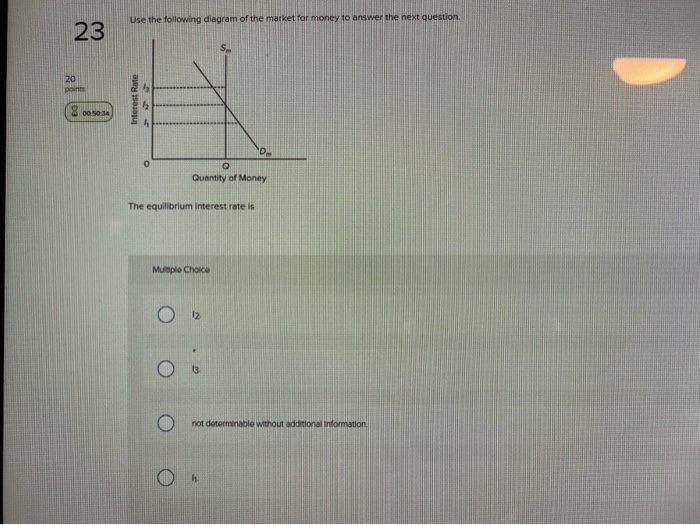
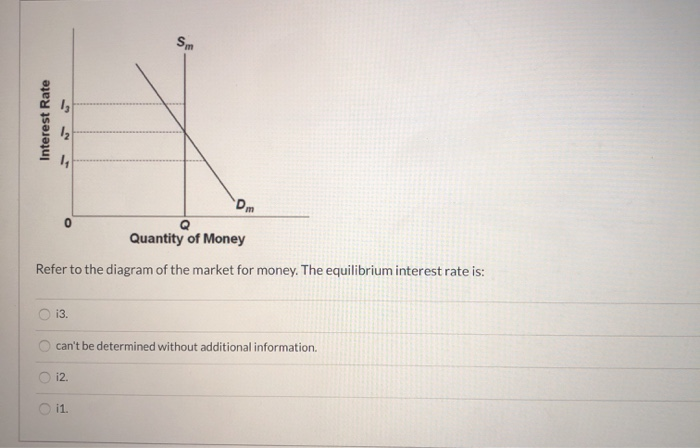
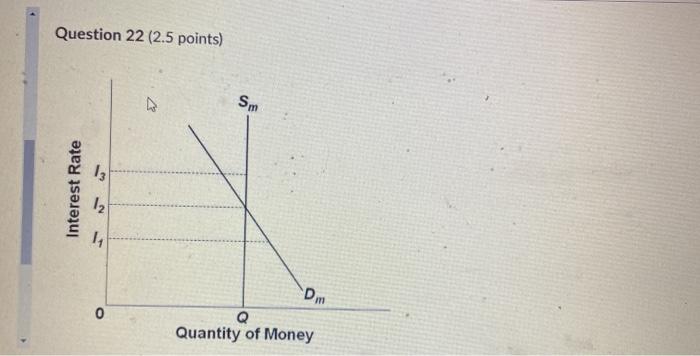
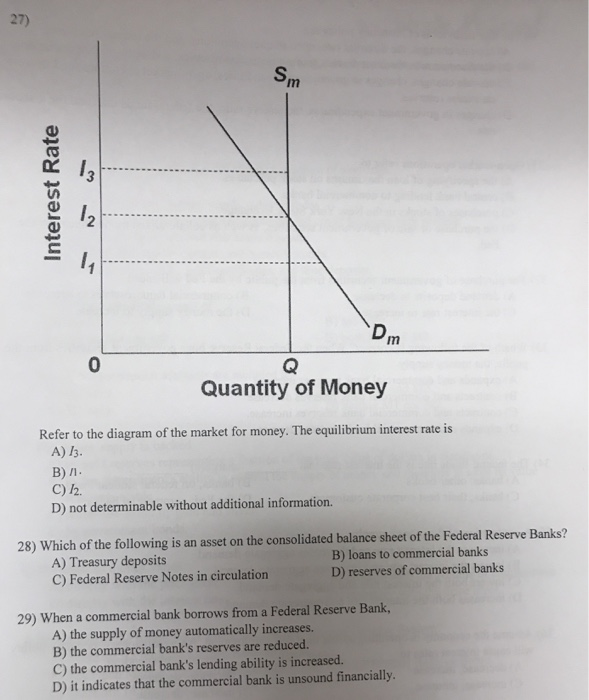
37 refer to the diagram of the market for money. the equilibrium interest rate is
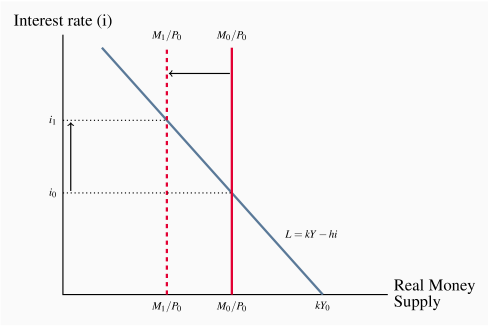
The interest rate falls: 0.5 = Hs = Hd = 3.68 - 18.4i i=17.28% The increased supply of high-powered money requires the interest rate be lowered to spur demand for high-powered money (market clearing). At a lower interest rate consumers will demand more money, as the opportunity cost of holding money has declined. Refer to the above market for money diagrams. If the Federal Reserve