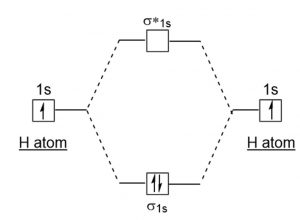
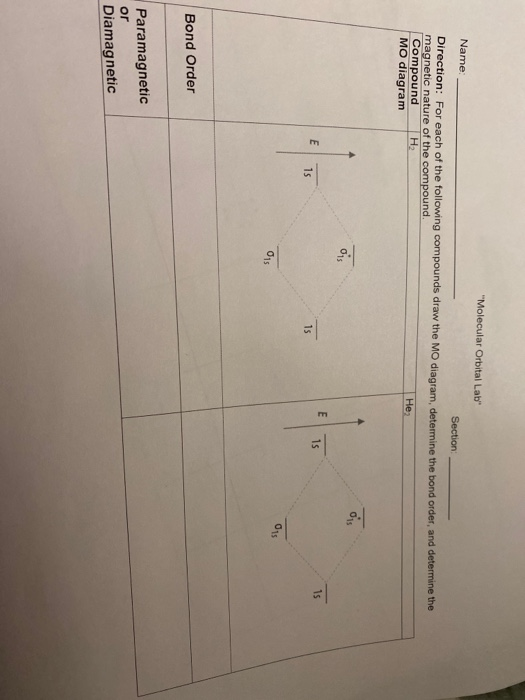
39 use the mo diagram given to find the bond order for h2-.
Write the molecular orbital diagram of N2+ and calculate their bond order why nitrogen have different structure of molecular orbital theory An atomic orbital is monocentric while a molecular orbital is polycentric. Chemistry questions and answers. Use the MO diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether H2 exists. Enter the bond order as a decimal number, eg. 0.5. 1.0, 1.5, etc ?* ???Y-average energy H2ls. Question: Use the MO diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether H2 exists.
The bond order shows the number of chemical bonds present between a pair of atoms. For instance, the bond order of diatomic nitrogen N≡N is 3 and bond order between the carbon atoms in H-H≡C-H is also three. The bond order describes the stability of the bond. The molecular orbital provides an easy understanding of the concept of the bond ...
Use the mo diagram given to find the bond order for h2-.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine Feb 3, 2021 — For H2, bond order = 1/2 (2-0) = 1, which means H2has only one bond. The antibonding orbital is empty. Thus, H2 is a stable molecule. Again, in ... 4:32The bond order of H2- is also calculated and the meaning of this ... and how to determine this for any ...Jan 3, 2021 · Uploaded by Principia
Use the mo diagram given to find the bond order for h2-.. Bond order of B2 molecule. So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = .5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond. Valence Bond Model vs. Molecular Orbital Theory . Because arguments based on atomic orbitals focus on the bonds formed between valence electrons on an atom, they are often said to involve a valence-bond theory.. The valence-bond model can't adequately explain the fact that some molecules contains two equivalent bonds with a bond order between that of a single bond and a double bond. In molecular orbital theory, bond order is also defined as half of the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. For a straightforward answer: use this formula: Bond order = [(Number of electrons in bonding molecules) - (Number of electrons in antibonding molecules)]/2. 5:31and anti bonding molecular orbitals are empty. So as all the electrons in hydrogen molecule are paired up ...Jun 8, 2020 · Uploaded by Edmerls
