37 ferris wheel free body diagram
Draw the Free-body Diagram Of the Wheel. centripetal force problems - the physics hypertextbook the figure labeled "side view" draw and label arrows ing out of the coin to represent the forces acting on the coin you do not need to draw the mounting gas struts does this formula look right hey all i m just having some trouble mounting some gas struts to a canopy that i m building the door ... 8. A person of mass 60.0 kg is riding on a Ferris wheel as illustrated. Draw the free body diagram for the person when she is on the lowest position of the ride. Suppose that the wheel rotates at a speed that causes the person to experience three times her weight at that lowest point. Find the speed of the wheel under those conditions if the ...
During your ride, you are sitting on one of the Ferris Wheel gondolas. The linear speed at the rim of the Ferris wheel is a constant y = 7 m/s. a) (5 points) Draw a free-body diagram showing all he forces acting on you while at the top of; Question: 3. (20 points) In an amusement park, you take a ride on a Ferris wheel with a radius R=14 m.
Ferris wheel free body diagram
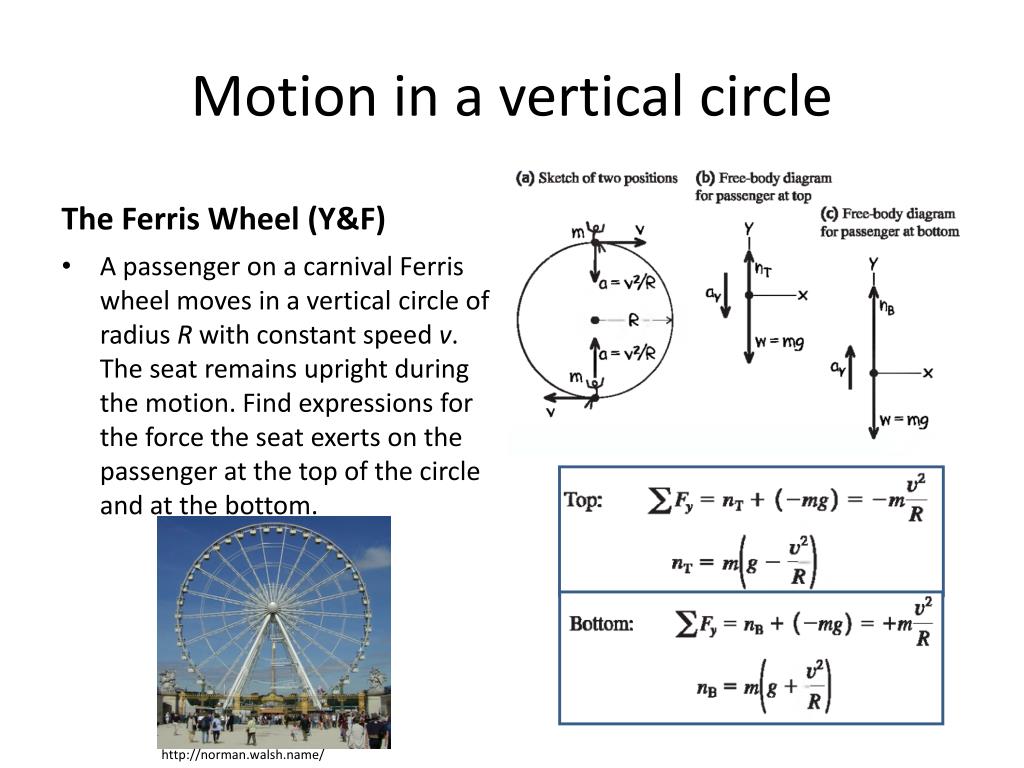
What forces act on a person at the bottom of the Ferris Wheel? What are the directions of these forces? Draw a free-body diagram for the passenger at the highest point. Draw a free-body diagram for the passenger at the lowest point. Show the direction of acceleration off to the side of each of the free-body diagrams. Consider R2D2 (a droid) with mass 30kg riding on a Ferris wheel with diameter 25m, with a velocity of 2.8m/s. a) Compute the free body diagram for R2D2 at the exact top, exact bottom and at both horizontal positions. Remember to include gravity. (Note: The forces act in different directions relative to the acceleration of the Ferris wheel. The free-body diagrams of the student at the top and bottom of the Ferris wheel are shown below. At the top (the highest point in the circular motion) the seat pushes up on the student with a force of magnitude F N, t o p , while the Earth pulls down with a force of magnitude mg. Newton's second law for the radial direction gives
Ferris wheel free body diagram. Ferris wheel when he/she is at the point shown on the diagram? c) Suppose the Ferris wheel is in outer space with no significant gravitational field, and the seat with the person breaks off the wheel. Sketch the path of motion in ... (Make a free body diagram.) o Earth - the force of gravity will point straight down o The seat must exert a ... Follow my blog: https://xmphysics.wordpress.comFollow me on facebook: https://www.facebook.com/xmphysics Free-body diagram for block B gEonB Free-body diagram for system S gEonS F NBonA F gEonA F NTonB F F fTonB F HonB F NAonB F NTonS F F fTonS HonS. ... A Ferris wheel (vertical circular ride) has a diameter of 50m and completes one revolution every 45s. If a rider has a mass of 65kg, what is the magnitude of the normal ... Free Body Diagram: The free-body diagram or FBD is a useful physics tool to simplify a given complex system and calculate the force on the bodies of that system individually. The different types ...