increased the stock of money, the: A. S curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise. B. S curve would shift rightward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall. C. D3would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall. D.
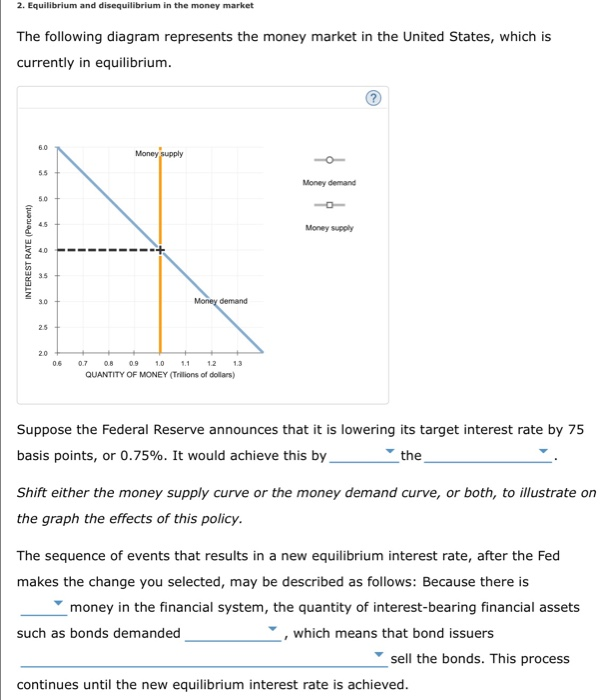
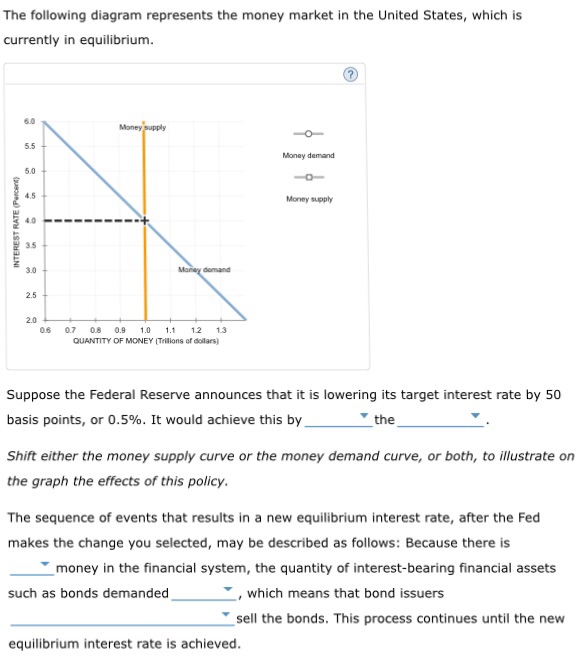
The equilibrium interest rate is: 2 percent. 4 percent. 6 percent. 8 percent. 1 points QUESTION 19 1. Refer to the above table. An increase in the money supply of $20 billion will cause the equilibrium interest rate to: fall by 4 percentage points. fall by 2 percentage points. rise by 4 percentage points. rise by 2 percentage points.

