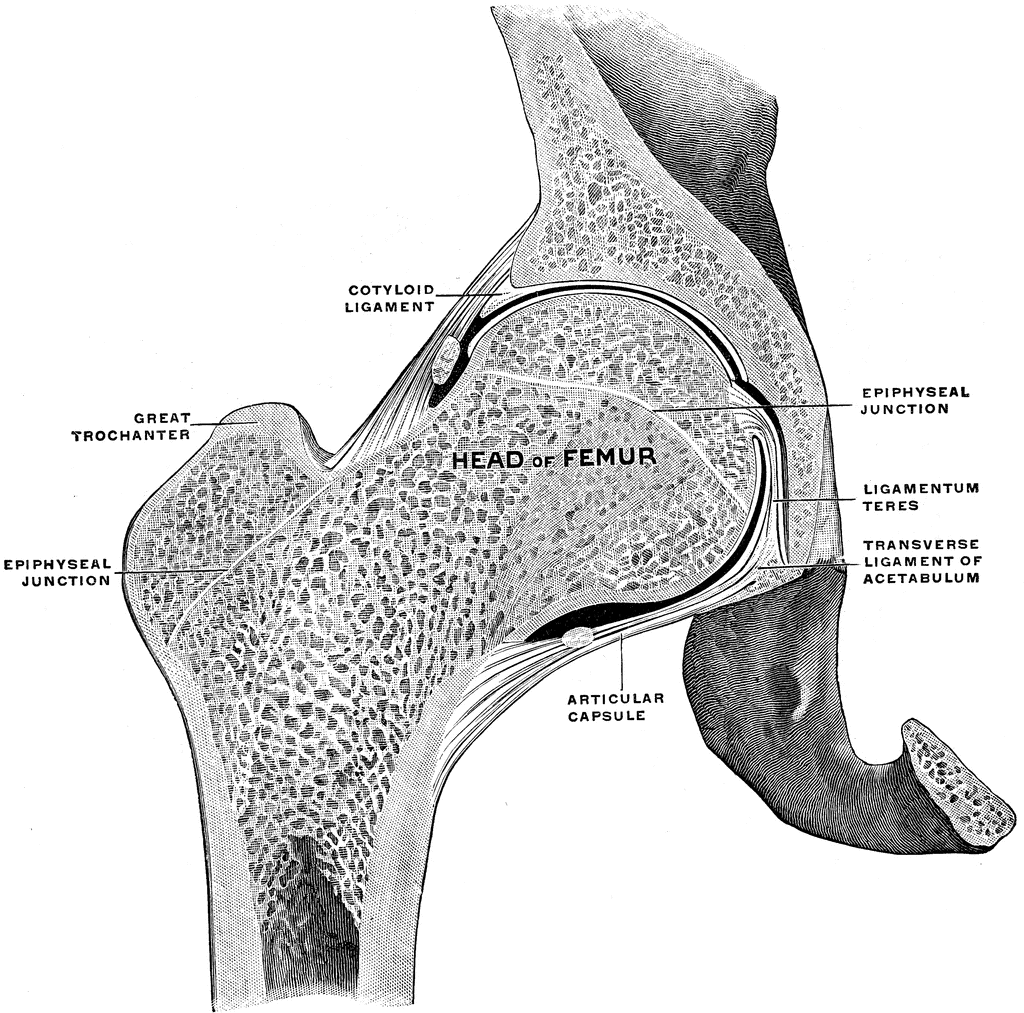
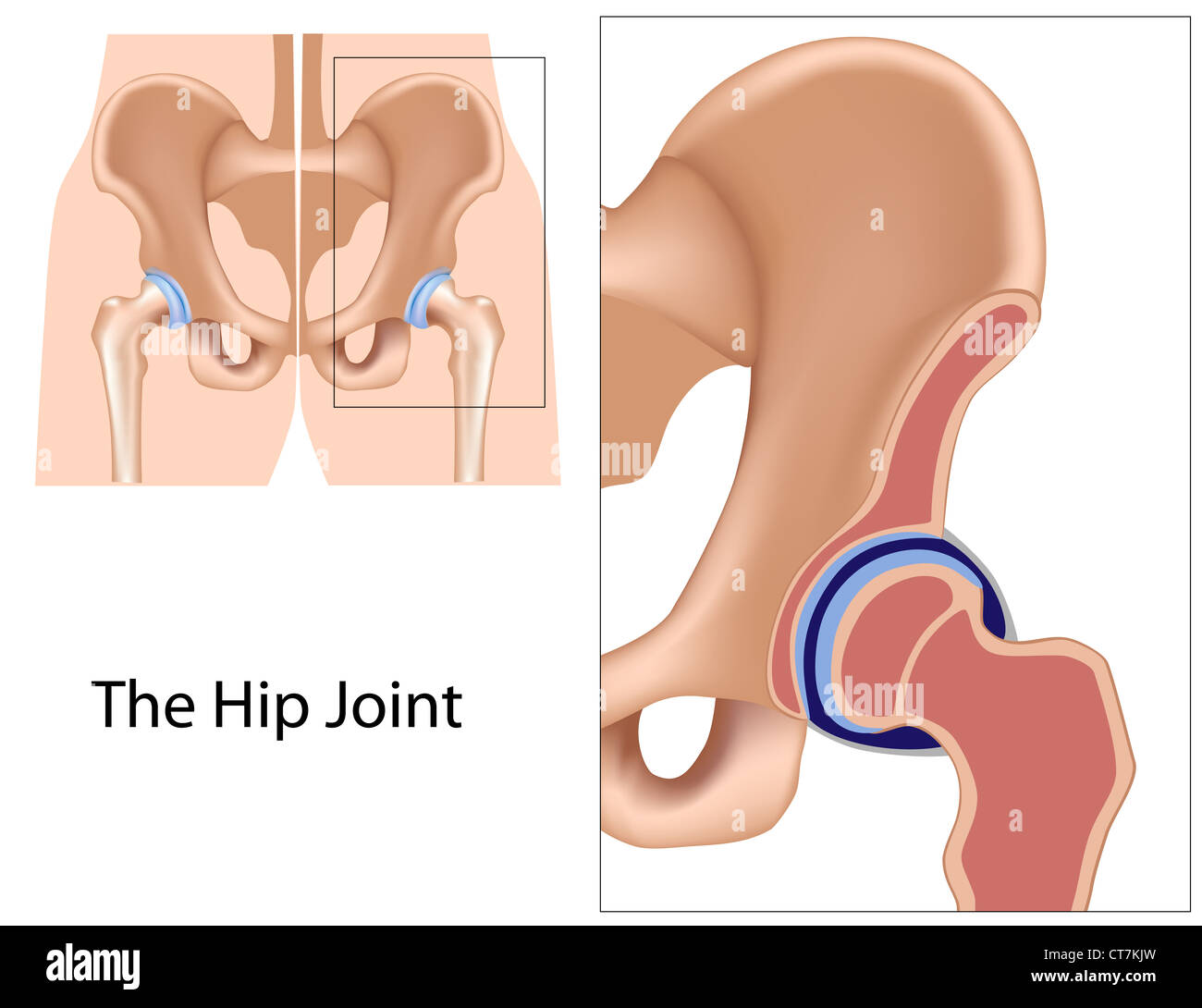
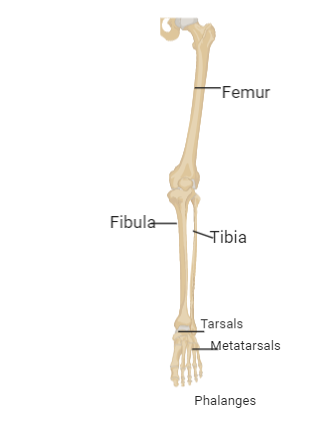
39 the diagram shows a frontal section of the hip joint
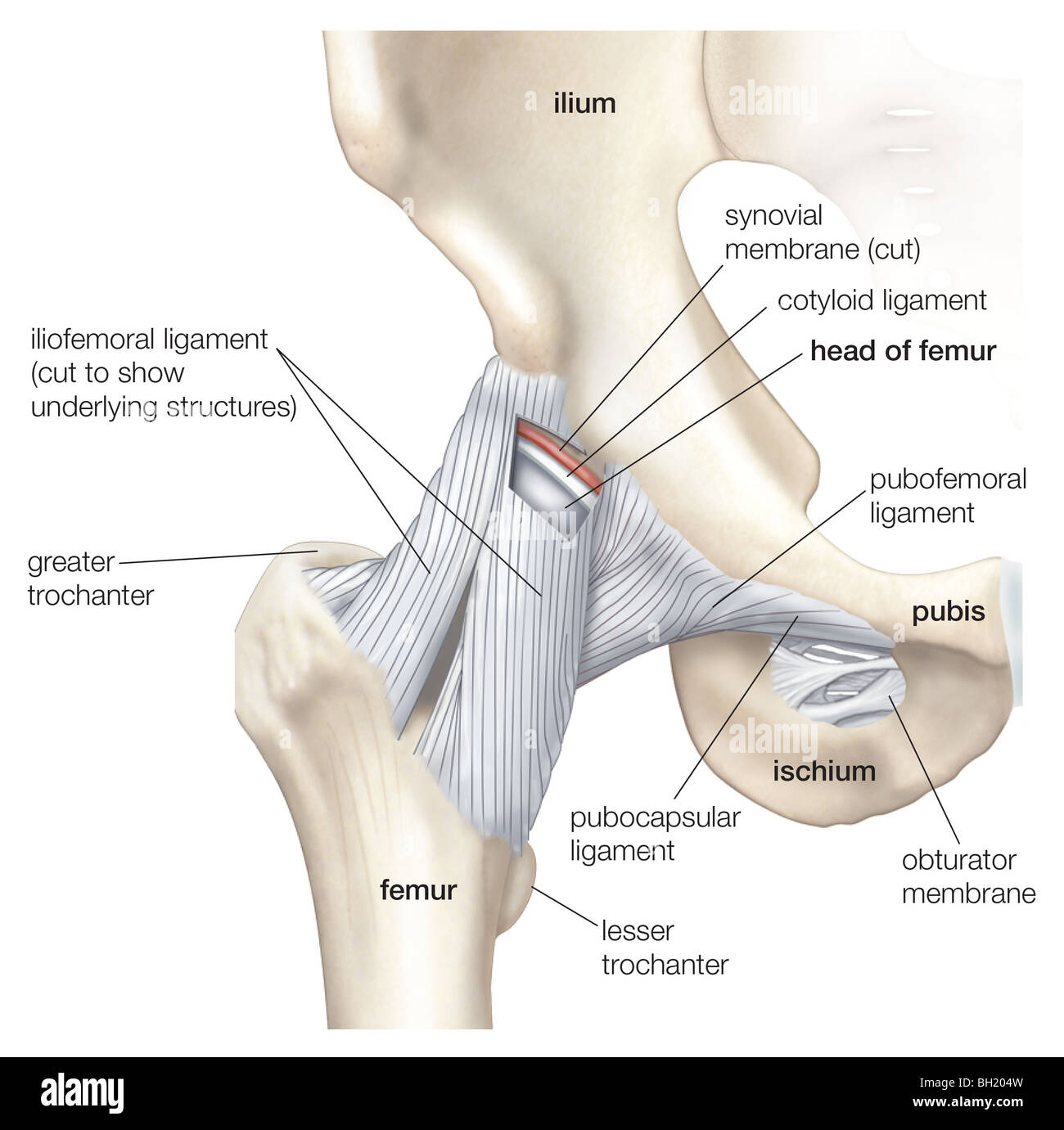
Start studying hip joint frontal section. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Hip Anatomy, Function and Common Problems Front View of the Hip Joint Bones. Normally, a smooth cushion of shiny white hyaline (or articular) cartilage about 1/4 inch thick covers the femoral head and the acetabulum.The articular cartilage is kept slick by fluid made in the synovial membrane (joint lining).