The person will be in free fall, for a moment, at the top of the ferris wheel. And so it's a little bit of bookkeeping work; we have to get the radius of this ferris wheel and it's half the diameter so that's 25 meters over 2 and that's 12.5 meters. A 35 kg child rides a ferris wheel of radius 12 m. The child moves a vertical circle at a constant speed and completes one rotation every 9.0 s. a) As the child travels over the top, what is the ... Draw and label a free body diagram for the object at the bottom of the circular path b) Calculate the tension In the connecting rod at this ... a) What is the magnitude of the centripetal force acting on the Ferris wheel passenger at the top and at the bottom? Same m, v and r at top and bottom, so Fc is the same magnitude at the top and bottom. g c b) Complete the freebody diagrams showing all the forces acting on the passenger at the top and at the bottom of the Ferris wheel. Label ... The Ferris wheel consists of an upright wheel with passenger gondolas (seats) attached to the rim. ... The figure below shows a free-body diagram for the passengers at these locations. Where: mg is the force of gravity pulling down on the passengers, where m is the mass of the passengers and g is the acceleration due to gravity, ...
The free-body diagram of a block being pushed up a rough ramp is best represented by a. A d. D b. B e. E c. C ... A passenger on a Ferris wheel of diameter 22 m makes one complete revolution every 45 s. What is the pas- ... happening is that the rim of the wheel is pushing the people toward the hub as it overcomes their inertia to al- The Ferris Wheel has radius, r, and rotates with speed, v. Figure 4. A person at three possible positions on a Ferris Wheel. Figures 5, 6 and 7 show the free body diagrams for the three positions shown in Figure 4. Figure 5. Free body analysis when the person is at the top. Figure 6. Free body analysis when the person is at the bottom. Figure 7 ... Roller coaster vs. Ferris Wheel [classic] Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. You can edit this template and create your own diagram. Creately diagrams can be exported and added to Word, PPT (powerpoint), Excel, Visio or any other document. The free-body diagram on the left is a side-view of the car. Notice that the upward direction is the y-direction, and the forward direction, tangent to the turn, is the t-direction. The free-body diagram on the right is a rear-view of the car. This is what you would see if you stood directly behind the car.
The free-body diagram shows all forces acting on a box supported by a horizontal surface, where the length of each force vector is proportional to its magnitude. Which statement below is correct? a. The box is accelerating downwards because the force of gravity is greater than the normal force. ... As the Ferris wheel rotates with a constant ...