Refer to the diagram of the market for money. the equilibrium interest rate is
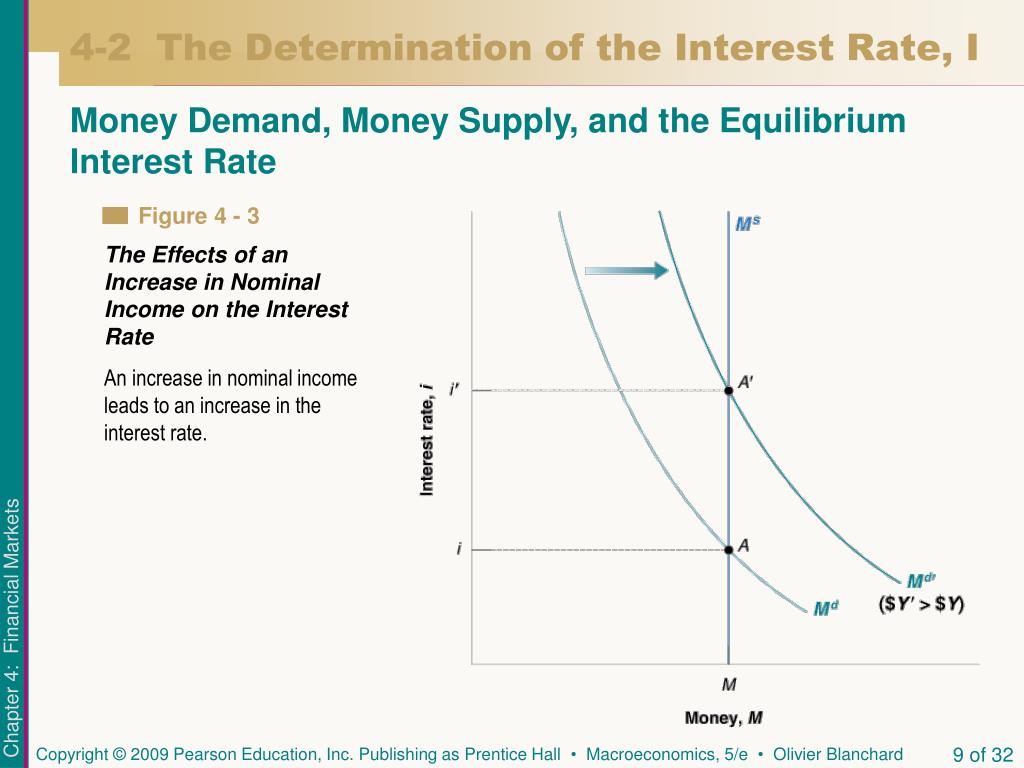
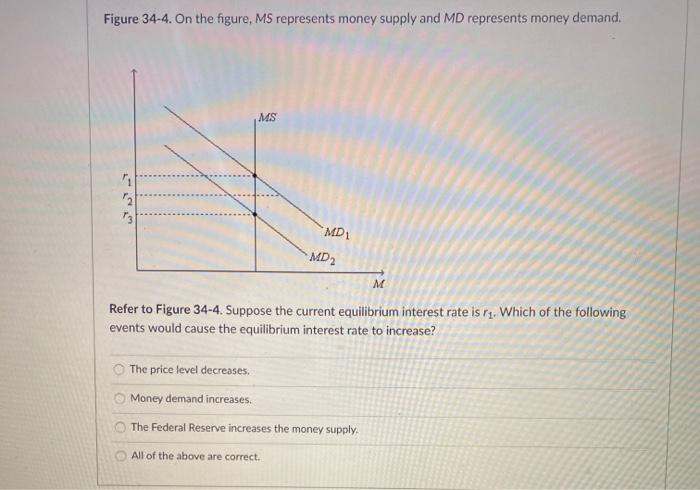
The LM curve represents the combinations of income and the interest rate at which the money market is in equilibrium. If money demand does not depend on the interest rate, then we can write the LM equation as M/P = L(Y). For any given level of real balances M/P, there is only one level of income at which the money market is in equilibrium. Thus, Money Market Equilibrium Stories. Any equilibrium in economics has an associated behavioral story to explain the forces that will move the endogenous variable to the equilibrium value. In the money market model the endogenous variable is the interest rate. This is the variable that will change to achieve the equilibrium. Refer to the given market-for-money diagrams. If the Federal Reserve increased the stock of money, the D3 curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise. S curve would shift rightward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall. D3 curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall.
Refer to the diagram of the market for money. the equilibrium interest rate is. In this market for credit card borrowing, the demand curve (D) for borrowing financial capital intersects the supply curve (S) for lending financial capital at equilibrium €. At the equilibrium, the interest rate (the "price" in this market) is 15% and the quantity of financial capital being loaned and borrowed is $600 billion. And then the nominal interest rate gets set essentially by this equilibrium point. Now, in the world that we live in, it