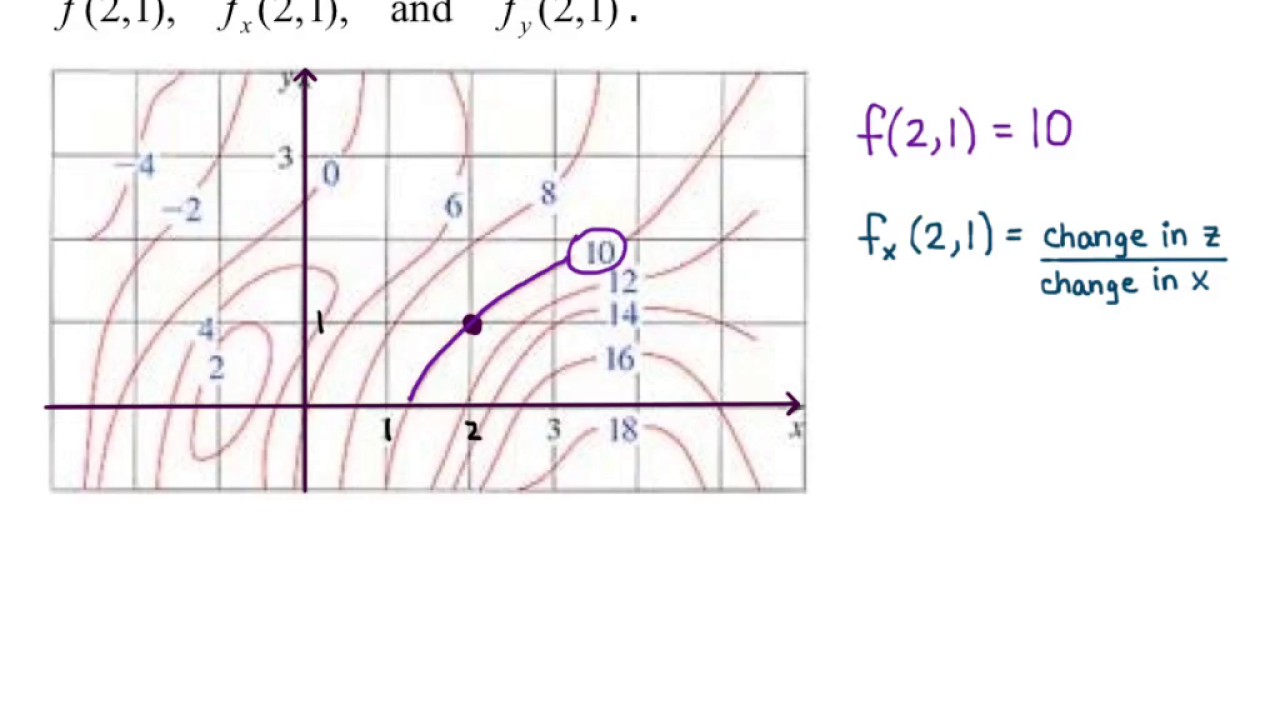
ASSIGNMENT 6 SOLUTION JAMES MCIVOR 1. Stewart 14.3.10 [3 pts] A contour map for a function fis given. Use it to estimate f x(2;1) and f y(2;1). Solution: We can estimate f
Figure 10.3: At left, the graph of f(x;y) = 3 x 2y; at right, its contour plot. (h)Explain how your results are reflected in Figure10.4. Compare this limit to the limit in
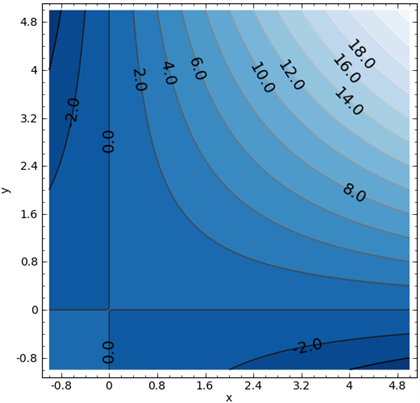
2. Level curves of G (x, y) are shown in the figure below. Find its approximate x- and y-derivatives at (3, 3). Ans: {10/1.3, 10/1.4} 3. Let the figure below be the contour diagram of f (x,y ). Find an approximate x derivative at (2, 2) by using the centered difference quotient. Ans:1/2 4.
16.A contour map is shown below. Elevations are shown in feet. Which side of Amethyst Hill has the steepest slope? A)200 ft/mi B)400 ft/mi C)800 ft/mi D)1,000 ft/mi 17.The topographic map below shows the island of Hawaii. Elevations are measured in feet. What is the approximate average gradient along line XY?
Graphs of Surfaces and Contour Diagrams - 1 Picturing f(x;y): Contour Diagrams (Level Curves) We saw earlier how to sketch surfaces in three dimensions. However, this is not always easy to do, or to interpret. A contour diagram is a second option for picturing a function of two variables.
Contour maps give a way to represent the function while only drawing on the two-dimensional input space. Step 1: Start with the graph of the function. Example function graph. Step 2: Slice the graph with a few evenly-spaced level planes, each of which should be parallel to the -plane.