A 500 N child travels in a circular path on a ferris wheel. Which free body diagram best shows the forces which could act on the child as she passes the lowest point? * 1 point. Option 2. Option 1. Option 4. Option 3. In a popular amusement park ride, a large cylinder is set in rotation. The floor then drops away leaving the riders suspended ...
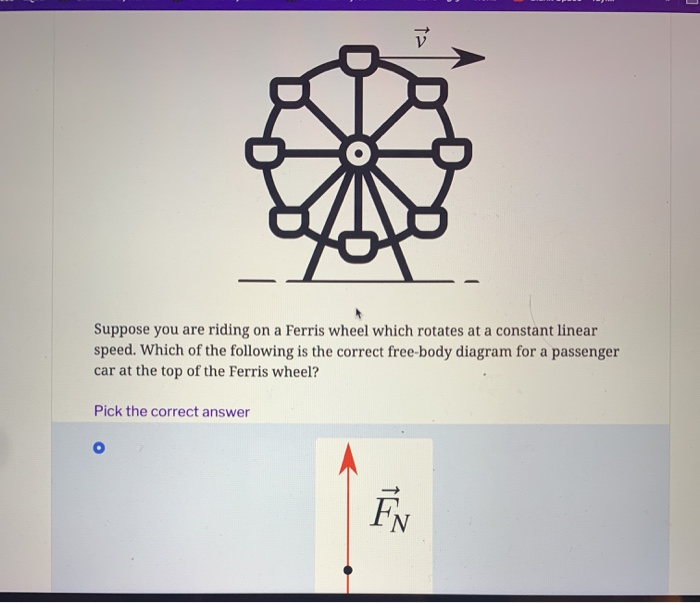
Which of the following free body diagrams is correct for a Ferris wheel rider at the top of the cycle? Little bit of normal force up and more weight downward If the radius in which an object moves in uniform circular motion is doubled while the speed remains constant, the centripetal force is multiplied by a factor of
Free Body Diagrams on a Loop‐the‐Loop Roller Coaster Draw the free body diagrams for a coaster at the boom and top of a loop and write the equaons for the net force. mg F net F N F net =ma = ma c The net force in the loop must be centripetal force F net = F N
A 500 N child travels in a circular path on a ferris wheel. Which free body diagram best shows the forces which could act on the child as she passes the lowest point? A. F g = 500 N B. F g = 500 N F N = 400 N C. F g = 500 N F = 500 N D. F g = 500 N F N = 600 N - 2 - 7. A car travels at a uniform speed through a level circular curve in the road.
In the animation, a Ferris wheel rotates at constant speed as shown (position is given in meters and time is given in minutes). Each square represents a chair on the Ferris wheel. Restart. Draw the free-body diagram for a chair on the Ferris wheel when it is at the points (a), (b), (c), and (d).
http://www.physicshelp.caGO AHEAD and click on this site...it wont hurt.Free simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website
Ferris Wheel Free Body Diagram. About Ferris Wheel Free Body Diagram. If you are search for Ferris Wheel Free Body Diagram, simply cheking out our links below : Recent Posts. Vigenere Cipher Online.