actually goes the other way around. Central banks actually target a nominal interest rate. And if the central bank is able to achieve that target interest rate, well, that's going to impact the actual quantity of money. Figure 25.10 An Increase in the Money Supply. The Fed increases the money supply by buying bonds, increasing the demand for bonds in Panel (a) from D1 to D2 and the price of bonds to Pb2. This corresponds to an increase in the money supply to M ′ in Panel (b). The interest rate must fall to r2 to achieve equilibrium. Refer to the given market-for-money diagrams. If the Federal Reserve increased the stock of money, the D3 curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise. S curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise. S curve would shift rightward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall.
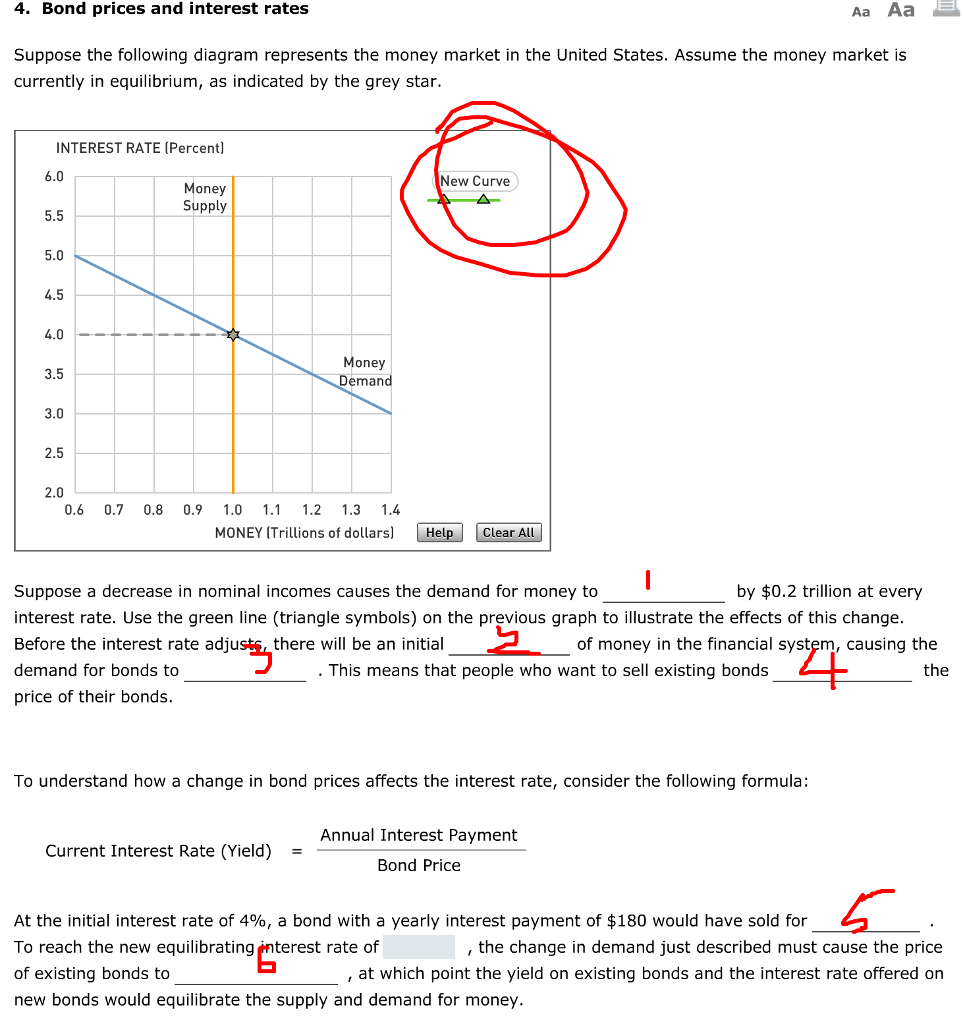
Result: People will sell bonds and thus asset price will fall leading to rise in interest rate. Thus, due to increase in demand for money the interest rate will increase and, thus, move up on the LM 1 curve till a new equilibrium point is reached. This is at point E 2.. Thus, At point E 2: both product and money market is in equilibrium (IS = LM,). 156. Refer to the above diagram of the money market. Given Dm and Sm, an interest rate of i3 is not sustainable because the: A) supply of bonds in the bond market will decline and the interest rate will rise. B) supply of bonds in the bond market will increase and the interest rate will decline. The new equilibrium gives us a higher level of output (1200, compared to 1000 in part (b)) and a higher interest rate (10%, compared to 5% in