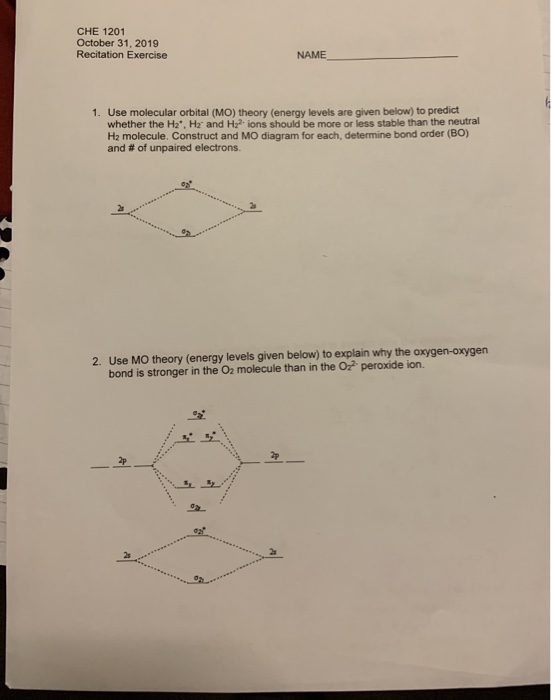
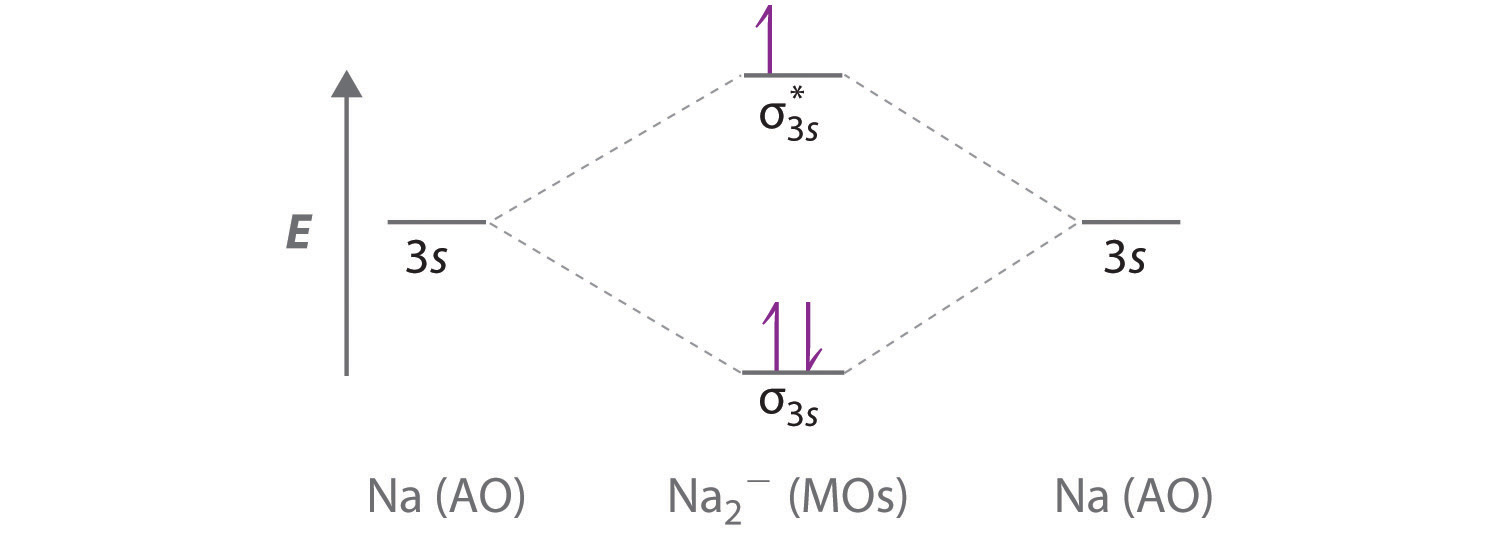
9:53In this video, we take a detailed look at the molecular orbitals of ... in this video are: bonding MO's ...Aug 6, 2011 · Uploaded by Ben's Chem Videos Use the drawing of the MO energy diagram to predict the bond order of Li2+. Express the bond order as an integer or fraction. Part B. Use the drawing of the MO energy diagram to predict the bond order of Li2?. Express the bond order as an integer or fraction. Part C. Which molecules are predicted to exist in the gas phase? Check all that apply 4:22This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the H2+ ion. The bond order of H2+ ...Jan 2, 2021 · Uploaded by PrincipiaMissing: find | Must include: find From the M. O. Diagram of H2 molecule, we get bond order of H2 = (Nb - Na)/2 = (2–0)/2 = 1.2 answers · Top answer: In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to be drawn. According ...
Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, H− 2 has three electrons while H+ 2 has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one σ1s and one σ* 1s MO by conservation of orbitals. If you calculate their bond order, you get: BOH+ 2 = 1 2(Bonding − ... In the article Bond order formula, you have grasped the formulas to find the bond order based on Molecular Orbital Theory and Lewis structure. You can explain the information conveyed by the bond order, such as stability, number of bonds, etc. Use an MO diagram to find the bond order and predict whether H2- exists. Molecular orbitals: Molecular orbitals are gotten by joining the nuclear orbitals on the particles in the atom. Hint: First draw a molecular orbital diagram (MOT) where the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The total electrons associated with the molecules are filled in the MOT diagram. To solve this question, we need to write the molecular orbital configuration. To find out the bond order from the molecular orbital configuration is:
The correlation diagrams for nitrogen and carbon monoxide and the first are nearly parallel to the corresponding orbital energy curves. Bond order for N2 is 3; bond order for N2- is and bond order for N2+ is I have not included pictures of the MO diagrams that show the orbital energies. N2+ has less bond energy.