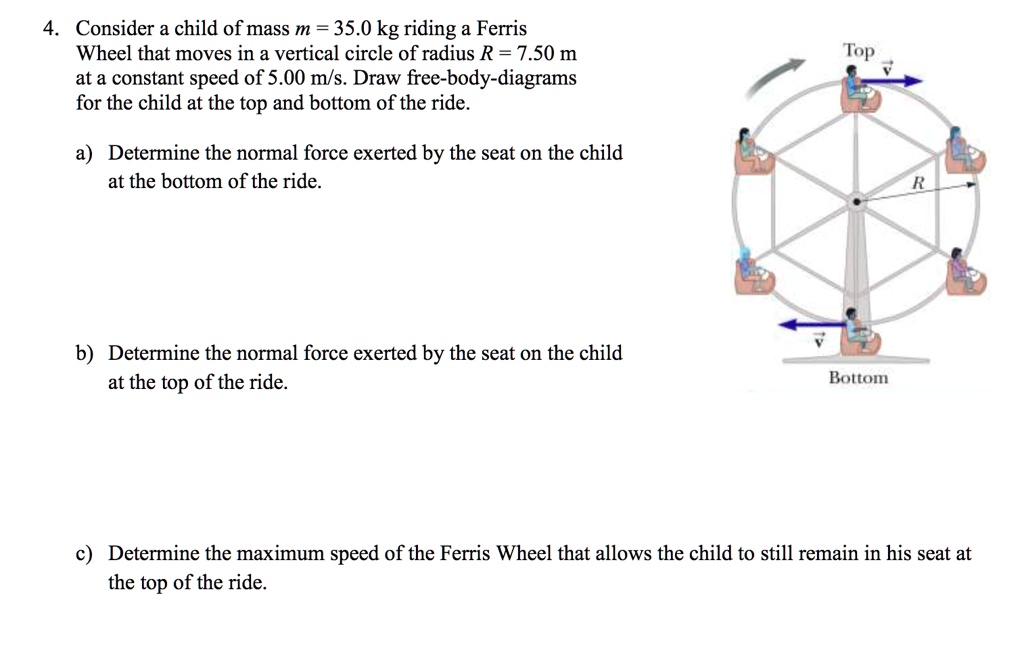
Draw the free body diagram for the person when she is on the lowest position of the ride. Suppose that the wheel rotates at a speed that causes the person to experience three times her weight at that lowest point. Find the speed of the wheel under those conditions if the radius of the Ferris wheel is 6.0 m.
In addition, the rotational speed of the wheel can be varied from -20 m/s to 20 m/s. By selecting the checkbox, the free-body diagram can be shown. The Ferris Wheel Model was created using the ...
The free-body diagrams of the student at the top and bottom of the Ferris wheel are shown below. At the top (the highest point in the circular motion) the seat pushes up on the student with a force of magnitude F N, t o p , while the Earth pulls down with a force of magnitude mg. Newton's second law for the radial direction gives
Consider R2D2 (a droid) with mass 30kg riding on a Ferris wheel with diameter 25m, with a velocity of 2.8m/s. a) Compute the free body diagram for R2D2 at the exact top, exact bottom and at both horizontal positions. Remember to include gravity. (Note: The forces act in different directions relative to the acceleration of the Ferris wheel.
What forces act on a person at the bottom of the Ferris Wheel? What are the directions of these forces? Draw a free-body diagram for the passenger at the highest point. Draw a free-body diagram for the passenger at the lowest point. Show the direction of acceleration off to the side of each of the free-body diagrams.