part (b)). Consumption rises from 400 in (c) to 450. Question 3 This question deals with bond prices and interest rates. P b = price of the bond today in $ i = interest rate on a bond This causes income to decline. As income declines, there are repercussions in the money market. Now, demand for money will decline as income declines. So, rate of interest must decline. If the equilibrium is stable, r and Y tend to change until point E is reached. Thus, E is a stable equilibrium point.
Figure 25.12 An Increase in the Money Supply. The Fed increases the money supply by buying bonds, increasing the demand for bonds in Panel (a) from D1 to D2 and the price of bonds to Pb2. This corresponds to an increase in the money supply to M ′ in Panel (b). The interest rate must fall to r2 to achieve equilibrium. On a diagram where the interest rate and the quantity of money demanded are shown on the vertical and horizontal axes respectively, the transactions demand for money can be represented by: a line parallel to the horizontal axis. a vertical line. a downsloping line or curve from left to right. an upsloping line or curve from left to right. Goods and Money Market Equilibrium (With Diagram) The IS-LM model finds the value of income and interest rate which simultaneously clears the goods and money market. The interest rate and the income level should be such that both the markets are in equilibrium. The IS-LM shows the interaction between the goods and the money market. Draw both the money market and the bond market in equilibrium. Next, use a diagram to explain what happens to the interest rate and the price of bonds as a result of the Federal Reserve increasing ...