Lubricants Free Full Text Improvement In The Hard Milling Of Aisi D2 Steel Under The Mqcl Condition Using Emulsion Dispersed Mos2 Nanosheets Html
the value on the boundary is given by the boundary conditions. Namely ui;j = g(xi;yj) for (xi;yj) 2@ and thus these variables should be eliminated in the equation (5). There are several ways to impose the Dirichlet boundary condition. One approach is to let aii = 1;aij = 0;j6= iand fi = g(xi) for nodes xi 2 . Note
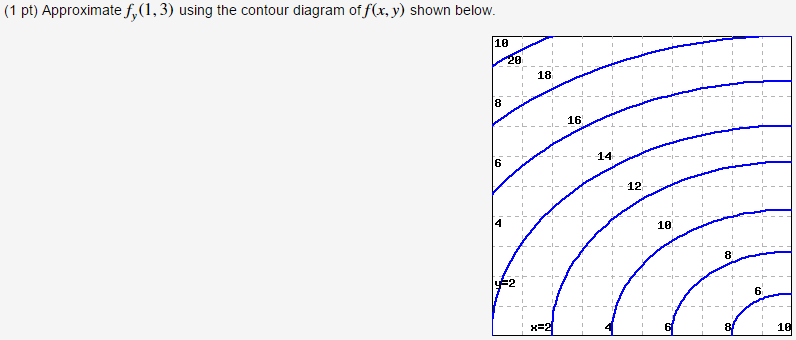
This problem has been solved! ... Approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. 1 point) Approximate f,(1,3) ...
27 Tangent Planes to Level Surfaces Suppose S is a surface with equation F(x, y, z) = k, that is, it is a level surface of a function F of three variables, and let P(x 0, y 0, z 0) be a point on S. Let C be any curve that lies on the surface S and passes through the point P.Recall that the curve C is described by a continuous vector function r(t) = 〈x(t), y(t), z(t)〉.
f x(1;3) = u0(1) = 18. Similarly, f y(1;3) is the derivative of v(y) = f(1;y) at y= 3. Since v(y) = 3y and v0(y) = 3, then f y(1;3) = 3. Remark 2.2. In general, to compute the partial derivative f x(x;y) we hold yconstant and take the (usual) derivative with respect to x. Similarly, to compute f y(x;y), we hold xconstant and take the derivative ...

Answer The Following Questions For The Given Contour Diagram Of F X Y Below A Estimate F 4 Homeworklib
Transcribed image text: Approximate fy( 1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. Consider the surface F(x, y, z) = x3z9 + sin(y3z9) +4=0.
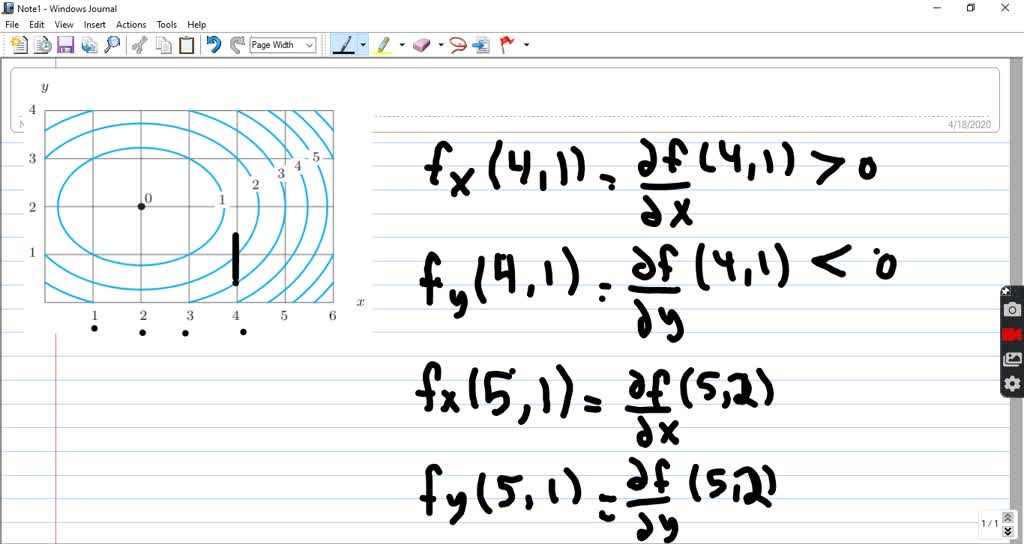
Solved Using The Contour Diagram For F X Y In Figure 8 36 Decide Whether Each Of These Partial Derivatives Is Positive Negative Or Approximately Zero A Quad F X 4 1 B F Y 4 1 C F X 5 2 D Quad
Let f(x,y) denote a function of two variables and suppose that every circle centered at the origin is a level curve, then the graph z = f(x,y) is a sphere ... whose gradient is always nonzero. Suppose that fy = 2 fx. Then the level curves of f(x,y) are straight lines of slope -2. False. Find an equation of the tangent plane to the parametric ...
Question: Approximate f_y (1, 3) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. f_y (1, 3) = This problem has been solved! See the answer ...