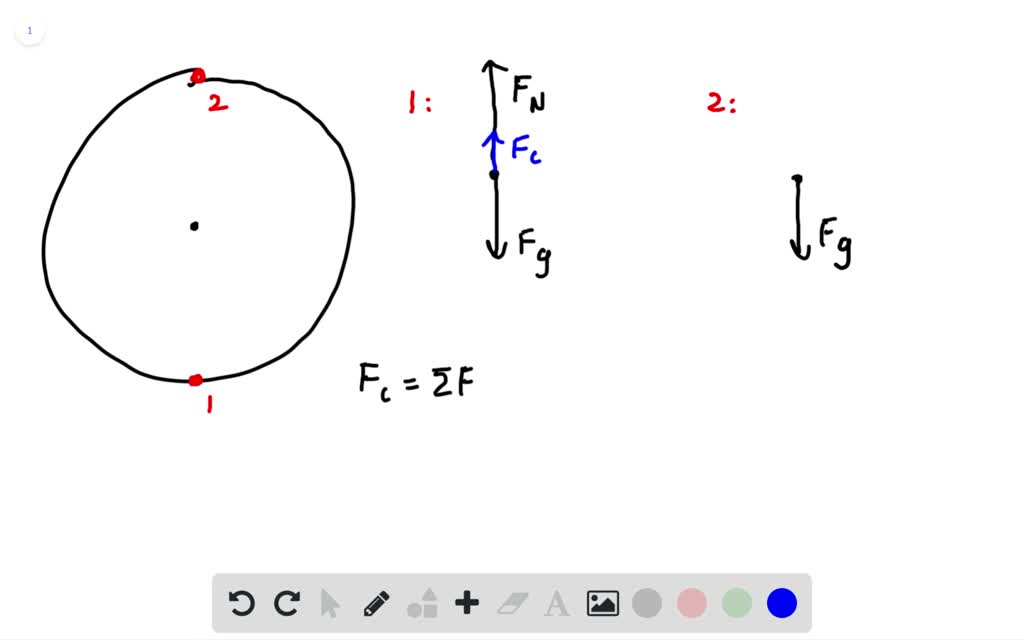
Solved Ferris Wheel You Are Sitting On A Rotating Ferris Wheel Draw A Force Diagram For Yourself When You Are At The Bottom Of The Circle And When You Are At The Top

A Circular Motion Addict Of Mass 80 Kg Rides A Ferris Wheel Around In A Vertical Cycle Of Radius 10 M At A Constant Speed Of 6 1 M S A



















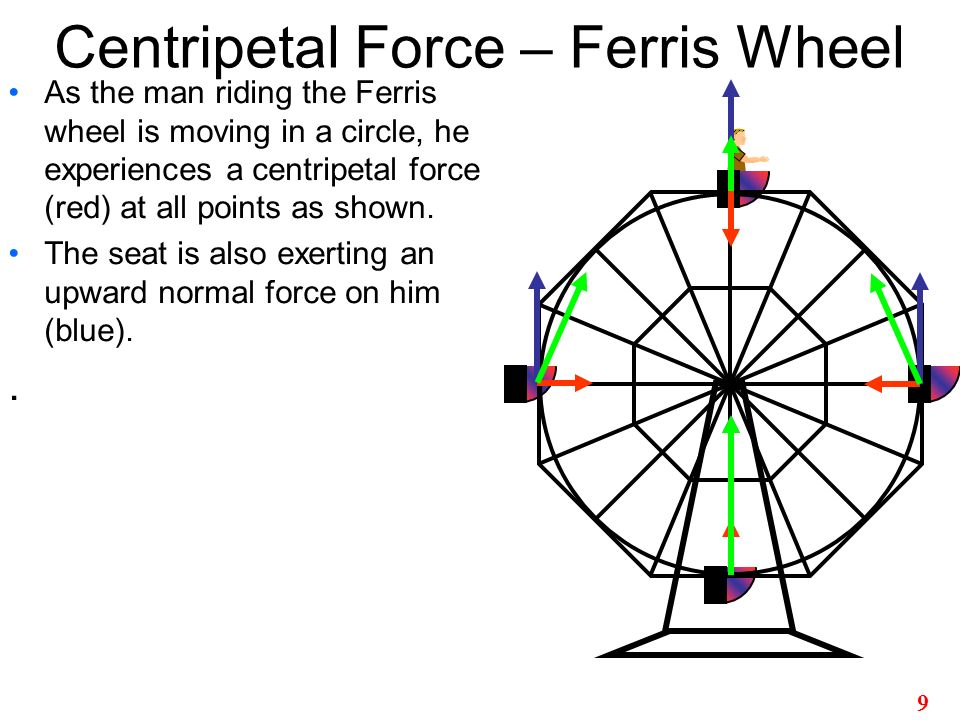


0 Response to "37 ferris wheel free body diagram"
Post a Comment