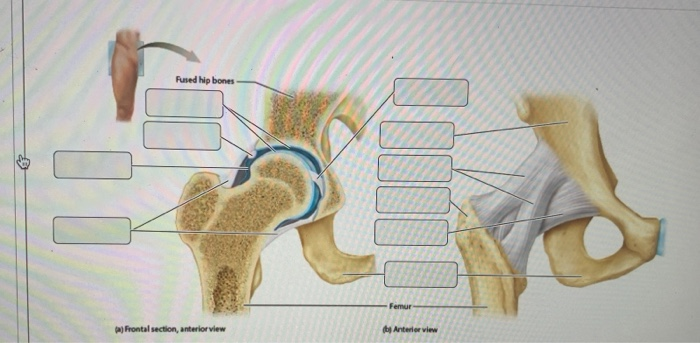
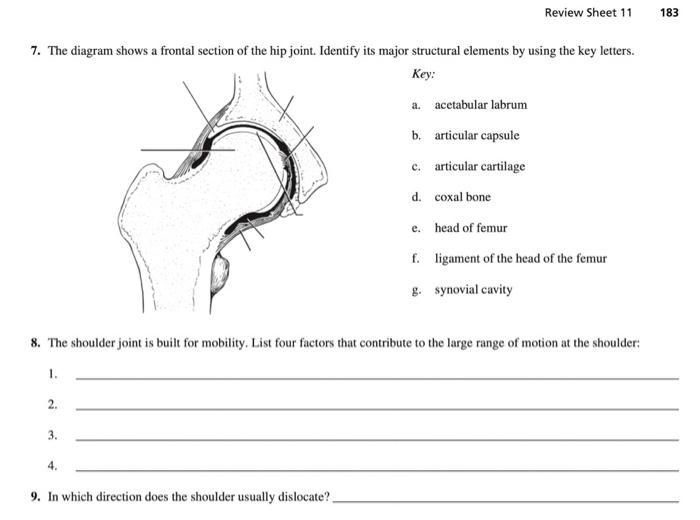
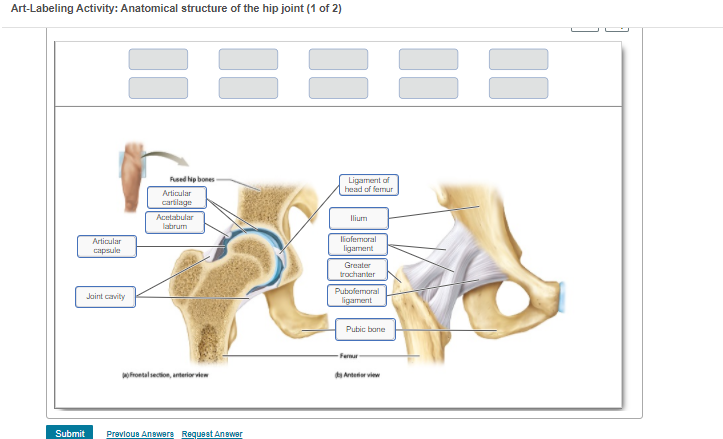
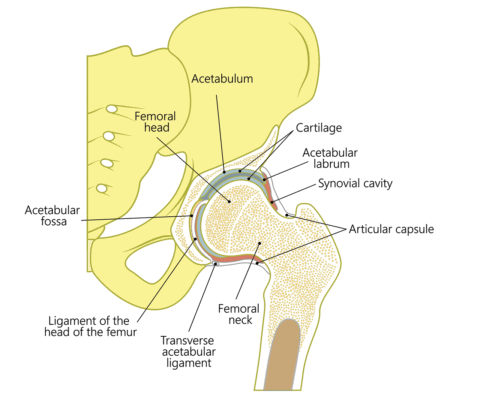
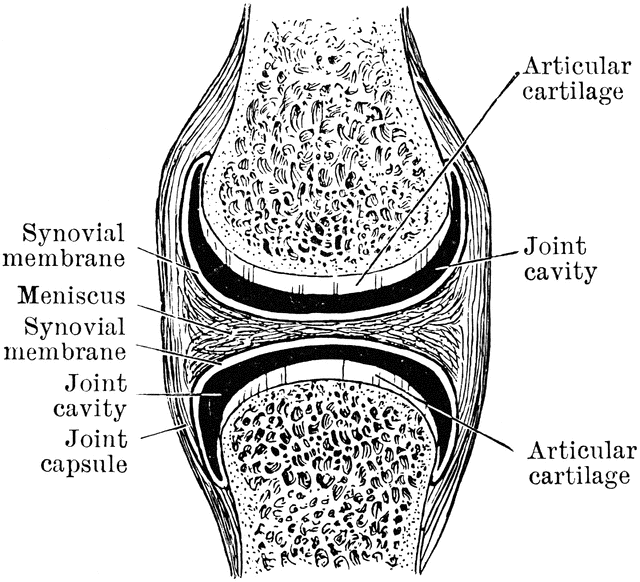
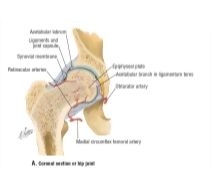
The diagram shows a frontal section of the hip joint. Identity its major structural elements by using the letters Key: a. acetabular labrum b. articular capsule c. articular cartilage d. head of femur e. hip bone f. joint cavity g. ligament of the bead of the femur The shoulder joint is built for mobility.

The diagram shows a frontal section of the hip joint
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 9. Which of the following types of joints lacks a joint cavity and is held together by a fibrous connective tissue? 1. Fibrous joints. 2. Cartilaginous joints. 3. Synovial joints. Most of the freely movable joints of the body could be classified both structurally and functionally as __________. The hip joint is one of the most flexible joints in the entire human body. The many muscles of the hip provide movement, strength, and stability to the hip joint and the bones of the hip and thigh. These muscles can be grouped based upon their location and function. The four groups are the anterior group, the posterior group, adductor group ... The hip joint is a ball-and-socket synovial joint formed between the os coxa (hip bone) and the femur. A round, cup-shaped structure on the os coxa, known as the acetabulum, forms the socket for the hip joint. The rounded head of the femur. Join our Newsletter and receive our free ebook: Guide to Mastering the Study of Anatomy.