So, the formula to find bond order is. Bond order = 1 2 (Number of electrons in BMO) - (Number of electrons in ABMO) Bond order = 1 2 (8) - (2) Bond order = 1 2 (6) Bond order = 3. - N 2 molecules are diamagnetic, with no unpaired electrons. This means half of the electrons spin clockwise and half of the electrons spin anticlockwise.
In the formation of B 2 molecule, three valence electrons of each boron atom i.e. 6 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies. MO electronic configuration: Bond order: Here Nb = 4, Na = 2 Bond order = The two boron atom is B2 molecules are linked by one covalent bond.
Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms; in diatomic nitrogen (N≡N) for example, the bond order is 3, while in acetylene (H−C≡C−H), the bond order between the two carbon atoms is 3 and the C−H bond order is 1. Bond order indicates the stability of a bond. In a more advanced context, bond order does not need ...
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [(2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the if we draw its MOT DIAGRAM, 2 e's enter the Bonding molecular Orbital and 2 .
Answer (1 of 2): In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to be drawn. According to MOT number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to total number of molecular orbitals formed.Electronic configuration of H is 1s1. when two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on combi...
Then, find the minimum energy of this curve two ways. (a) Use the bond energy found in Table 8.1 to calculate the energy for one single HCl bond (Hint: How many bonds are in a mole?) (b) Use the enthalpy of reaction and the bond energies for H 2 and Cl 2 to solve for the energy of one mole of HCl bonds.

Use Molecular Orbital Theory To Determine Whether He2 2 Or He2 Is More Stable Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For Each And Explain Study Com
The bond order tells us the average number of bonds between the bonded atoms. In a diatomic molecule such as `O_2`, the bond order simply tells the number of bonds between the two atoms. The bond order can be interpreted from MO diagrams using the following formula: `"Bond Order" = 1/2 [("Bonding "e^-)-("Antibonding " e^-)]`
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and σ∗. 1s is higher in energy. Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical ...
Energy Level Diagram For Molecular Orbitals Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Chemistry Class 11
A further example is given using the NH3 MO diagram. Here, they calculate the bond order as 3, ignoring the fact that the NH3 a1 orbital is weakly bonding. If we were to in theory calculate the MO diagram for NH3 in a trigonal planar geometry (same as for BH3), we would also get the bond order as 3.
The order of a covalent bond is a guide to its strength; a bond between two given atoms becomes stronger as the bond order increases (Table 1 in Chapter 8.1 Valence Bond Theory). If the distribution of electrons in the molecular orbitals between two atoms is such that the resulting bond would have a bond order of zero, a stable bond does not form.
The bond order of N2 (nitrogen) - nitrogen molecule has a triple bond, so the bond order is three. Step 1. Write the electron configuration of a N2 molecule. Electronic configuration of N2 = (σ2s)2 (σ*2s)2 n (2px)2 n (2py)2 n (2pz)2. Step 2. From the above electron configuration, put the values in the formula.

Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of H2 02 And N2 Molecules And Calculatetheir Bond Orders As Brainly In
The bond order varies from one molecule to another. Oxygen is a diatomic molecule. Let us first know what is meant by bond order. Bond order. The bond order may be defined as half the difference between the number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals (Nonbonding) and the number of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital. Formula ...
Problem Details. Use an MO diagram to find the bond order and predict whether H 2− exists. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Bond Order Concept Videos. All Chemistry Practice Problems MO Theory: Bond Order Practice Problems. Q. Draw Lewis structures and MO diagrams for CN+, CN, and CN-. According to the Lewis model, which species is ...
Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration.
Answer (1 of 4): Hi guys let me tell u one short trick for finding bond order… First of all for the given molecule add up the total no of electrons present in that molecule.. For example here in N2 we have 7+7 =14 electrons. Now remember this table.. ELECTRONS = BOND ORDER 10 = 1 11 = 1.5 ...
2:20Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hydrogen Gas (H2).Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total.Bonding ...Jun 9, 2017 · Uploaded by chemistNATE
Bond Order. The bond order for a molecule can be determined as follows: bond order = ½ (bonding electrons − antibonding electrons). Therefore, the H 2 molecule has a bond order of ½ (2 − 0) = 1. In other words, there is a single bond connecting the two H atoms in the H 2 molecule. In the case of He 2, on the other hand, the bond order is ...
4:32The bond order of H2- is also calculated and the meaning of this ... and how to determine this for any ...Jan 3, 2021 · Uploaded by Principia
Feb 3, 2021 — For H2, bond order = 1/2 (2-0) = 1, which means H2has only one bond. The antibonding orbital is empty. Thus, H2 is a stable molecule. Again, in ...