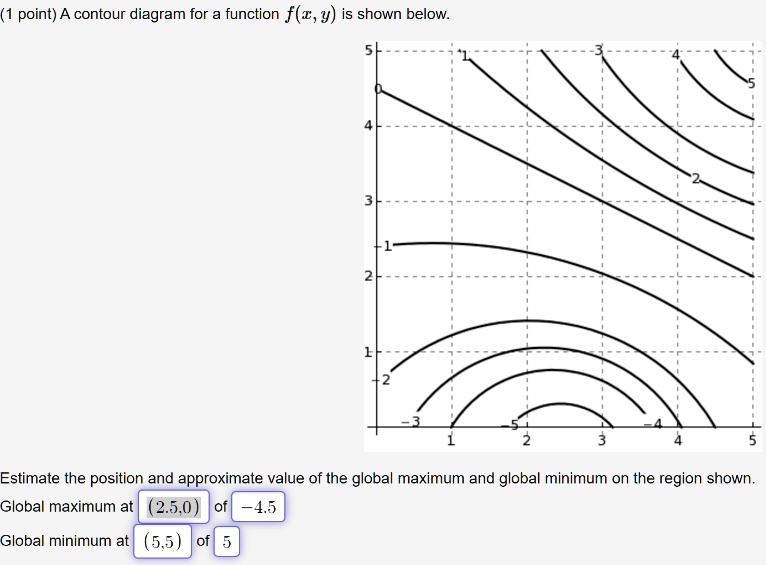
A Contour Diagram For A Function F X Y Is Shown Below Estimate The Position And Approximate Value Of The Global Maximum And Global Minimum On The Region Shown Study Com
(fy), so if we fix x and allow y to vary, fyy is the rate of change of fy as y increases. The level curves are closer together (in the y -direction) at points above P than at those below P , demonstrating that f increases more quickly with respect to y above P .
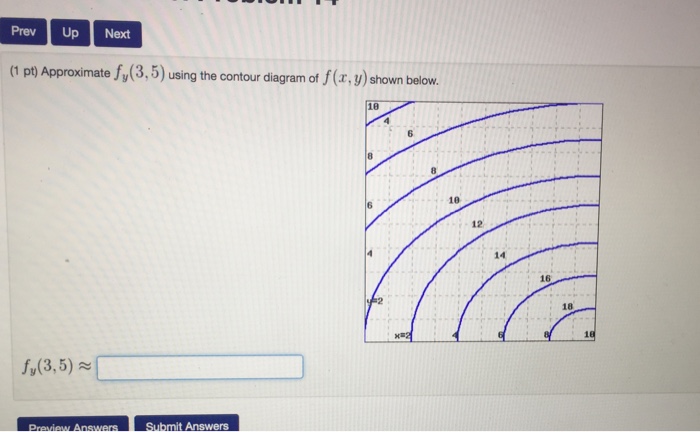
fullscreen Expand. Transcribed Image Text. Approximate f (3, 5) using the contour diagram of f (x, y) shown below. 18 12 10 6 X=2 10. check_circle.
Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. fx(3,5)? ... What happens next? After payment, your answer will be immediately delivered to your email (so don't forget to check your spam folder in case you don't see anything!)
Question: Approximate fy(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
Question: Approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. The lower left corner is (0,0). fy(1,3)? ...
• Revisit the function f (x,y) = x ln y2 − x. Sketch the domain, as done in Figure 3 of the text. Then go on to sketch the set of points (x, y) where f (x, y) = 0, f (x,y) > 0, f (x,y) < 0. • Pass around some interesting solid figures, and have the students attempt to sketch the appropriate contour lines for the solids. WORKSHOP/DISCUSSION
Math 205 HWK 11 Solns continued §14.7 p687 Problem 19, §14.7, p687. Use the given level curves of the function z = f(x,y) to decide the sign (positive, negative, or zero) of each of the following partial derivatives at the point P indicated
Answer to Approximate fy(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. ...
Ask about how fx changes in the y-direction and about fy. 6. Figure 9.7 is a contour diagram for f(x,y) with the x and y axes in the usual directions. At the point P, if x increases, what is true of fx(P)? If y increases, what is true of fy(P)? (a) Have the same sign and both increase. (b) Have the same sign and both decrease.
sponding point (1;0) is one of the corners, and we will consider it separately below. the line y= 0: f(x;0) = x2 2x: Computing the derivative and setting it to 0 we find 2x 2 = 0 =)x= 1. This gives the corner (1;0) as before. the line y= 2: f(x;2) = x2 +2x+4 with critical point x= 1 which is again a corner. Finally, we check the four corners
This video explains how to use the slope of a secant line to determine the value of a partial derivative using a contour map.Site: http://mathispower4u.com
Answer to Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below....

An Improved Meshless Artificial Viscosity Technology Combined With Local Radial Point Interpolation Method For 2d Shallow Water Equations Sciencedirect











0 Response to "40 approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below."
Post a Comment