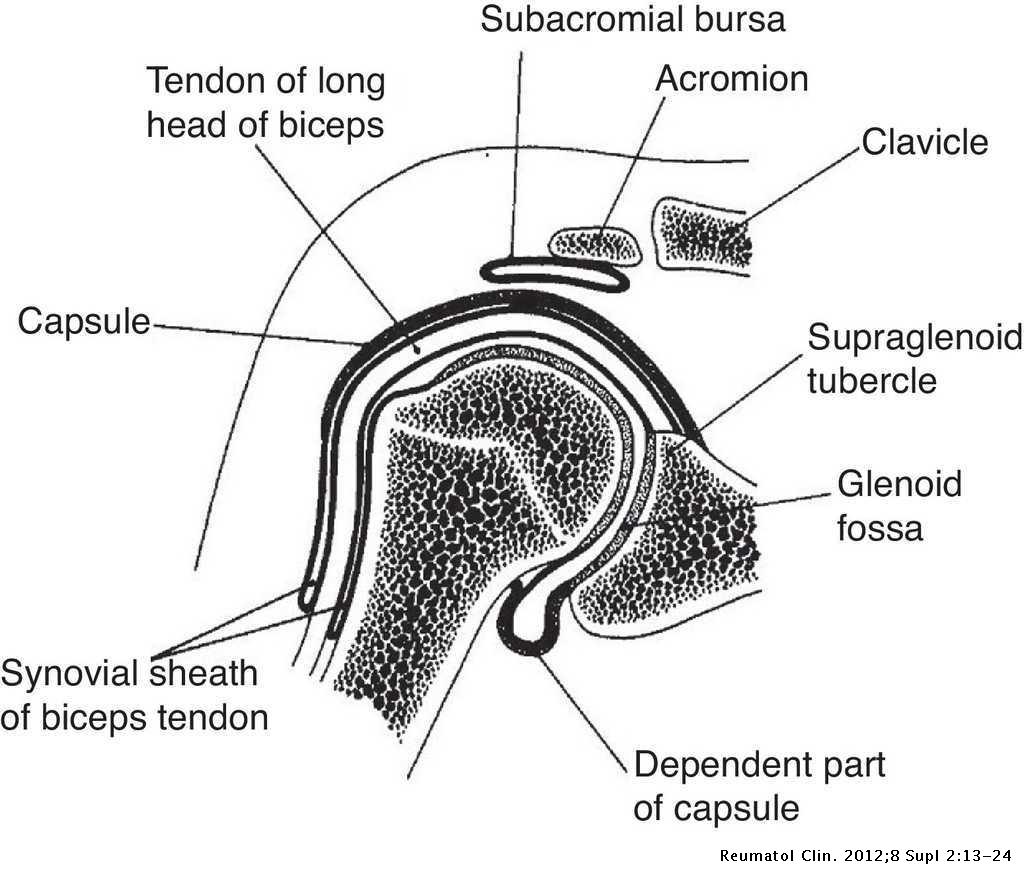
The diagram shows a frontal section of the hip joint. The diagram shows a frontal section of the hip joint. Identity its major structural elements by using the letters Key: a. acetabular labrum b. articular capsule c. articular cartilage d. head of femur e. hip bone f. joint cavity g. ligament of the bead of the femur The shoulder joint is built for mobility. 7. The diagram shows a frontal section of the hip joint. Identify its major structural elements by using the key letters. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS ... – in frontal plane right pelvis moves inferiorly in relation to left pelvis; either right pelvis rotates downward or left pelvis rotates upward; right lateral tilt ©2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. Right hip joint. Posterior half, viewed from in front. The joint surfaces have been somewhat pulled apart.
View Pearson eText15 from BIO 201 at Pima County Community College. Review Sheet 11 183 7. The diagram shows a frontal section of the hip joint. The diagram shows a frontal section of the hip joint. Identify its major structural elements by using the key letters. Key: a. acetabular labrum b. articular capsule c. articular cartilage d. coxal bone e. head of femur f. ligament of the head of the femur g. synovial cavity 8. The shoulder joint is built for mobility. The bones of the hip include the femur, the ilium, the ischium, and the pubis. The pubis, ischium, and ilium together constitute the pelvis while the thigh bone is the femur. The bones together make up the hip. The hip itself is a ball and socket joint, much like the shoulder.The structures necessary to create this joint are the socket, the joint capsule, muscle, ligaments, and the neck ... The hip joint is a ball-and-socket synovial joint formed between the os coxa (hip bone) and the femur. A round, cup-shaped structure on the os coxa, known as the acetabulum, forms the socket for the hip joint. The rounded head of the femur. Join our Newsletter and receive our free ebook: Guide to Mastering the Study of Anatomy.
The hip joint is one of the most flexible joints in the entire human body. The many muscles of the hip provide movement, strength, and stability to the hip joint and the bones of the hip and thigh. These muscles can be grouped based upon their location and function. The four groups are the anterior group, the posterior group, adductor group ... Anatomy & Physiology Ch 9. Which of the following types of joints lacks a joint cavity and is held together by a fibrous connective tissue? 1. Fibrous joints. 2. Cartilaginous joints. 3. Synovial joints. Most of the freely movable joints of the body could be classified both structurally and functionally as __________.




















0 Response to "39 the diagram shows a frontal section of the hip joint"
Post a Comment