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine

Complete This Molecular Orbital Diagram For Cn Then Determine The Bond Order Note That The 1s Homeworklib






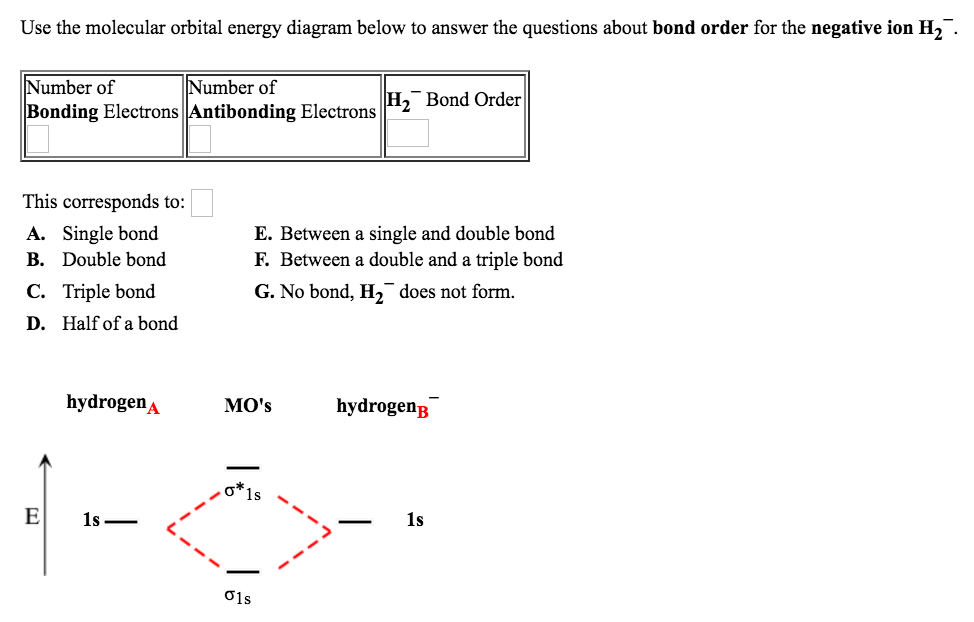

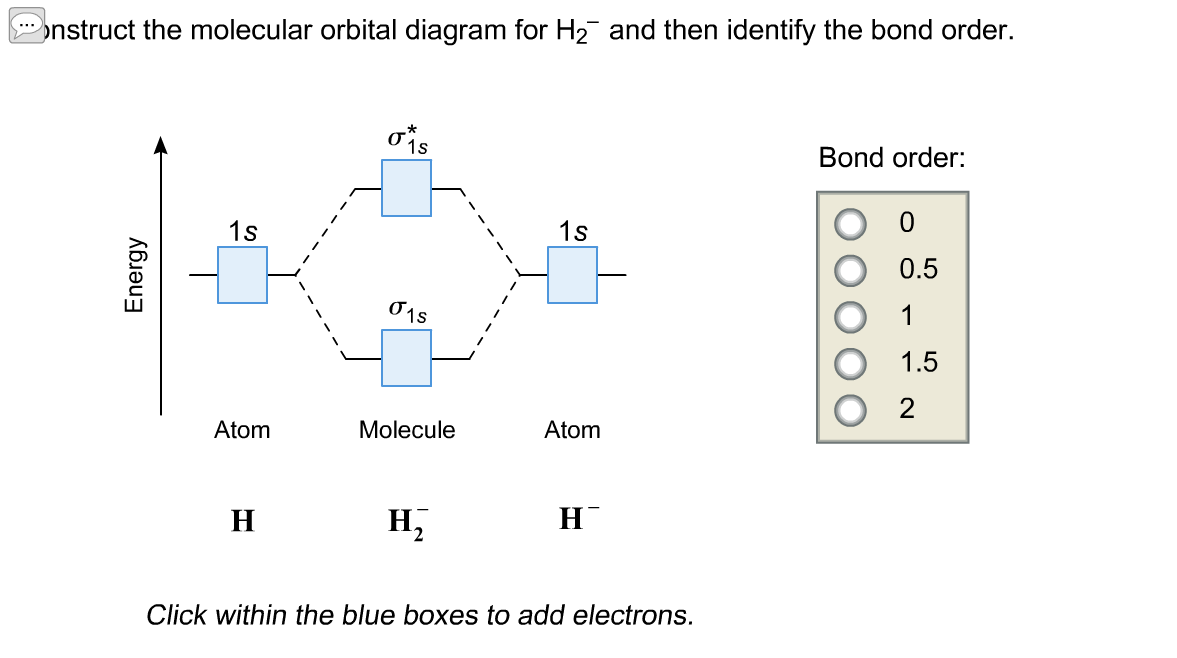











0 Response to "39 use the mo diagram given to find the bond order for h2-."
Post a Comment