Answer. In the goods market, the equilibrium interest rate when output is at its full employment level is r= 1 3 2000 (640) = 0:040 Now for the asset market equilibrium condition to hold, we can substitute the full employment level of output Y = 640 and the equilibrium interest rate r= 0:040 and solve for the price level P. Md P = 100 + 0:2Y ...
Money market is in equilibrium at a rate of interest when demand for money is equal to the fixed money supply. Thus money market is in equilibrium when. MS = MD. Money demand (MD) is determined by the level of income and rate of interest. Assuming that money demand is a linear function, we can write it as.
The equilibrium rate of interest in the market for money is determined by the intersection of the. ... Refer to the given market-for-money diagrams. If the Federal Reserve increased the stock of money, the ... On a diagram where the interest rate and the quantity of money demanded are shown on the vertical and horizontal axes, respectively, the ...
Solved Using A Carefully Labeled Ae Pc Graphs Show And Explain How An Economy Can Get Out Of A Liquidity Trap Via Fiscal Policy Label The Axes Course Hero
The equilibrium interest rate is: i 1. i 2. i 3 . not determinable without additional information. 1 points QUESTION 10 1. Refer to the above market for money diagrams.
Transcribed image text: Sm Interest Rate 13 12 Dm 0 Quantity of Money Refer to the diagram of the market for money. The equilibrium interest rate is 13. not determinable without additional information. The discount rate is the interest yield on long-term government bonds. rate at which commercial banks lend to the public rate at which the Federal Reserve Banks lend to commercial banks, rate at ...
Solved Changes In The Money Supply The Following Graph Represents The Money Market In A Hypothetical Economy As In The United States This Econom Course Hero
10. If the money market in the diagram is not in equilibrium at the interest rate i 1: portfolio managers will sell bonds to increase their money holdings, pushing bond prices down & interest rates up until equilibrium is reached 11. According to the monetary transmission mechanism, an increase in the money supply: decreases interest rates, raises AE, increases AD & increases equilibrium Y 12.
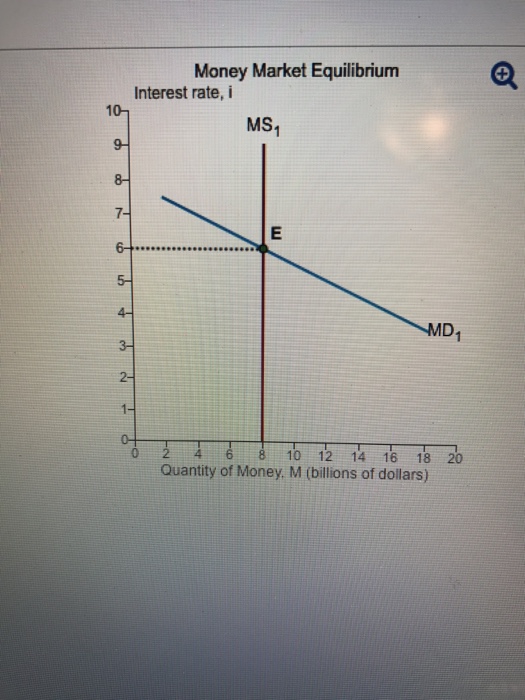
In any market, an equilibrium occurs when the quantity supplied is equal to the quantity demanded. Prices adjust until the market is in equilibrium. The money market is no exception. The only difference between the markets we saw in Unit 1 and the money market is: The price is the nominal interest rate The supply curve is vertical.
If the interest rate is above the equilibrium rate, there will be an _____ money and the interest rate will _____. A. excess demand for; rise B. excess supply of; fall C. excess demand for; fall D. excess supply of; rise E. excess supply of; remain the same 35. Use the "Money Market II" Figure 28-1. If the rate of interest is below the ...
Refer to the diagram of the market for money. Given Dm and Sm, an interest rate of i3 is not sustainable because the: demand for bonds in the bond market will rise and the interest rate will fall.
Since the interest rate is identical to the rate of return on dollar assets from a U.S. dollar holder's perspective (i.e., RoR $ = i $), we can now place the RoR diagram directly on top of the rotated money market diagram as shown in Figure 7.8 "Money-Forex Diagram".The equilibrium interest rate (i′ $), shown along the horizontal axis above the rotated money market diagram, determines the ...
Looking at the IS-LM diagram first; a monetary expansion causes the money supply to rise from M 0 to M 1, and so the LM Curve shifts from LM 0 to LM 1.The new equilibrium is at A 1, with a consequent rise in the output level and a fall in the interest rate. This causes the AD curve to shift to the right, with the price level rising from P
Refer to the given market-for-money diagrams. If the Federal Reserve increased the stock of money, the D3 curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise. S curve would shift rightward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall. D3 curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall.
Money Market Equilibrium Stories. Any equilibrium in economics has an associated behavioral story to explain the forces that will move the endogenous variable to the equilibrium value. In the money market model the endogenous variable is the interest rate. This is the variable that will change to achieve the equilibrium.
The LM curve represents the combinations of income and the interest rate at which the money market is in equilibrium. If money demand does not depend on the interest rate, then we can write the LM equation as M/P = L(Y). For any given level of real balances M/P, there is only one level of income at which the money market is in equilibrium. Thus,

Describe What Happens To The Equilibrium Interest Rate When Inflation Is Expected To Decrease Provide A Drawing With Axes Labeled And Equilibrium Identified Along With A Short Explanation Study Com











/GettyImages-106682757-59f9e4b1396e5a001a95becf.jpg)

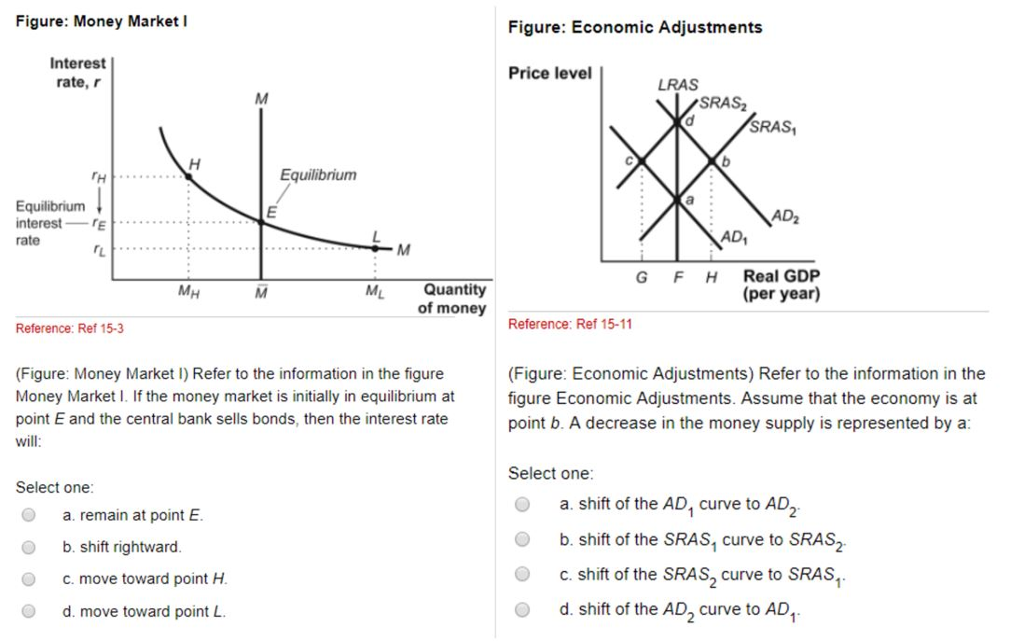
0 Response to "37 refer to the diagram of the market for money. the equilibrium interest rate is"
Post a Comment